pasch
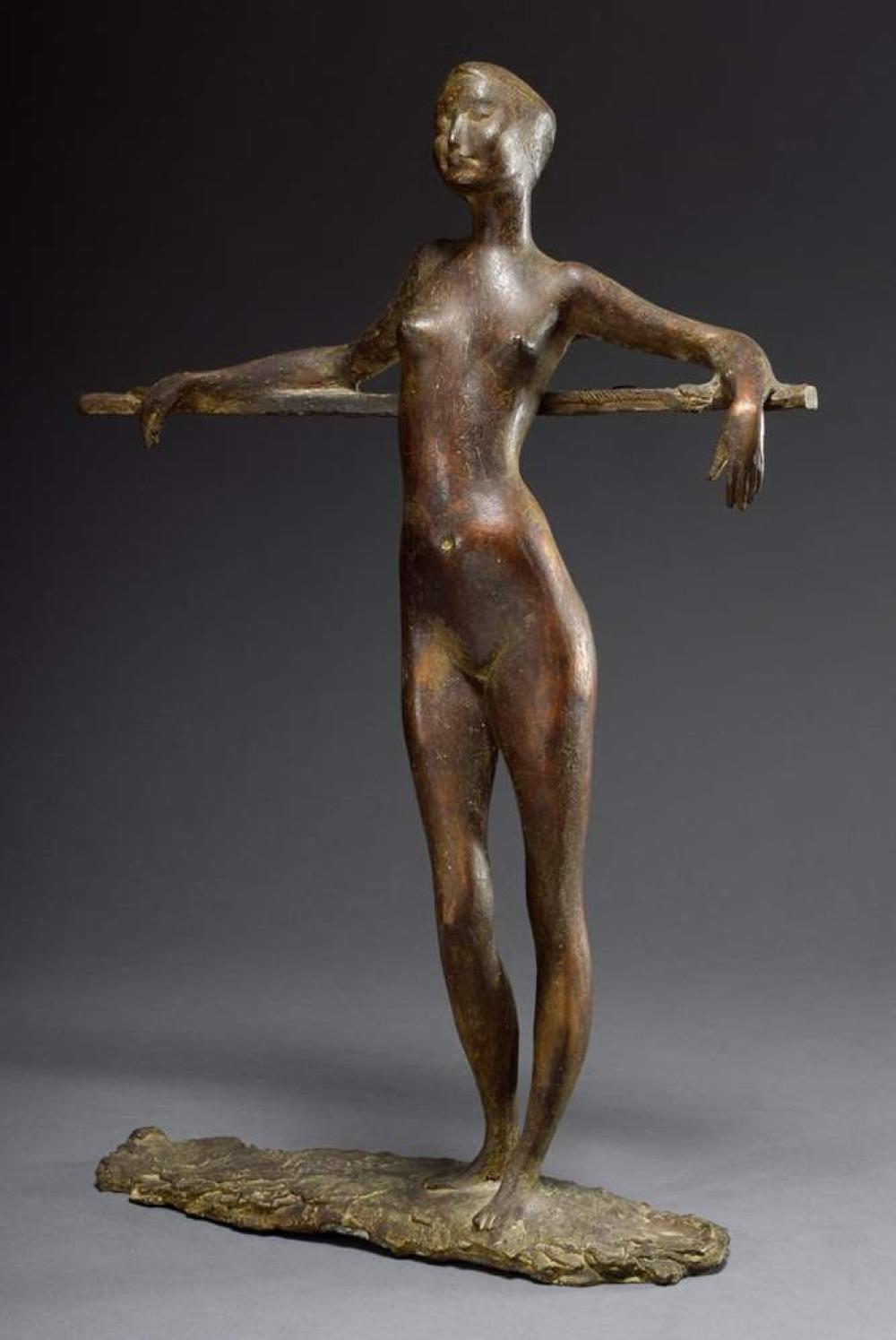

Clemens Pasch was a German sculptor and painter.


Clemens Pasch was a German sculptor and painter.


Clemens Pasch was a German sculptor and painter.
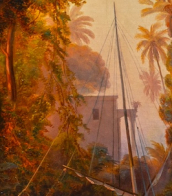

Clemens Pasch was a German sculptor and painter.
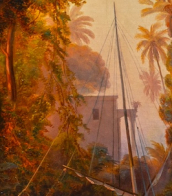

Clemens Pasch was a German sculptor and painter.
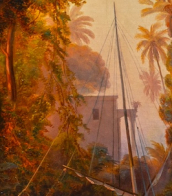

Clemens Pasch was a German sculptor and painter.


Clemens Pasch was a German sculptor and painter.


Clemens Pasch was a German sculptor and painter.
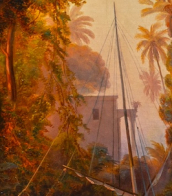

Clemens Pasch was a German sculptor and painter.
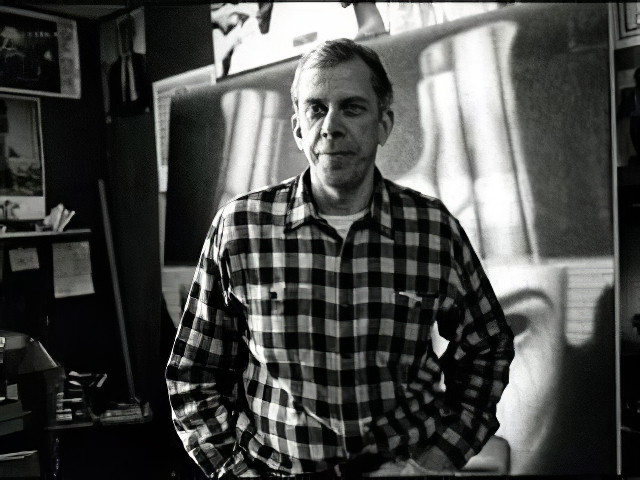

Ed (Edward Francis) Paschke was an American artist celebrated for his confrontational and vibrant paintings. Born on June 22, 1939, in Chicago, Illinois, Paschke found inspiration in comic strips and the work of Burne Hogarth, the creator of the Tarzan comic. His early fascination with visual storytelling translated into a unique art style that combined elements of pop culture, often in a sexualized or grotesque manner.
Paschke's art journey began at the School of the Art Institute of Chicago, where he honed his skills in draftsmanship. However, he struggled with abstract and Expressionist painting, the dominant styles of the 1950s. His career took a notable turn in 1961 when he started working as an illustrator for Playboy magazine, a position he held until 1989. This experience, coupled with a brief stint working in a mental institution, significantly influenced his art, particularly his theme of portraying society's marginalized figures.
Throughout his career, Paschke's work evolved in both style and medium. In his early paintings, he reimagined legendary figures in unusual contexts, like setting Marilyn Monroe's head atop an accordion player's body in "Pink Lady" (1970), or reinterpreting Claudette Colbert as a tattooed lady in "Painted Lady" (1971). His later works, such as "Matinee" (1987), showcased a shift towards electronic media, with images disintegrating into electronic disturbances. This evolution in his art reflected a deeper exploration of American values' underside—fame, violence, sex, and money—a theme he shared with Andy Warhol, one of his major influences.
Paschke's innovative technique involved using an overhead projector to layer images, which he then meticulously rendered in oil paints. He started with a black and white underpainting, followed by layers of colored glazing or impasto, creating vibrant, neon-colored finishes. This process paralleled the historical transition from black-and-white to color in printing, film, and television.
Despite his unique approach and contributions to the art world, Paschke remained somewhat distant from the mainstream New York art scene. Nevertheless, his work is celebrated in many museum collections, including the Art Institute of Chicago, the Madison Museum of Contemporary Art, and the Whitney Museum of American Art, among others. His influence extends beyond his lifetime, as seen in the opening of the Ed Paschke Art Center in Chicago in 2014, which commemorates his works alongside other Chicago artists.
Edward Francis Paschke passed away on November 25, 2004, but his legacy continues to inspire and challenge the art world, emphasizing the power of visual media to explore and critique societal norms and values.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Paschke's work offers a unique blend of cultural commentary and bold visual experimentation. To stay updated on new product sales and auction events related to Edward Francis Paschke, sign up for our updates. This subscription is a gateway to exploring the fascinating world of Paschke's art and its enduring impact on contemporary culture.


Ed (Edward Francis) Paschke was an American artist celebrated for his confrontational and vibrant paintings. Born on June 22, 1939, in Chicago, Illinois, Paschke found inspiration in comic strips and the work of Burne Hogarth, the creator of the Tarzan comic. His early fascination with visual storytelling translated into a unique art style that combined elements of pop culture, often in a sexualized or grotesque manner.
Paschke's art journey began at the School of the Art Institute of Chicago, where he honed his skills in draftsmanship. However, he struggled with abstract and Expressionist painting, the dominant styles of the 1950s. His career took a notable turn in 1961 when he started working as an illustrator for Playboy magazine, a position he held until 1989. This experience, coupled with a brief stint working in a mental institution, significantly influenced his art, particularly his theme of portraying society's marginalized figures.
Throughout his career, Paschke's work evolved in both style and medium. In his early paintings, he reimagined legendary figures in unusual contexts, like setting Marilyn Monroe's head atop an accordion player's body in "Pink Lady" (1970), or reinterpreting Claudette Colbert as a tattooed lady in "Painted Lady" (1971). His later works, such as "Matinee" (1987), showcased a shift towards electronic media, with images disintegrating into electronic disturbances. This evolution in his art reflected a deeper exploration of American values' underside—fame, violence, sex, and money—a theme he shared with Andy Warhol, one of his major influences.
Paschke's innovative technique involved using an overhead projector to layer images, which he then meticulously rendered in oil paints. He started with a black and white underpainting, followed by layers of colored glazing or impasto, creating vibrant, neon-colored finishes. This process paralleled the historical transition from black-and-white to color in printing, film, and television.
Despite his unique approach and contributions to the art world, Paschke remained somewhat distant from the mainstream New York art scene. Nevertheless, his work is celebrated in many museum collections, including the Art Institute of Chicago, the Madison Museum of Contemporary Art, and the Whitney Museum of American Art, among others. His influence extends beyond his lifetime, as seen in the opening of the Ed Paschke Art Center in Chicago in 2014, which commemorates his works alongside other Chicago artists.
Edward Francis Paschke passed away on November 25, 2004, but his legacy continues to inspire and challenge the art world, emphasizing the power of visual media to explore and critique societal norms and values.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Paschke's work offers a unique blend of cultural commentary and bold visual experimentation. To stay updated on new product sales and auction events related to Edward Francis Paschke, sign up for our updates. This subscription is a gateway to exploring the fascinating world of Paschke's art and its enduring impact on contemporary culture.


Ed (Edward Francis) Paschke was an American artist celebrated for his confrontational and vibrant paintings. Born on June 22, 1939, in Chicago, Illinois, Paschke found inspiration in comic strips and the work of Burne Hogarth, the creator of the Tarzan comic. His early fascination with visual storytelling translated into a unique art style that combined elements of pop culture, often in a sexualized or grotesque manner.
Paschke's art journey began at the School of the Art Institute of Chicago, where he honed his skills in draftsmanship. However, he struggled with abstract and Expressionist painting, the dominant styles of the 1950s. His career took a notable turn in 1961 when he started working as an illustrator for Playboy magazine, a position he held until 1989. This experience, coupled with a brief stint working in a mental institution, significantly influenced his art, particularly his theme of portraying society's marginalized figures.
Throughout his career, Paschke's work evolved in both style and medium. In his early paintings, he reimagined legendary figures in unusual contexts, like setting Marilyn Monroe's head atop an accordion player's body in "Pink Lady" (1970), or reinterpreting Claudette Colbert as a tattooed lady in "Painted Lady" (1971). His later works, such as "Matinee" (1987), showcased a shift towards electronic media, with images disintegrating into electronic disturbances. This evolution in his art reflected a deeper exploration of American values' underside—fame, violence, sex, and money—a theme he shared with Andy Warhol, one of his major influences.
Paschke's innovative technique involved using an overhead projector to layer images, which he then meticulously rendered in oil paints. He started with a black and white underpainting, followed by layers of colored glazing or impasto, creating vibrant, neon-colored finishes. This process paralleled the historical transition from black-and-white to color in printing, film, and television.
Despite his unique approach and contributions to the art world, Paschke remained somewhat distant from the mainstream New York art scene. Nevertheless, his work is celebrated in many museum collections, including the Art Institute of Chicago, the Madison Museum of Contemporary Art, and the Whitney Museum of American Art, among others. His influence extends beyond his lifetime, as seen in the opening of the Ed Paschke Art Center in Chicago in 2014, which commemorates his works alongside other Chicago artists.
Edward Francis Paschke passed away on November 25, 2004, but his legacy continues to inspire and challenge the art world, emphasizing the power of visual media to explore and critique societal norms and values.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Paschke's work offers a unique blend of cultural commentary and bold visual experimentation. To stay updated on new product sales and auction events related to Edward Francis Paschke, sign up for our updates. This subscription is a gateway to exploring the fascinating world of Paschke's art and its enduring impact on contemporary culture.
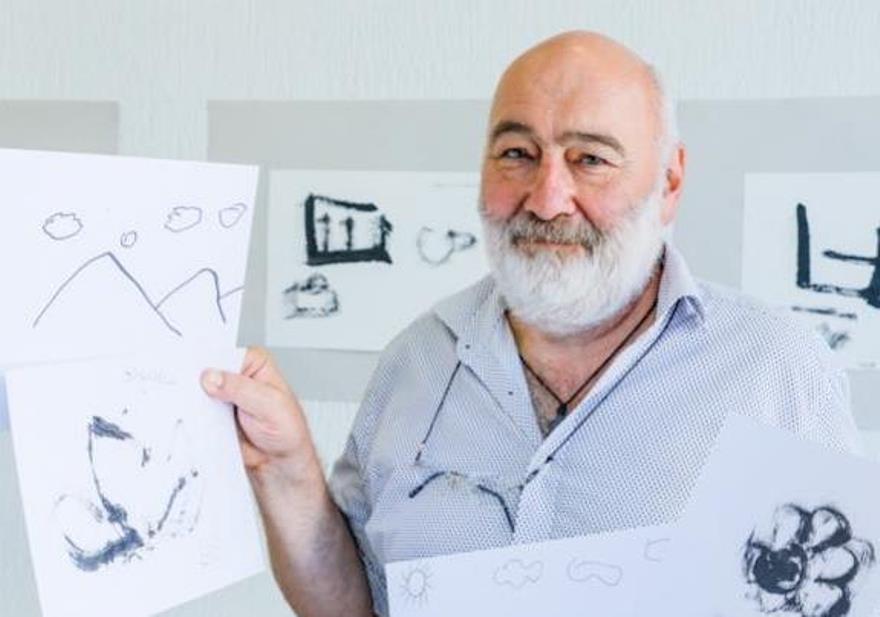


George Guraspaschvili is a Georgian painter and sculptor, professor at the Georgian State Academy of Art in Tbilisi, and member of the Union of Artists of the USSR. Since the mid-1990s his works have been exhibited internationally, particularly in Germany and China.
Guraspashvili has won numerous awards, including the Gold Medal for watercolor at the Malta Biennale. He is actively engaged in the promotion of young, talented artists from the Caucasus.
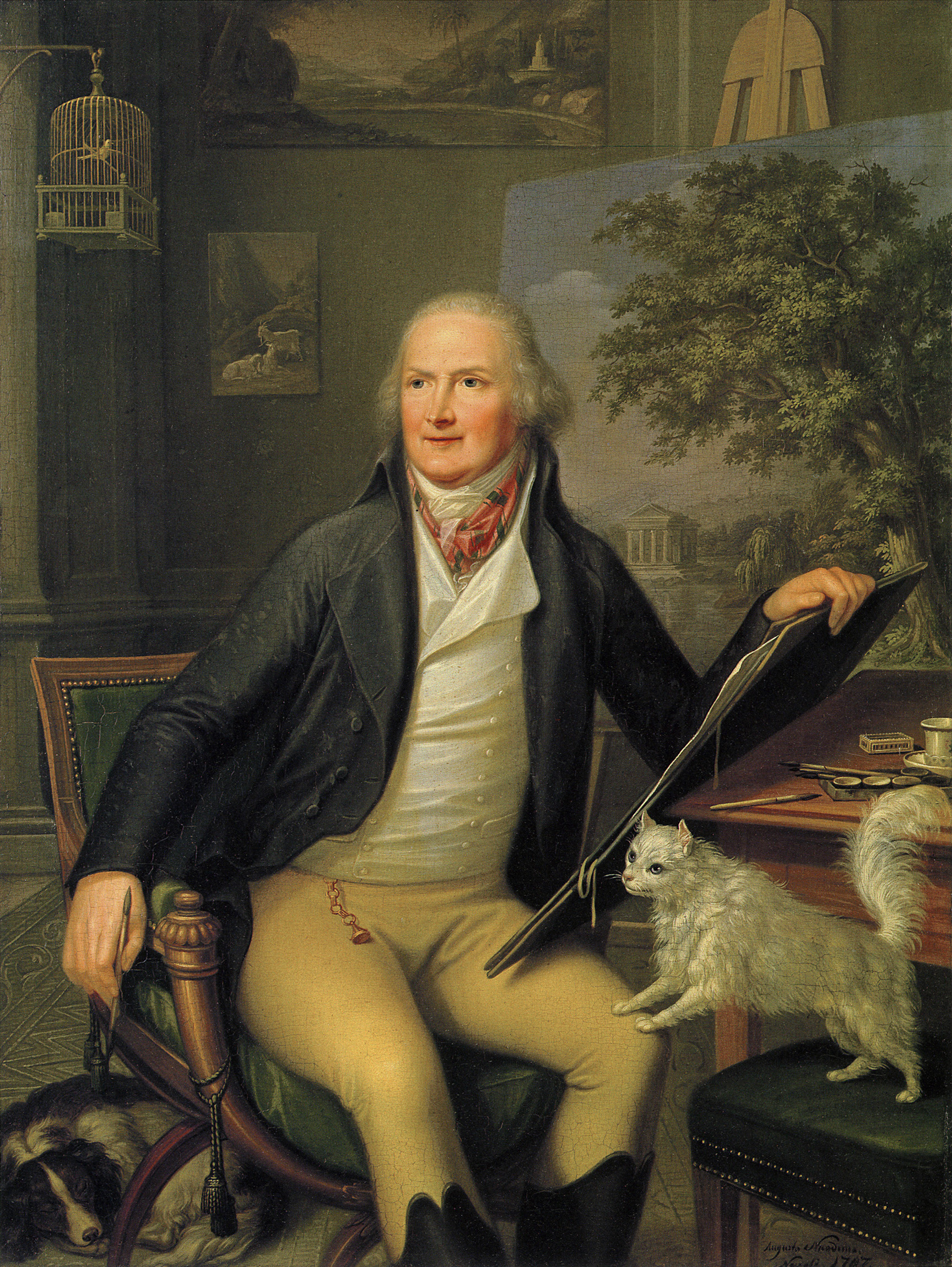


Jakob Philipp Hackert was a German painter of the second half of the 18th and early 19th centuries. He is known as a landscape painter and printmaker, a representative of neoclassicism and romanticism.
Hackert reached the peak of creative activity in 1770-1780. He was recognized by the European aristocracy, and for a time served as court painter to King Ferdinand IV of Naples, as well as receiving commissions from representatives of the Russian imperial family, such as Empress Catherine II and the heir to the throne, Paul Petrovich. His work, according to critics, was characterized by high craftsmanship and aristocratic elegance.








































































