letter
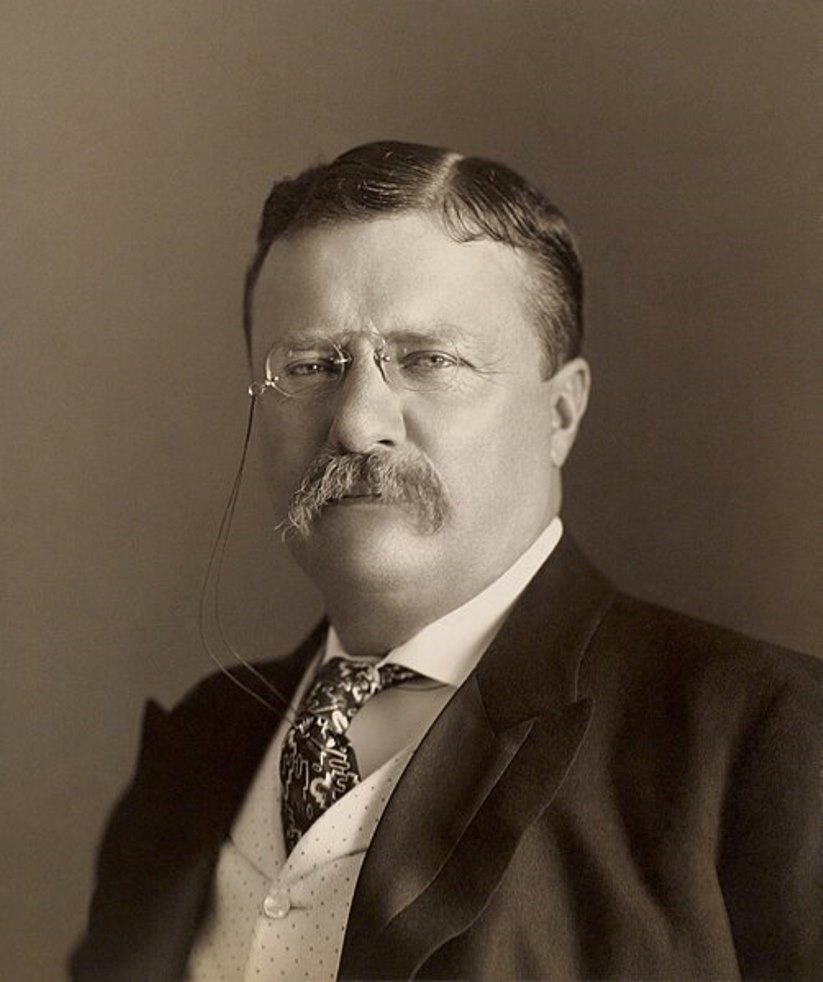
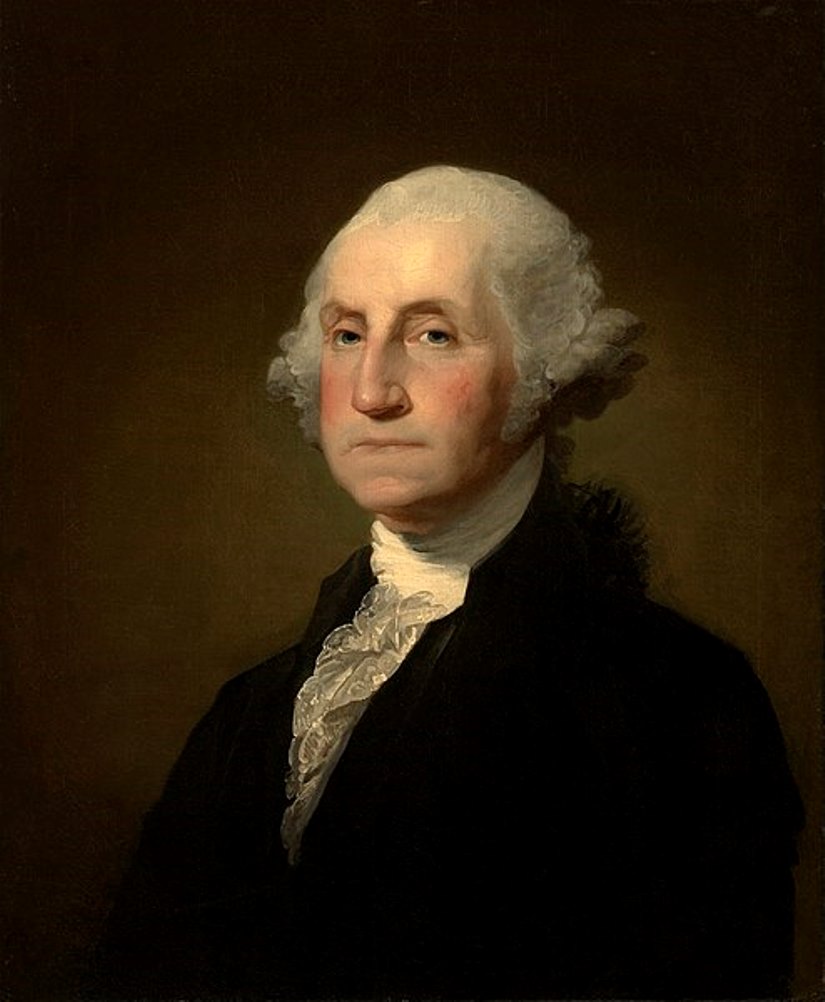



George Washington is the first popularly elected president of the United States of America and one of the founding fathers of the United States.
Born into a noble family in colonial Virginia in February 1732, George Washington served as a Virginian officer with British troops during the French-Indian War (1754-1763) from 1754-1758. This was a territorial war fought largely between the colonies of Britain and France that escalated into a worldwide conflict between the two countries. J. Washington was at the center of the conflicts in the disputed Ohio River Valley area.
In June 1775, he was elected commander-in-chief of the Continental forces in the war already for independence from Great Britain. He commanded American troops throughout the war, becoming famous for his perseverance and bravery.
In 1787, J. Washington represented the state of Virginia as a delegate to the Constitutional Convention. This convention created the Constitution of the United States. In 1789, the Electoral College unanimously elected George Washington president, and in 1792 he was re-elected for a second term. Thus George Washington was in office as President of the United States from April 30, 1789 to March 4, 1797.
As head of state, he helped to strengthen the Union, implement the principles of the Constitution and build the capital of the United States. He was engaged in the formation of the central authorities and system of government, created precedents for the institution of presidents, encouraged the development of the economy, maintained friendly relations with Congress. In foreign policy Washington avoided interference in the affairs of European states.
After leaving the post of president, George Washington lived in Mount Vernon Manor.
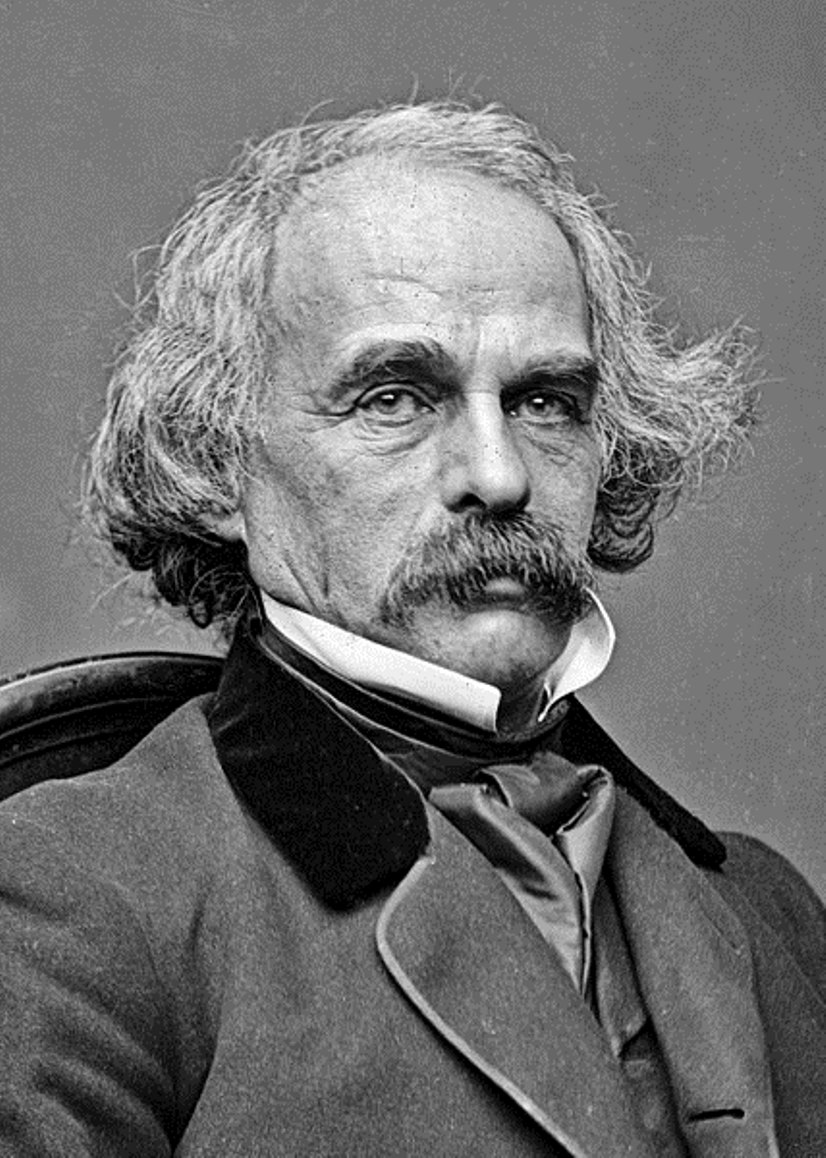


Nathaniel Hawthorne is an American writer and author.
Hawthorne is a recognized short story writer and a master of allegorical and symbolic narrative. One of the first fiction writers in American literature, he is best known for his works The Scarlet Letter (1850) and The House of Seven Gables (1851). Hawthorne's artistic works are considered part of the American Romantic movement and, in particular, of so-called dark Romanticism, a popular mid-19th-century fascination with the irrational, the demonic, and the grotesque.


Nathaniel Hawthorne is an American writer and author.
Hawthorne is a recognized short story writer and a master of allegorical and symbolic narrative. One of the first fiction writers in American literature, he is best known for his works The Scarlet Letter (1850) and The House of Seven Gables (1851). Hawthorne's artistic works are considered part of the American Romantic movement and, in particular, of so-called dark Romanticism, a popular mid-19th-century fascination with the irrational, the demonic, and the grotesque.


Nathaniel Hawthorne is an American writer and author.
Hawthorne is a recognized short story writer and a master of allegorical and symbolic narrative. One of the first fiction writers in American literature, he is best known for his works The Scarlet Letter (1850) and The House of Seven Gables (1851). Hawthorne's artistic works are considered part of the American Romantic movement and, in particular, of so-called dark Romanticism, a popular mid-19th-century fascination with the irrational, the demonic, and the grotesque.
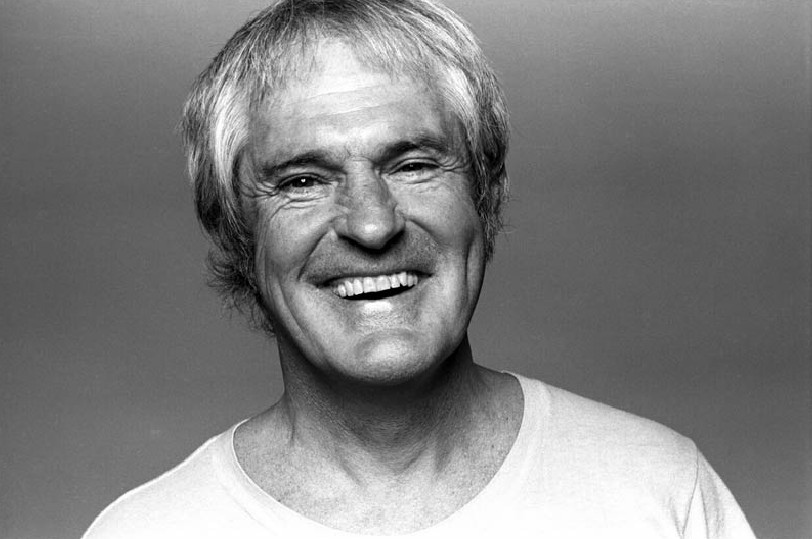



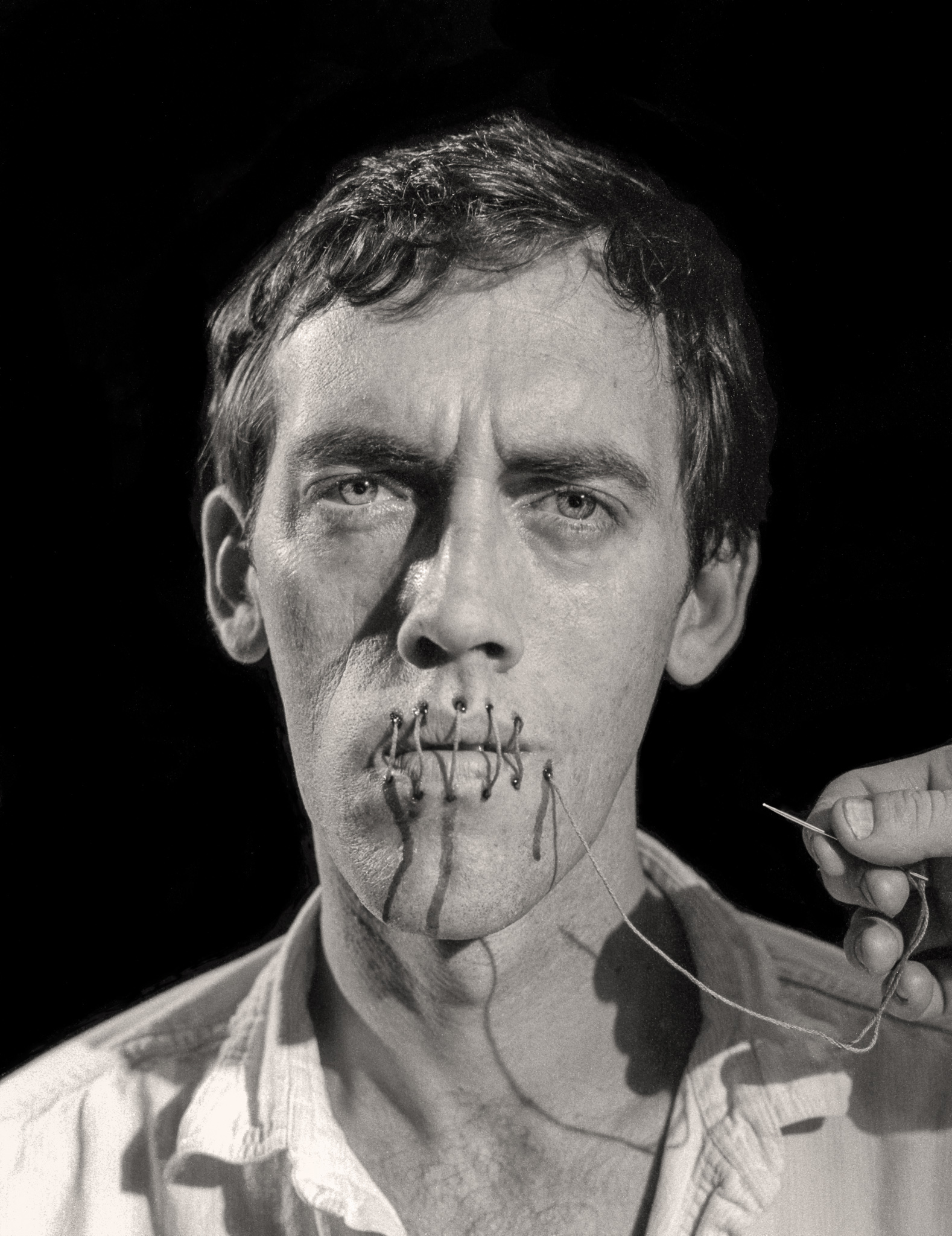
David Wojnarowicz was an American artist known for his multifaceted work, which included painting, film, video, performance, writing, and music. His art often addressed themes such as society's fragmentation, consumerism, and the juxtaposition of natural and industrial landscapes. After being diagnosed with AIDS at 33, Wojnarowicz's work became more activist-oriented, focusing on his sexuality and his illness, as exemplified in his piece "Untitled," also known as "One Day This Kid".
David Wojnarowicz's childhood was tumultuous, marked by abuse and neglect, which profoundly influenced his later work. Despite dropping out, he eventually completed his high school education and immersed himself in New York's underground art scene. His art from the 1980s, particularly after the death of his mentor and close friend Peter Hujar, increasingly addressed AIDS and became more politically charged.
His legacy includes notable works like "A Fire in My Belly," which sparked controversy and highlighted the ongoing struggles of the LGBTQ+ community and those affected by AIDS. Wojnarowicz's work continues to inspire and provoke, as seen in exhibitions like the Whitney Museum's retrospective, "David Wojnarowicz: History Keeps Me Awake at Night," and his influence on various artists and cultural movements.
For those interested in exploring the depth and breadth of David Wojnarowicz's work, staying informed about upcoming exhibitions and available collections can provide valuable insights into his impactful legacy. Subscribing to updates from art galleries and museums that feature his work is an excellent way to stay connected to the evolving appreciation and interpretation of his art.
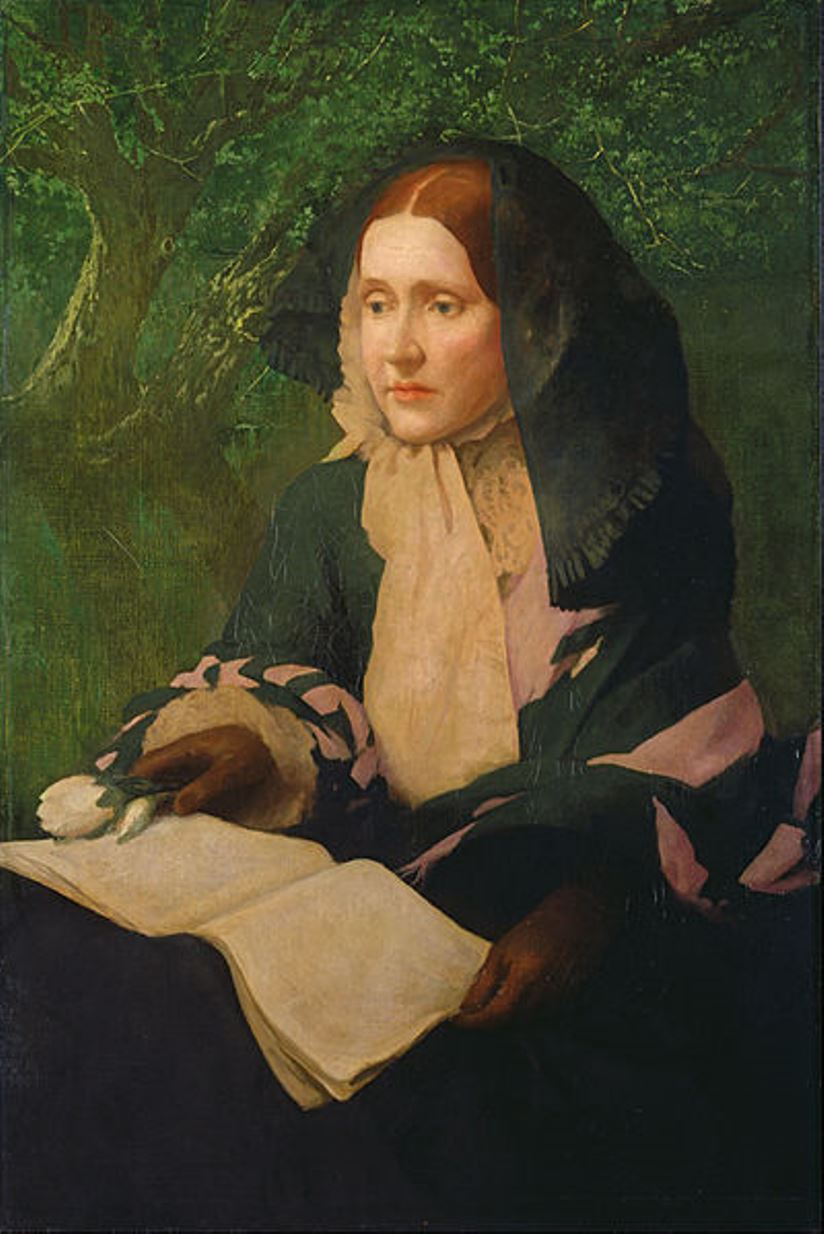


Julia Ward Howe is an American writer and poet, philosopher, abolitionist, and feminist.
Born into a well-to-do family and privately educated, Julia Ward married educator Samuel Gridley Howe and settled in Boston. She published her first collection of poems, Passionate Flowers, in 1854.Julia's early poems were praised by Hawthorne, Whittier, and Longfellow for their intellectual intensity. For a time Howe published the abolitionist newspaper Commonwealth with her husband. And in February 1862, The Atlantic Monthly published her poem "Battle Hymn of the Republic," which became the semi-official Civil War song of the Union Army, and Howe gained fame.
After the war, Howe began fighting for women's rights. In 1868, she was elected the first president of the New England Women's Suffrage Association. In 1868, she helped found the New England Woman's Club and became its president in 1871, the same year she became the first president of the American branch of the International Women's Peace Association. She was later active in the International Federation of Women's Clubs. Howe continued to write throughout her life, publishing travel books, poems, collections of essays, and biographies.
In 1870, she co-founded Woman's Journal and then served as its editor for 20 years. She traveled extensively until her advanced old age. In 1908, she became the first woman elected to the American Academy of Arts and Letters.


Nathaniel Hawthorne is an American writer and author.
Hawthorne is a recognized short story writer and a master of allegorical and symbolic narrative. One of the first fiction writers in American literature, he is best known for his works The Scarlet Letter (1850) and The House of Seven Gables (1851). Hawthorne's artistic works are considered part of the American Romantic movement and, in particular, of so-called dark Romanticism, a popular mid-19th-century fascination with the irrational, the demonic, and the grotesque.
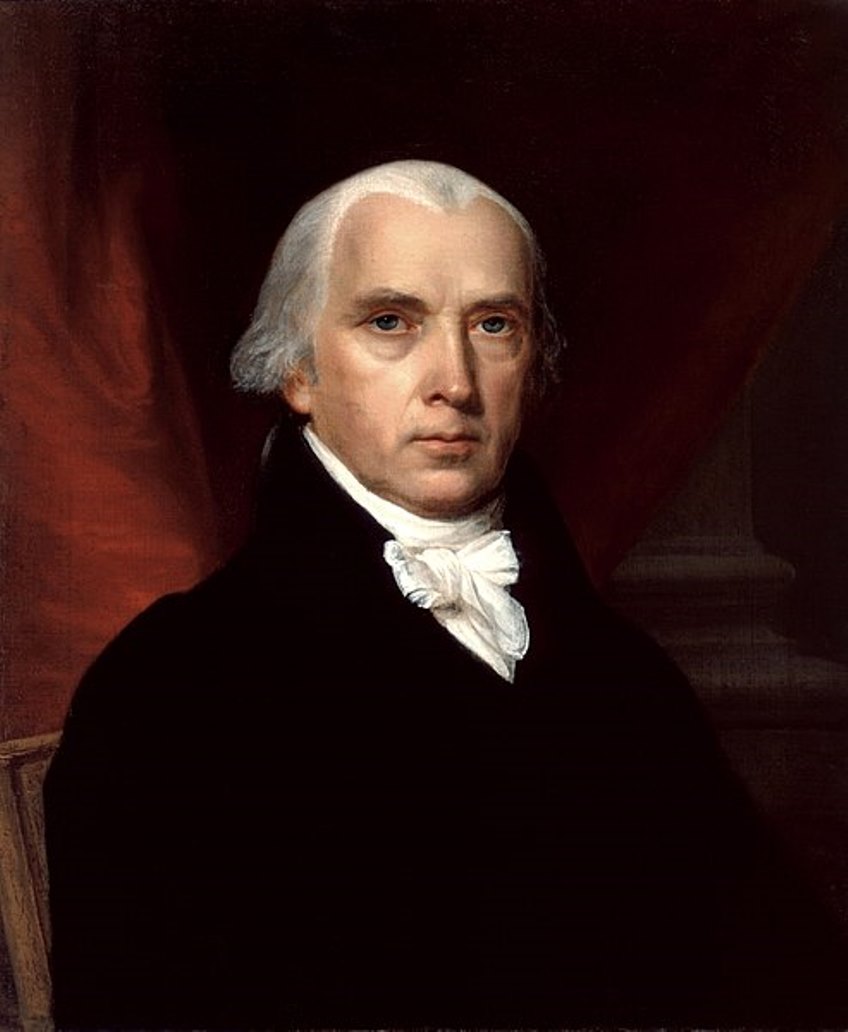


James Madison was an American politician and statesman, the fourth President of the United States (1809-1817).
Madison attended Princeton and studied history, government, and law. He participated in the drafting of the Virginia Constitution in 1776, and in 1780 was chosen to represent Virginia in the Continental Congress (1780-83 and 1786-88). James Madison contributed greatly to the ratification of the Constitution, writing, with Alexander Hamilton and John Jay, The Federalist (1788). He was later called the "father of the Constitution."
In 1792, Madison and Thomas Jefferson (1743-1826) founded the Democratic-Republican Party, which has been called America's first opposition political party. When Jefferson became the third president of the United States, Madison served as his secretary of state. In Congress, he was involved in drafting the Bill of Rights and passing the first revenue legislation. As Secretary of State to President Jefferson (1801-1809), Madison protested to warring France and Great Britain that their seizure of American ships was contrary to international law.
Madison was elected president in 1808, succeeding Jefferson. Continued British interference in shipping, as well as other grievances, led to the War of 1812. During Madison's second term as president, the war was still ongoing, and he and his wife were even forced to flee in the face of advancing British troops who set Washington, D.C. on fire. Despite this, in 1815, the United States declared its victory in the war.
After the end of his second term, Madison remained active in public affairs. He edited his Journal of the Constitutional Convention, was co-chairman of the Virginia Constitutional Convention from 1829-1830, and chancellor of the University of Virginia from 1826-36. He was also Monroe's foreign policy advisor. Although Madison was a slave owner all his life, in the last years of his life he was active in the American Colonization Society, whose mission was to resettle slaves in Africa. James Madison died at the age of 85 in 1836.
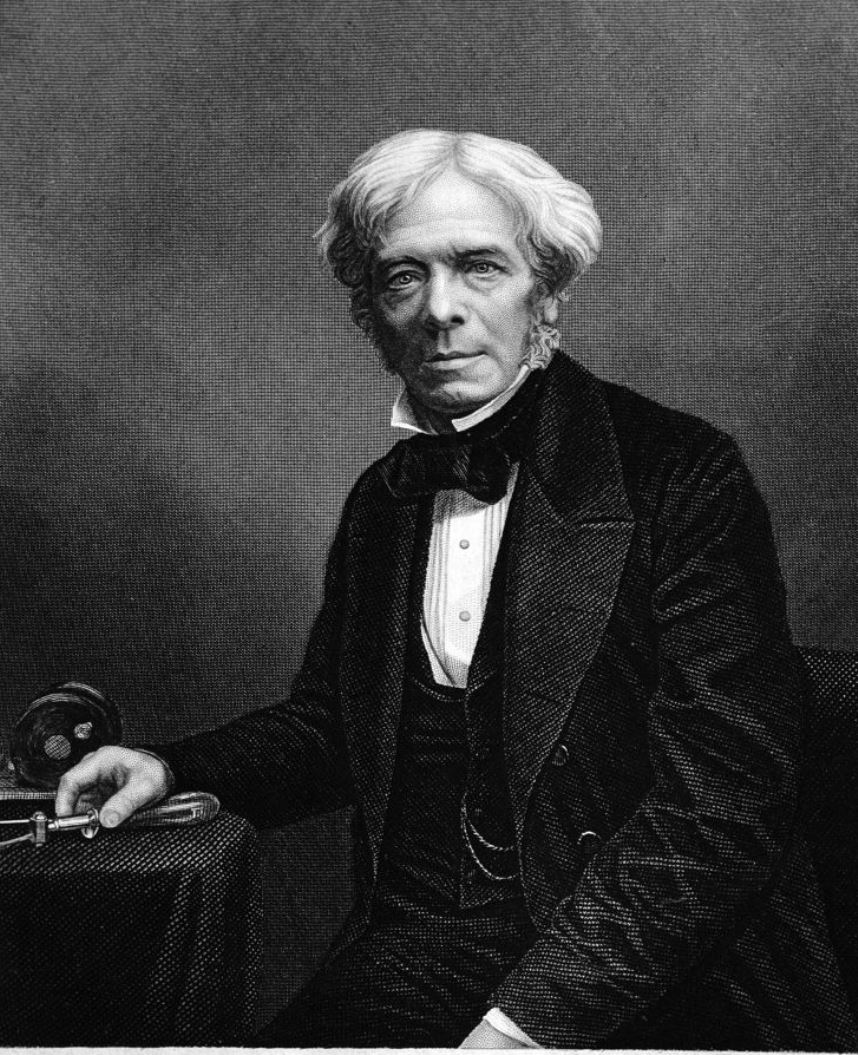


Michael Faraday was a British physicist and chemist, explorer and experimenter.
Faraday, because of his family's poverty, was unable to receive a formal education, but at the bookbinding shop in London where he worked, he read many books, including encyclopedias and textbooks on chemistry and physics. He persevered in self-education, attending hearings at the City Philosophical Society and later lectures by Sir Humphry Davy at the Royal Institution, who as a result took the able student on as an apprentice. In 1825 he replaced the seriously ill Davy in the management of the laboratory of the Royal Institution.
In 1833 Faraday was appointed to a research chair of chemistry created especially for him, where, among other achievements, the scientist liquefied various gases, including chlorine and carbon dioxide. His study of heating and lighting oils led to the discovery of benzene and other hydrocarbons, and he experimented extensively with various steel alloys and optical glasses. Faraday was an excellent experimentalist who presented his ideas in simple language. He is best known for his contributions to the understanding of electricity and electrochemistry. The concepts behind electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism, and electrolysis were some of his most important discoveries. His electromagnetic research formed the basis of the electromagnetic equations that James Clerk Maxwell developed in the 1850s and 1860s.
Between 1831 and 1855, Faraday read a series of 30 papers before the Royal Society, which were published in his three-volume Experimental Investigations in Electricity. His bibliography numbers some 500 printed articles. By 1844 he had been elected a member of some 70 scientific societies, including the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences.


Michael Faraday was a British physicist and chemist, explorer and experimenter.
Faraday, because of his family's poverty, was unable to receive a formal education, but at the bookbinding shop in London where he worked, he read many books, including encyclopedias and textbooks on chemistry and physics. He persevered in self-education, attending hearings at the City Philosophical Society and later lectures by Sir Humphry Davy at the Royal Institution, who as a result took the able student on as an apprentice. In 1825 he replaced the seriously ill Davy in the management of the laboratory of the Royal Institution.
In 1833 Faraday was appointed to a research chair of chemistry created especially for him, where, among other achievements, the scientist liquefied various gases, including chlorine and carbon dioxide. His study of heating and lighting oils led to the discovery of benzene and other hydrocarbons, and he experimented extensively with various steel alloys and optical glasses. Faraday was an excellent experimentalist who presented his ideas in simple language. He is best known for his contributions to the understanding of electricity and electrochemistry. The concepts behind electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism, and electrolysis were some of his most important discoveries. His electromagnetic research formed the basis of the electromagnetic equations that James Clerk Maxwell developed in the 1850s and 1860s.
Between 1831 and 1855, Faraday read a series of 30 papers before the Royal Society, which were published in his three-volume Experimental Investigations in Electricity. His bibliography numbers some 500 printed articles. By 1844 he had been elected a member of some 70 scientific societies, including the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences.
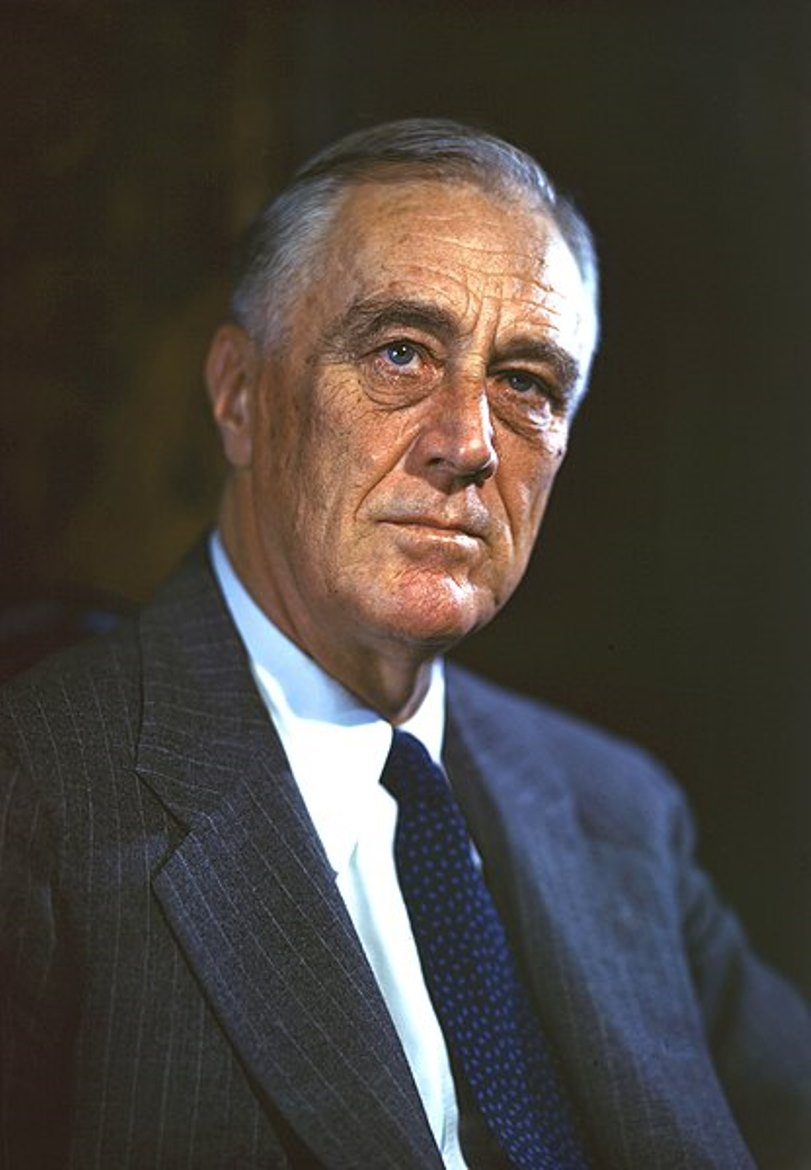


Franklin Delano Roosevelt was an American politician and statesman, the 32nd President of the United States (1932-1945).
Franklin was educated at Harvard University and Columbia Law School. His cousin was President Theodore Roosevelt, and Franklin also went into public service, but as a Democrat. He was elected to the New York Senate in 1910, President Wilson appointed him Assistant Secretary of the Navy, and Roosevelt became Governor of New York in 1928.
In November 1932, Franklin D. Roosevelt was elected president of the United States. Taking office in the midst of the Great Depression, Franklin D. Roosevelt, with his "Hundred Days" and "New Deal" programs, helped the American people regain faith in themselves. In 1936, he was re-elected by a large margin. During this difficult political period, he sought through neutrality legislation to keep the U.S. out of the war in Europe, but at the same time to strengthen countries that were threatened or attacked. Japan's surprise attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941, drew the country into the war.
In 1944, as Hitler's Germany was nearing its collapse, an ailing Roosevelt managed to win the presidency again. The following February, he met with Churchill and Stalin at the famous Yalta Conference. His health was deteriorating, and on April 12, 1945, Franklin Roosevelt died of a cerebral hemorrhage. He was the only U.S. president to be elected to office four times. Roosevelt successfully led the United States through two of the greatest crises of the 20th century: the Great Depression and World War II.
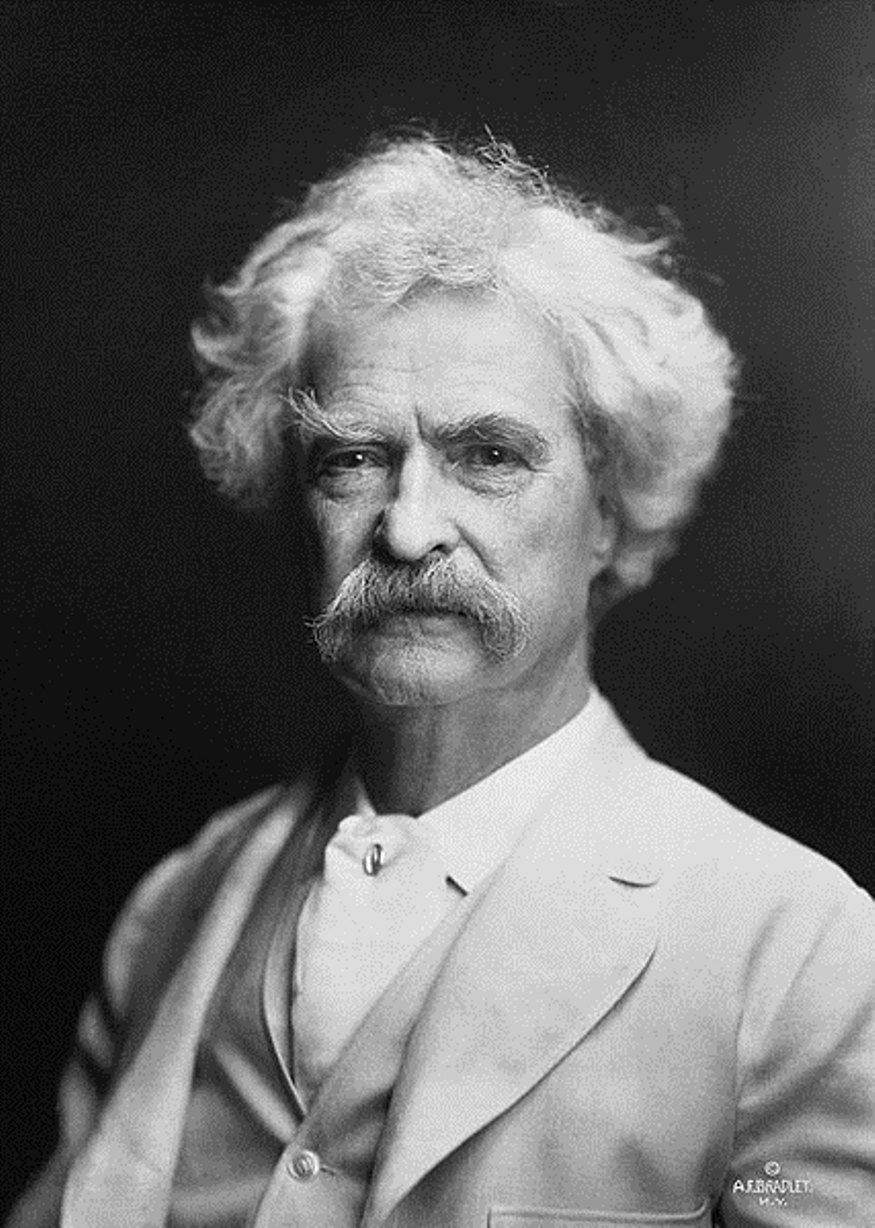




Mark Twain, real name Samuel Langhorne Clemens, was an American humanist writer, journalist, and social activist.
As a young man, Samuel worked in the printing press and in the gold mines, then went on a steamboat trip to Europe and the "Holy Land". His travel letters, full of vivid descriptions and ironic observations, were very well received by the public and were later revised into his first book, Innocents Abroad, published in 1869.
The pseudonym "Mark Twain" first appeared in 1863 under one of Samuel Clemens' short stories, and since then all his significant works have been signed by that name.
A talented storyteller, a peculiar humorist and moralist, Twain knew and loved his many diverse characters. His scandalizers and dreamers, caring aunts and ambitious politicians, grumpy widows and lying aristocrats, cunning but generous slaves, sentimental moralists, brave and naive children - all these types of American people Twain gave voice to thanks to his masterful command of colloquial language, slang and jargon. Twain wrote a lot and in a variety of genres: humor and satire, philosophical fiction and journalism and others, but he always stood on the position of humanist and democrat.
Mark Twain became world famous for his travel stories and adventure novels about his childhood, these are "The Adventures of Tom Sawyer" (1876) and "The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn" (1885). Twain is still one of America's, and indeed the world's, best and most beloved writers. His works have been and are still being published in many languages around the world.
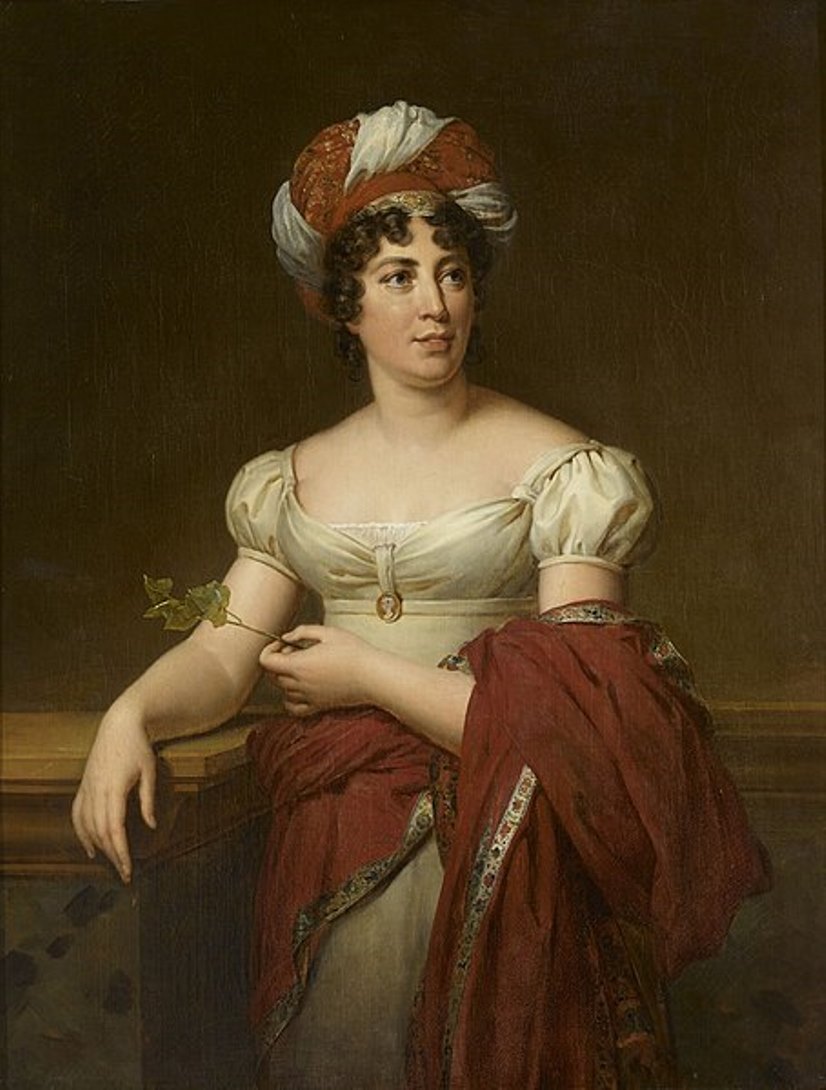



Anne-Louise-Germaine Necker, Baroness of Staël-Holstein, known as Madame de Staël, was a French writer, literary theorist, and publicist.
She was born into a Swiss family where her father was a banker and then finance minister to King Louis XVI, and her mother ran a brilliant literary and political salon in Paris where Voltaire, Diderot, and Hume frequented. Young Necker received a brilliant education, she absorbed the intellectual environment with great curiosity, becoming a witty and well-read conversationalist.
In 1786, she married the Swedish ambassador to Paris, Baron Eric de Staël-Holstein. It was a marriage of convenience, which ended in 1797 formal divorce.
Madame de Staël became known not only for her stunning and versatile works, but also for her enormous influence on the intellectual climate of that 19th century. During her lifetime she was known as a novelist, but she became much more famous as a political philosopher, literary critic, and theorist of Romanticism. Madame de Staël was an implacable opponent of Napoleon I and traveled around Europe for a decade during his reign from 1803. In 1810, the writer published one of her most famous and influential works, On Germany. She returned to Paris in 1814, after the fall of Napoleon, and wrote "Reflections on the Principal Events of the French Revolution."
In her travels, Madame de Staël met many politicians, artists and writers and was known for her cosmopolitanism and feminism. Madame de Staël epitomized the European culture of her time, combining ideas from neoclassicism to romanticism in her glittering salon for leading intellectuals.


























































![Autograph letter signed ('Eric A. Blair') to Dennis [Collings]](/assets/image/picture_3069379/6af83/a37bb91862ecb96e0686708f1d20b2561695852000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![Autograph letter signed ('Eric A. Blair') to Dennis [Collings]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3069379/6af83/a37bb91862ecb96e0686708f1d20b2561695852000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)



