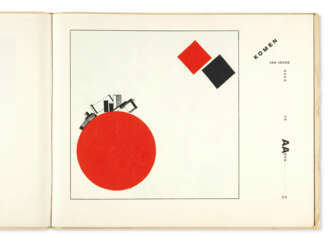
de stijl
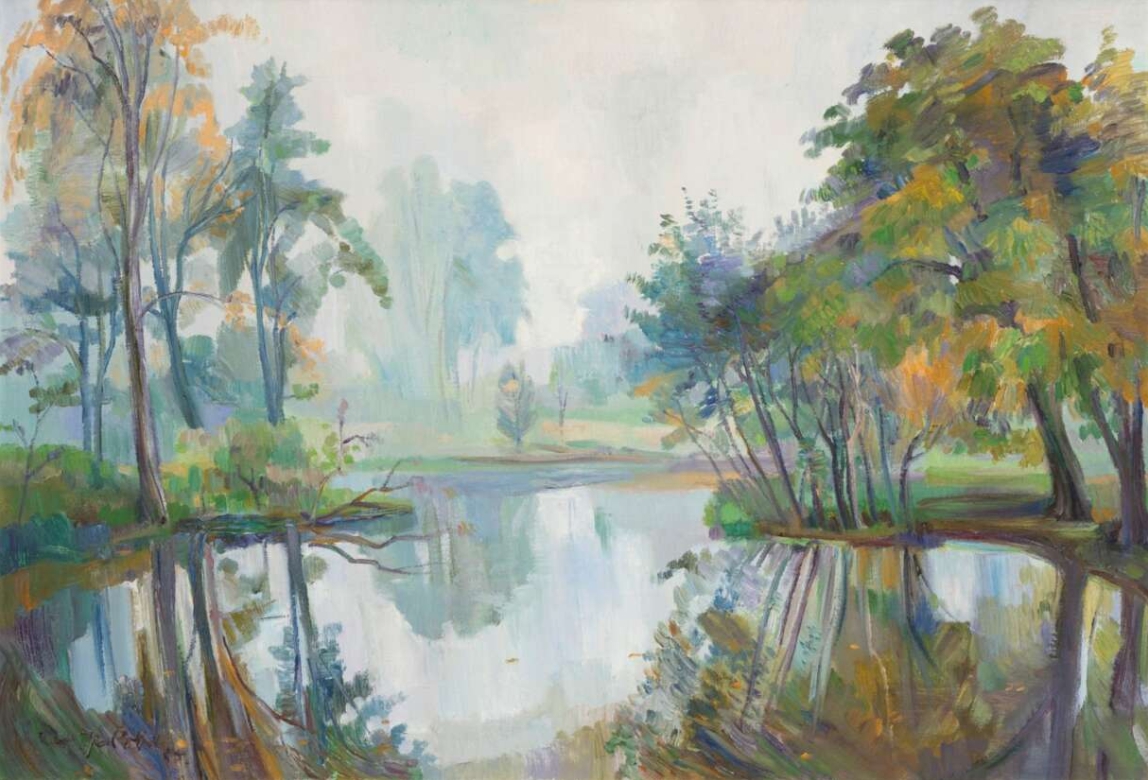

Karl Peter Röhl was a German painter and graphic artist.


Pieter Cornelis Mondriaan, later known as Piet Mondrian, was a Dutch painter and art theoretician, whose transformation from figurative art to an abstract modernist style revolutionized the visual arts landscape of the 20th century. Born on March 7, 1872, in Amersfoort, Netherlands, and passing away on February 1, 1944, in New York, Mondrian's journey in art began in a devoutly Calvinist home where both art and music were encouraged. His early works were influenced by his surroundings, featuring landscapes in an Impressionist manner, but it was his shift to Paris in 1911 that marked the beginning of his profound evolution towards abstraction.
Mondrian co-founded the De Stijl art movement, aiming to achieve a universal aesthetic through the simplification of visual elements to their essentials: straight lines, right angles, primary colors, and the use of black, white, and gray. This reductionist approach, termed Neoplasticism, was Mondrian's contribution to creating 'universal beauty'. His philosophy extended beyond the canvas, influencing architecture, design, and fashion, encapsulating the modernist ideal and becoming synonymous with Modernism itself.
Some of Mondrian's notable works, such as "Composition with Red, Blue, and Yellow" and "Broadway Boogie Woogie", exemplify his revolutionary style, characterized by an economy of color and a rigorously abstract geometry that aimed to express the dynamic equilibrium of universal forces. These masterpieces, along with his theoretical writings, left a lasting impact on the course of abstract painting and several major art movements including Color Field painting, Abstract Expressionism, and Minimalism.
Mondrian's art is celebrated in museums and galleries worldwide, notably at the Gemeentemuseum Den Haag and the Museum of Modern Art in New York, where his evolution from figuration to geometric abstraction continues to inspire and captivate audiences. His commitment to exploring the spiritual in art through a radical simplification of form and color has cemented his legacy as one of the pioneers of 20th-century abstract art.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Mondrian's works represent not just significant artistic achievements but also pivotal moments in the history of modern art. His influence extends far beyond his own creations, shaping the development of modern aesthetics in numerous fields. If you're intrigued by Mondrian's vision of harmony and order through abstraction, we invite you to sign up for updates. This subscription will keep you informed about new product sales and auction events related to Mondrian's work, ensuring you stay connected to the ever-evolving world of art and design inspired by this iconic figure.
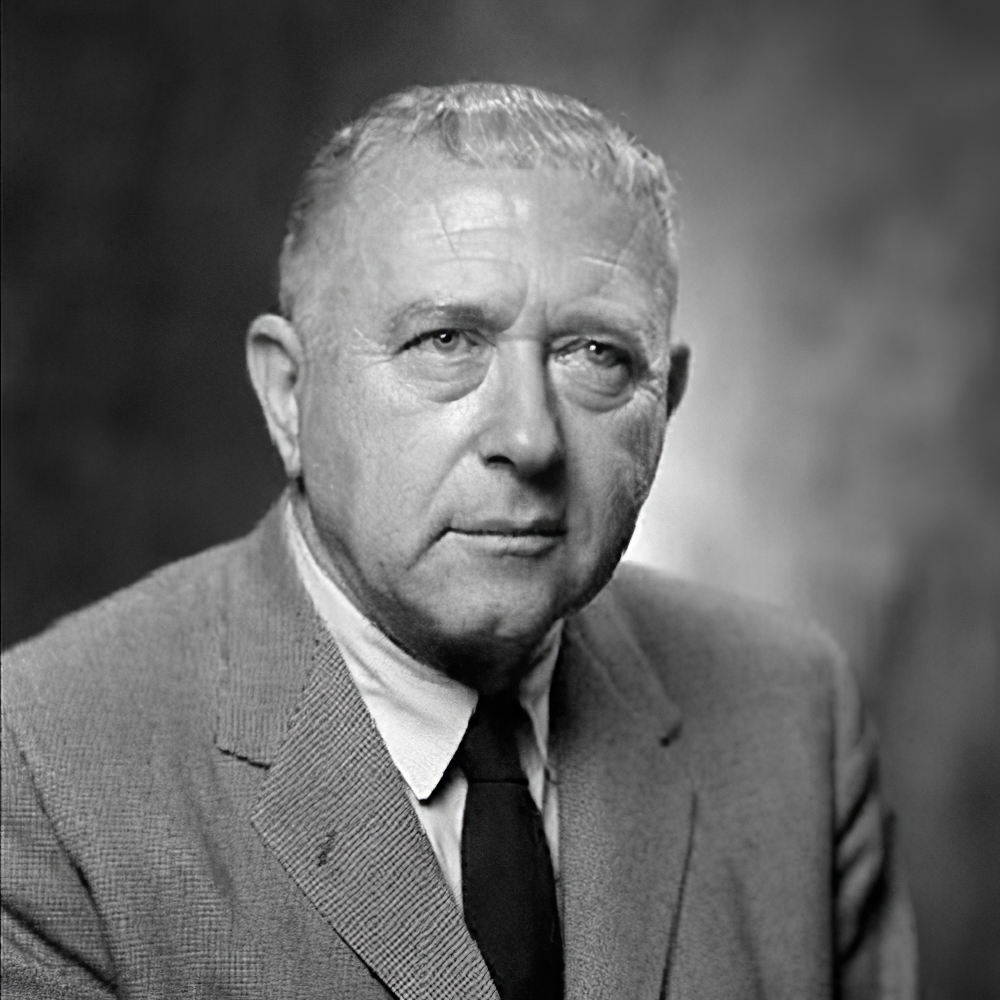


Marcel Lajos Breuer was a Hungarian American modernist architect and furniture designer. He moved to the United States in 1937 and became a naturalized American citizen in 1944.
At the Bauhaus he designed the Wassily Chair and the Cesca Chair, which The New York Times have called some of the most important chairs of the 20th century. Breuer extended the sculpture vocabulary he had developed in the carpentry shop at the Bauhaus into a personal architecture that made him one of the world's most popular architects at the peak of 20th-century design. His work includes art museums, libraries, college buildings, office buildings, and residences. Many are in a Brutalist architecture style, including the former IBM Research and Development facility which was the birthplace of the first personal computer. He is regarded as one of the great innovators of modern furniture design and one of the most-influential exponents of the International Style.
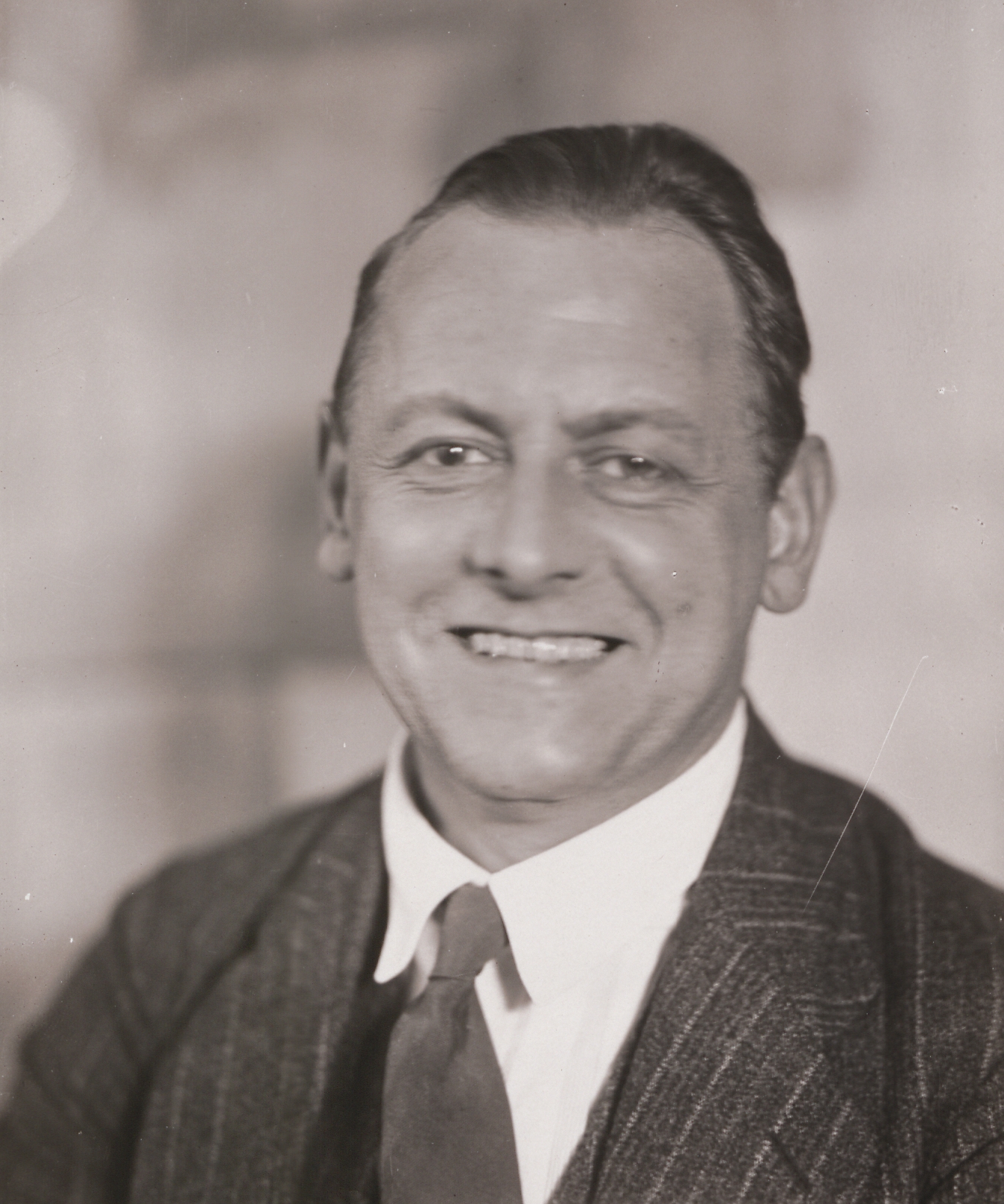


Kurt Schwitters (1887–1948) was a German artist renowned for his multifaceted contributions to modern art, encompassing painting, poetry, graphic design, and installation art. Born in Hanover, Germany, Schwitters developed a unique artistic vision that led to the creation of "Merz," a term he coined to describe his one-of-a-kind approach to art.
The concept of Merz originated from a fragment of the word "Kommerz" (commerce), which Schwitters incorporated into his early collages. This term came to represent his artistic philosophy, characterized by the assemblage of found objects and everyday materials into cohesive compositions. Through Merz, Schwitters sought to blur the boundaries between traditional art forms, integrating elements of Dadaism, Constructivism, and Surrealism.
One of Schwitters' most significant projects was the "Merzbau," an ambitious, evolving installation within his Hanover home. This project began around 1923 and transformed his living space into a labyrinthine structure filled with collages, sculptures, and found objects. The Merzbau was a physical manifestation of his Merz philosophy, embodying the synthesis of art and life. Unfortunately, the original Merzbau was destroyed during a British air raid in 1943.
In addition to his visual art, Schwitters made notable contributions to literature and sound art. His poem "An Anna Blume," published in 1919, is a seminal work that exemplifies his playful use of language and nonsensical style, aligning with the Dada movement's principles. Moreover, his "Ursonate," a sound poem composed between 1922 and 1932, showcases his innovative exploration of phonetic expression and rhythm, pushing the boundaries of traditional poetry.
The rise of the Nazi regime in Germany had a profound impact on Schwitters' life and work. Classified as a "degenerate" artist by the Nazis, he fled to Norway in 1937 to escape persecution. Following the German invasion of Norway in 1940, he sought refuge in the United Kingdom. During his internment at the Hutchinson Internment Camp on the Isle of Man, Schwitters continued to create art, producing over 200 works during his 16 months of confinement.
After his release, Schwitters settled in the Lake District of England, where he embarked on a new Merz construction known as the "Merzbarn." Although he was unable to complete this project due to his death in 1948, the Merzbarn stands as a testament to his unwavering commitment to his artistic vision. Today, Kurt Schwitters is celebrated as a pioneer of modern art, whose innovative techniques and ideas have left an indelible mark on the art world.
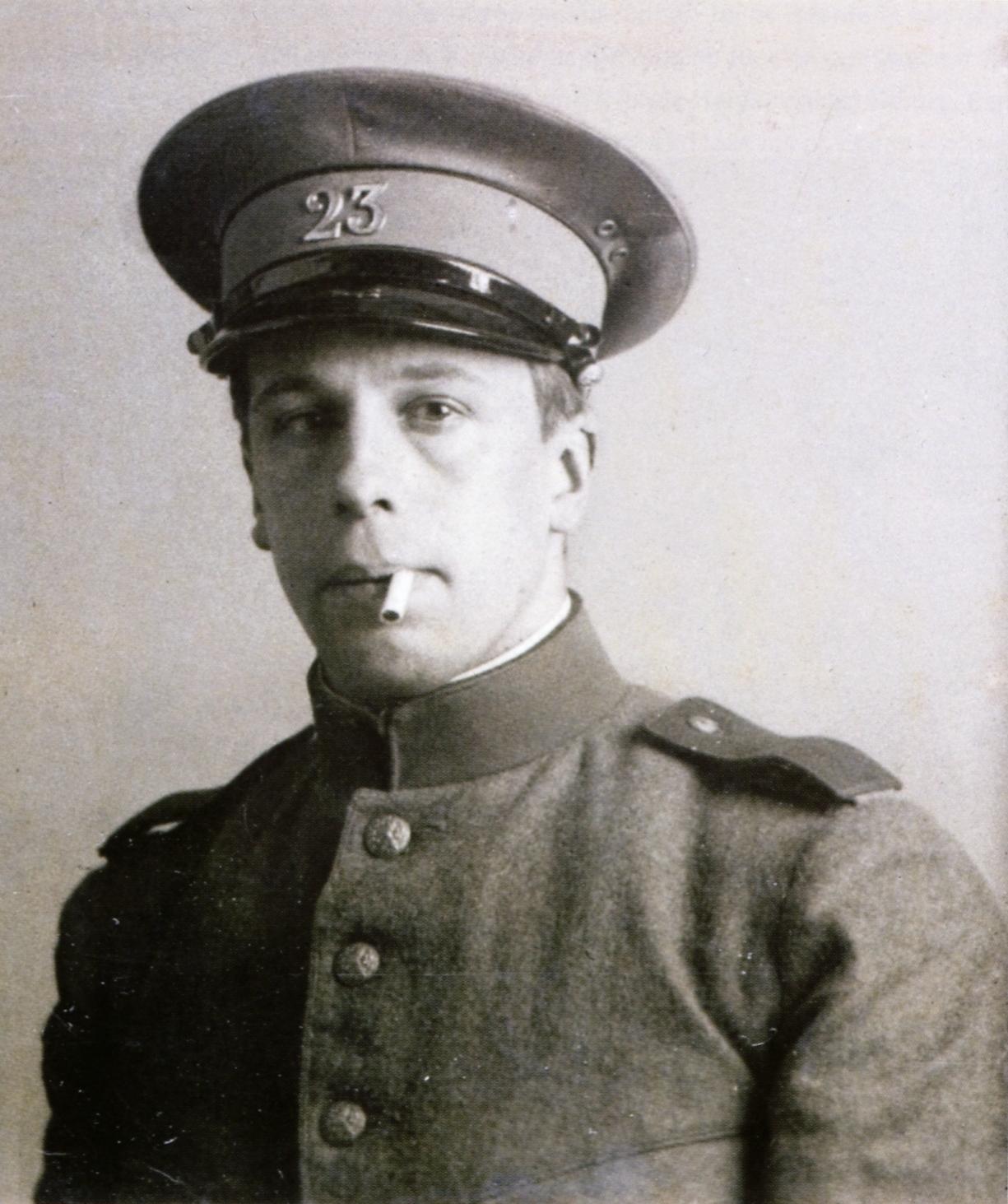


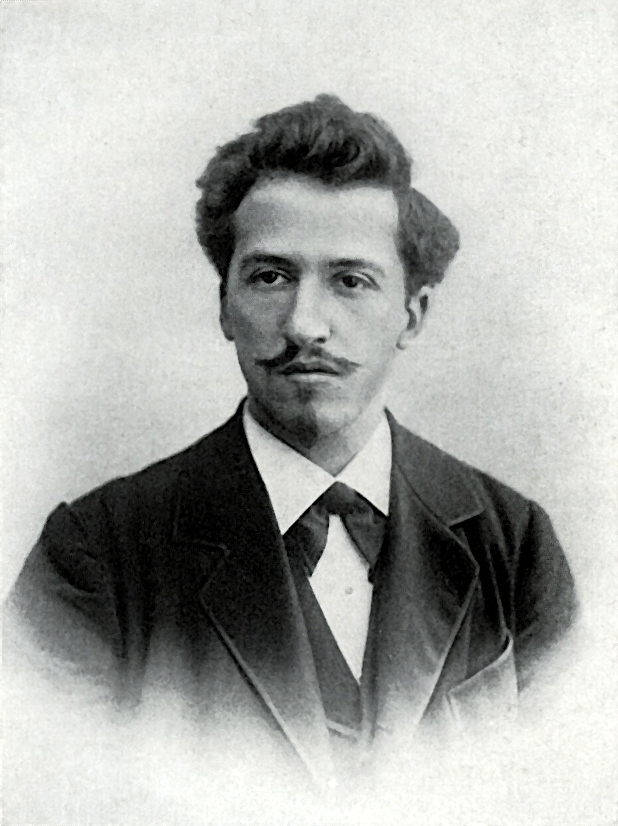
Theo van Doesburg, real name Christian Emil Marie Küpper, is a Dutch painter, architect and sculptor, art theorist, co-founder of the Style Group and of Neoplasticism.
Theo van Doesburg co-founded with Piet Mondrian the De Stijl abstract art movement. The basis of van Doesburg's views was the attempt to reduce all forms of objective harmony in a work of art to certain geometric elements. These new principles soon had a significant influence on the development of architecture, literature, graphics and music.
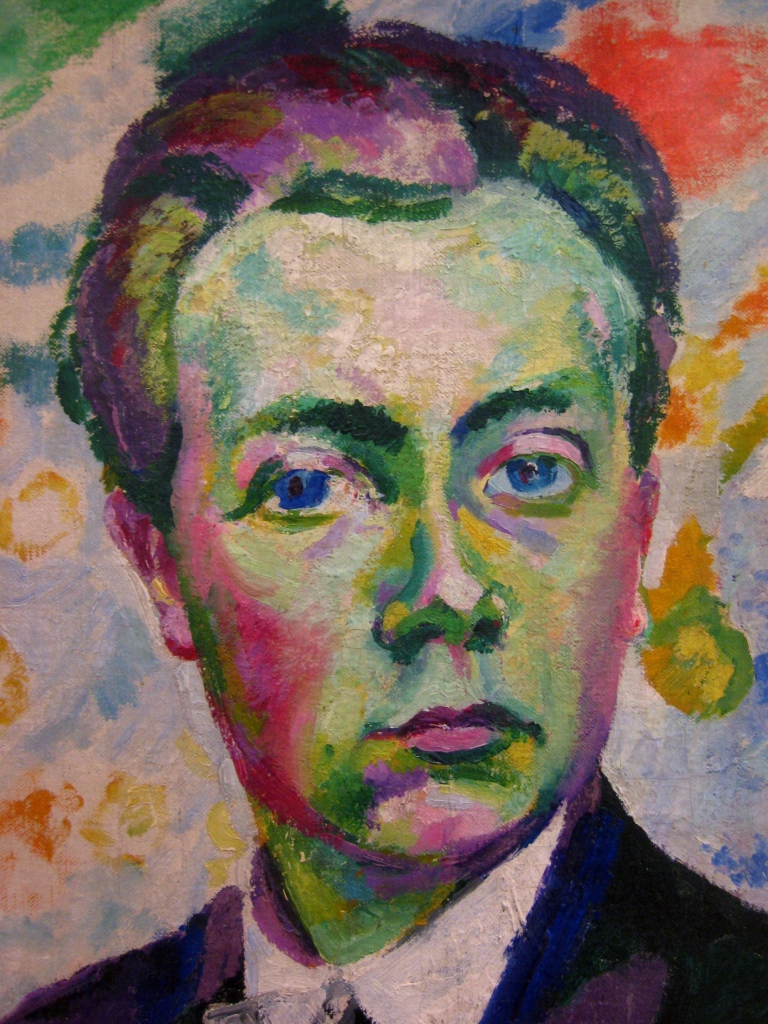


Robert Delaunay, a French artist, emerged as a pivotal figure in the development of early 20th-century art, blending the realms of painting and sculpture with his innovative approaches. His work is celebrated for its dynamic use of color and geometric shapes, making him a cornerstone in the Orphism movement, which he co-founded alongside his wife Sonia Delaunay and others. This movement is distinguished by its focus on vibrant colors and geometric forms, contributing significantly to the abstract art landscape.
Delaunay's artistic journey began earnestly at the age of 19 when he decided to fully dedicate himself to painting, contributing works to the Salon des Indépendants. His early career was marked by a deep engagement with Neo-Impressionism and Cubism, as evidenced by his collaborative work with Jean Metzinger and his exploration of color theory. Notable works from this period include "Paysage au disque" (1906–07) and "Champs de Mars: The Red Tower" (1911), showcasing his departure from representational art towards a more abstract, color-driven aesthetic.
Among Delaunay's celebrated series are the Eiffel Tower and Simultaneous Windows, reflecting his fascination with Parisian architecture and the dynamic interplay of light and color. These works, along with others like "L'Équipe de Cardiff" (1912-13) and "Endless Rhythm" (1934), are housed in prestigious museums such as the Musée d'Art Moderne de la Ville de Paris, The Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum, and the Tate collection. These pieces illustrate his evolving style, from the depiction of movement and technology in pre-war Paris to the rhythmic abstraction of later years.
Delaunay's influence extended beyond France, with significant contributions to exhibitions in Germany, Switzerland, and Russia, particularly through his involvement with Der Blaue Reiter group. His work not only captured the essence of the technological and cultural shifts of his time but also laid the groundwork for future artistic explorations into color and form.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Delaunay's oeuvre offers a rich study in the evolution of modern art, from its roots in Cubism and Neo-Impressionism to the heights of abstract expression. His works serve as a testament to the power of color and shape in conveying emotion and motion, making them invaluable to the understanding of 20th-century art history.
To stay informed on new sales, auctions, and exhibitions related to Robert Delaunay, sign up for updates. This subscription ensures you remain updated on opportunities to engage with Delaunay's influential body of work, reflecting the ongoing interest in his contributions to modern art.

Joseph Fernand Henri Léger was a French artist renowned for his innovative approach to Cubism and his transition towards a figurative, populist style. Born in Argentan, Orne, Lower Normandy, Léger's early career was marked by a stint as an architectural draftsman and a series of educational pursuits that eventually led him to Paris, where he embraced painting seriously. His artistic journey was significantly influenced by the bold abstractions of Cubism, characterized by geometric shapes and a vibrant palette, distinguishing his work from his contemporaries with what came to be known as "Tubism".
Léger's service in World War I profoundly impacted his artistic direction, leading him to adopt a 'mechanical' style that depicted the modern industrial world with sleek, tubular forms. This period saw creations like "Soldier with a Pipe" and "The Card Players," reflecting his war experiences and the mechanical aesthetics of the time. The post-war era encouraged Léger to explore the mechanical style further, evident in works like "The Bargeman" and "Mechanical Elements," highlighting the pace of technological advancement.
Throughout his career, Léger's work evolved, notably in the 1920s, where he aligned with Purist ideas, blending classicism with modernity. This phase is exemplified in "Woman with a Cat," showcasing a classical form with a modern, polished finish. By the 1930s, Léger's art took a more figurative, populist turn, aiming to democratize contemporary art and make it more accessible. His commitment to art education, especially for the common worker, underscored his belief in the social role of art.
For those intrigued by Joseph Fernand Henri Léger's groundbreaking contributions to modern art, his works can be found in prestigious museums worldwide. His legacy continues to inspire art collectors and enthusiasts alike. To stay updated on exhibitions and auction events featuring Léger's work, sign up for updates and embrace the unique opportunity to explore the richness of his artistic endeavors.


Pieter Cornelis Mondriaan, later known as Piet Mondrian, was a Dutch painter and art theoretician, whose transformation from figurative art to an abstract modernist style revolutionized the visual arts landscape of the 20th century. Born on March 7, 1872, in Amersfoort, Netherlands, and passing away on February 1, 1944, in New York, Mondrian's journey in art began in a devoutly Calvinist home where both art and music were encouraged. His early works were influenced by his surroundings, featuring landscapes in an Impressionist manner, but it was his shift to Paris in 1911 that marked the beginning of his profound evolution towards abstraction.
Mondrian co-founded the De Stijl art movement, aiming to achieve a universal aesthetic through the simplification of visual elements to their essentials: straight lines, right angles, primary colors, and the use of black, white, and gray. This reductionist approach, termed Neoplasticism, was Mondrian's contribution to creating 'universal beauty'. His philosophy extended beyond the canvas, influencing architecture, design, and fashion, encapsulating the modernist ideal and becoming synonymous with Modernism itself.
Some of Mondrian's notable works, such as "Composition with Red, Blue, and Yellow" and "Broadway Boogie Woogie", exemplify his revolutionary style, characterized by an economy of color and a rigorously abstract geometry that aimed to express the dynamic equilibrium of universal forces. These masterpieces, along with his theoretical writings, left a lasting impact on the course of abstract painting and several major art movements including Color Field painting, Abstract Expressionism, and Minimalism.
Mondrian's art is celebrated in museums and galleries worldwide, notably at the Gemeentemuseum Den Haag and the Museum of Modern Art in New York, where his evolution from figuration to geometric abstraction continues to inspire and captivate audiences. His commitment to exploring the spiritual in art through a radical simplification of form and color has cemented his legacy as one of the pioneers of 20th-century abstract art.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Mondrian's works represent not just significant artistic achievements but also pivotal moments in the history of modern art. His influence extends far beyond his own creations, shaping the development of modern aesthetics in numerous fields. If you're intrigued by Mondrian's vision of harmony and order through abstraction, we invite you to sign up for updates. This subscription will keep you informed about new product sales and auction events related to Mondrian's work, ensuring you stay connected to the ever-evolving world of art and design inspired by this iconic figure.


Kurt Schwitters (1887–1948) was a German artist renowned for his multifaceted contributions to modern art, encompassing painting, poetry, graphic design, and installation art. Born in Hanover, Germany, Schwitters developed a unique artistic vision that led to the creation of "Merz," a term he coined to describe his one-of-a-kind approach to art.
The concept of Merz originated from a fragment of the word "Kommerz" (commerce), which Schwitters incorporated into his early collages. This term came to represent his artistic philosophy, characterized by the assemblage of found objects and everyday materials into cohesive compositions. Through Merz, Schwitters sought to blur the boundaries between traditional art forms, integrating elements of Dadaism, Constructivism, and Surrealism.
One of Schwitters' most significant projects was the "Merzbau," an ambitious, evolving installation within his Hanover home. This project began around 1923 and transformed his living space into a labyrinthine structure filled with collages, sculptures, and found objects. The Merzbau was a physical manifestation of his Merz philosophy, embodying the synthesis of art and life. Unfortunately, the original Merzbau was destroyed during a British air raid in 1943.
In addition to his visual art, Schwitters made notable contributions to literature and sound art. His poem "An Anna Blume," published in 1919, is a seminal work that exemplifies his playful use of language and nonsensical style, aligning with the Dada movement's principles. Moreover, his "Ursonate," a sound poem composed between 1922 and 1932, showcases his innovative exploration of phonetic expression and rhythm, pushing the boundaries of traditional poetry.
The rise of the Nazi regime in Germany had a profound impact on Schwitters' life and work. Classified as a "degenerate" artist by the Nazis, he fled to Norway in 1937 to escape persecution. Following the German invasion of Norway in 1940, he sought refuge in the United Kingdom. During his internment at the Hutchinson Internment Camp on the Isle of Man, Schwitters continued to create art, producing over 200 works during his 16 months of confinement.
After his release, Schwitters settled in the Lake District of England, where he embarked on a new Merz construction known as the "Merzbarn." Although he was unable to complete this project due to his death in 1948, the Merzbarn stands as a testament to his unwavering commitment to his artistic vision. Today, Kurt Schwitters is celebrated as a pioneer of modern art, whose innovative techniques and ideas have left an indelible mark on the art world.
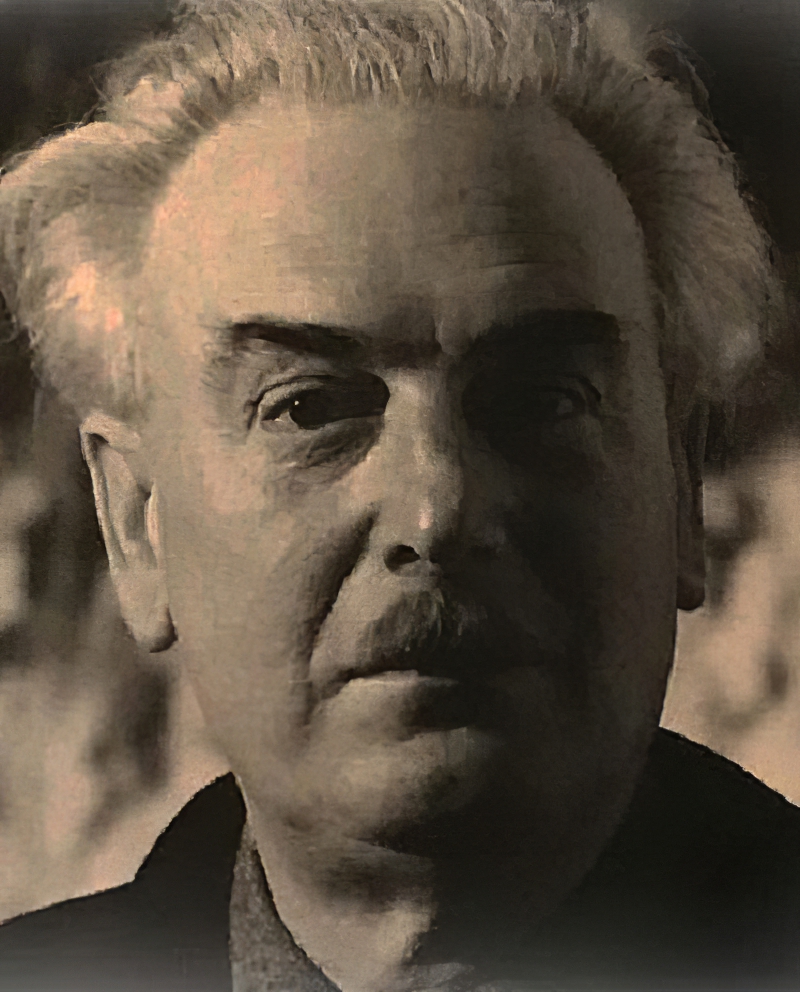


Heinrich Siepmann was a painter and belonged to the second generation of Constructivism.


Karl Peter Röhl was a German painter and graphic artist.

Karl Peter Röhl was a German painter and graphic artist.


Theo van Doesburg, real name Christian Emil Marie Küpper, is a Dutch painter, architect and sculptor, art theorist, co-founder of the Style Group and of Neoplasticism.
Theo van Doesburg co-founded with Piet Mondrian the De Stijl abstract art movement. The basis of van Doesburg's views was the attempt to reduce all forms of objective harmony in a work of art to certain geometric elements. These new principles soon had a significant influence on the development of architecture, literature, graphics and music.


Karl Peter Röhl was a German painter and graphic artist.


Karl Peter Röhl was a German painter and graphic artist.


Karl Peter Röhl was a German painter and graphic artist.
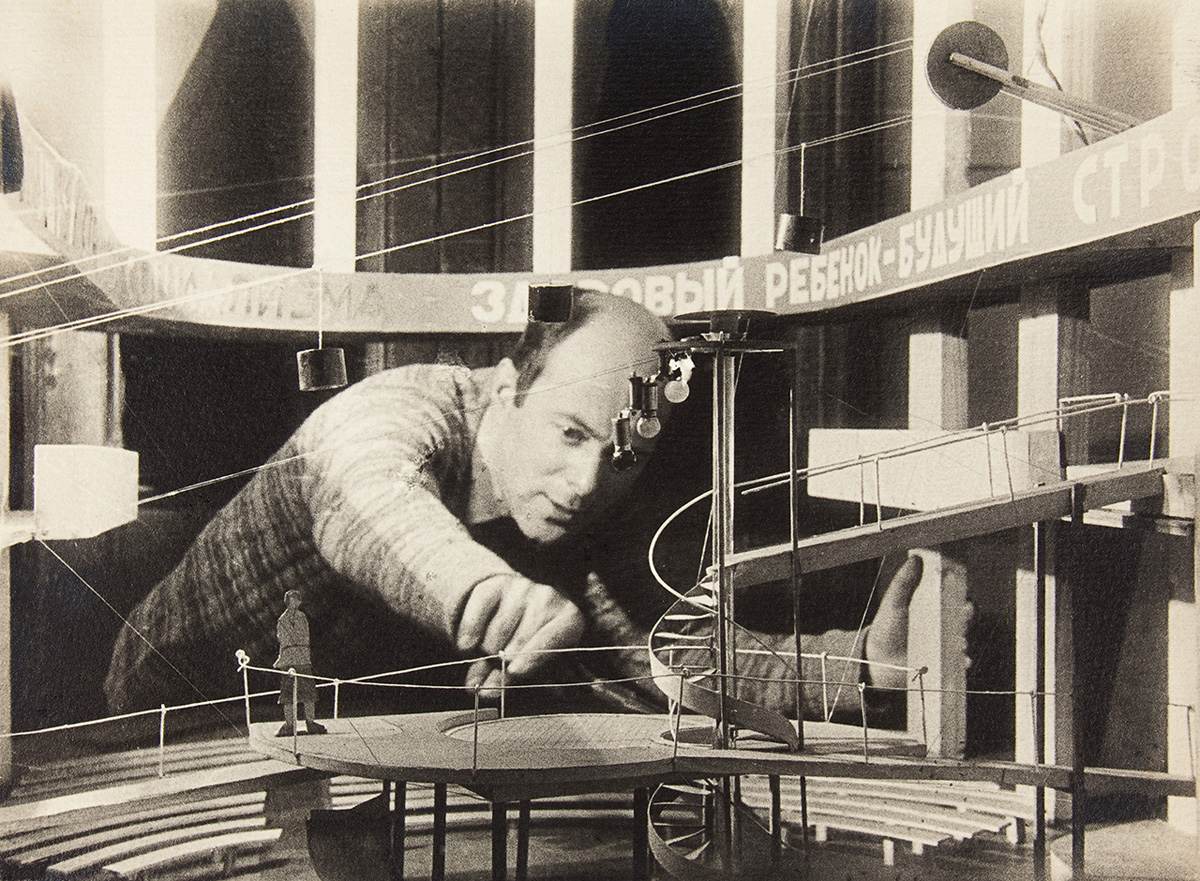


Lazar Markovich Lissitzky (Russian: Ла́зарь Ма́ркович Лиси́цкий) was a pivotal figure in the avant-garde art movement of the early 20th century, whose contributions spanned across multiple disciplines including painting, architecture, and graphic design. Born in Pochinok, Russian Empire (now in Smolensk Oblast, Russia), Lissitzky is renowned for his profound influence on the development of Constructivism, a movement characterized by the integration of technology and industry into the arts.
Lissitzky's work is distinguished by its innovative use of geometric forms, bold colors, and dynamic compositions, which sought not only to reflect the modern industrial world but also to actively participate in shaping it. His artworks and theories were instrumental in bridging the gap between the avant-garde movements in Russia and Western Europe, facilitating a cross-cultural exchange that enriched the development of modern art. Among his most notable contributions are his "Proun" series, an acronym for "Project for the Affirmation of the New" in Russian, which encapsulates his vision of art as a transformative social force.
His legacy is preserved in some of the world's most prestigious museums and galleries, including the Museum of Modern Art in New York and the Russian State Museum in Saint Petersburg. These institutions house key works that exemplify Lissitzky's groundbreaking approach to art and design, making them a focal point for collectors and experts in the field of art and antiques.
For those deeply invested in the evolution of modern art and its profound impact on culture and society, Lissitzky's work offers invaluable insights into the creative exploration of form and space. His contributions continue to inspire contemporary artists and designers, emphasizing the enduring relevance of his vision.
We invite collectors and art experts to sign up for updates on new product sales and auction events related to Lazar Markovich Lissitzky. This subscription is an opportunity to stay informed about the latest acquisitions and offerings that celebrate the legacy of a visionary artist whose work continues to resonate with audiences worldwide.


Kurt Schwitters (1887–1948) was a German artist renowned for his multifaceted contributions to modern art, encompassing painting, poetry, graphic design, and installation art. Born in Hanover, Germany, Schwitters developed a unique artistic vision that led to the creation of "Merz," a term he coined to describe his one-of-a-kind approach to art.
The concept of Merz originated from a fragment of the word "Kommerz" (commerce), which Schwitters incorporated into his early collages. This term came to represent his artistic philosophy, characterized by the assemblage of found objects and everyday materials into cohesive compositions. Through Merz, Schwitters sought to blur the boundaries between traditional art forms, integrating elements of Dadaism, Constructivism, and Surrealism.
One of Schwitters' most significant projects was the "Merzbau," an ambitious, evolving installation within his Hanover home. This project began around 1923 and transformed his living space into a labyrinthine structure filled with collages, sculptures, and found objects. The Merzbau was a physical manifestation of his Merz philosophy, embodying the synthesis of art and life. Unfortunately, the original Merzbau was destroyed during a British air raid in 1943.
In addition to his visual art, Schwitters made notable contributions to literature and sound art. His poem "An Anna Blume," published in 1919, is a seminal work that exemplifies his playful use of language and nonsensical style, aligning with the Dada movement's principles. Moreover, his "Ursonate," a sound poem composed between 1922 and 1932, showcases his innovative exploration of phonetic expression and rhythm, pushing the boundaries of traditional poetry.
The rise of the Nazi regime in Germany had a profound impact on Schwitters' life and work. Classified as a "degenerate" artist by the Nazis, he fled to Norway in 1937 to escape persecution. Following the German invasion of Norway in 1940, he sought refuge in the United Kingdom. During his internment at the Hutchinson Internment Camp on the Isle of Man, Schwitters continued to create art, producing over 200 works during his 16 months of confinement.
After his release, Schwitters settled in the Lake District of England, where he embarked on a new Merz construction known as the "Merzbarn." Although he was unable to complete this project due to his death in 1948, the Merzbarn stands as a testament to his unwavering commitment to his artistic vision. Today, Kurt Schwitters is celebrated as a pioneer of modern art, whose innovative techniques and ideas have left an indelible mark on the art world.