presumably paris


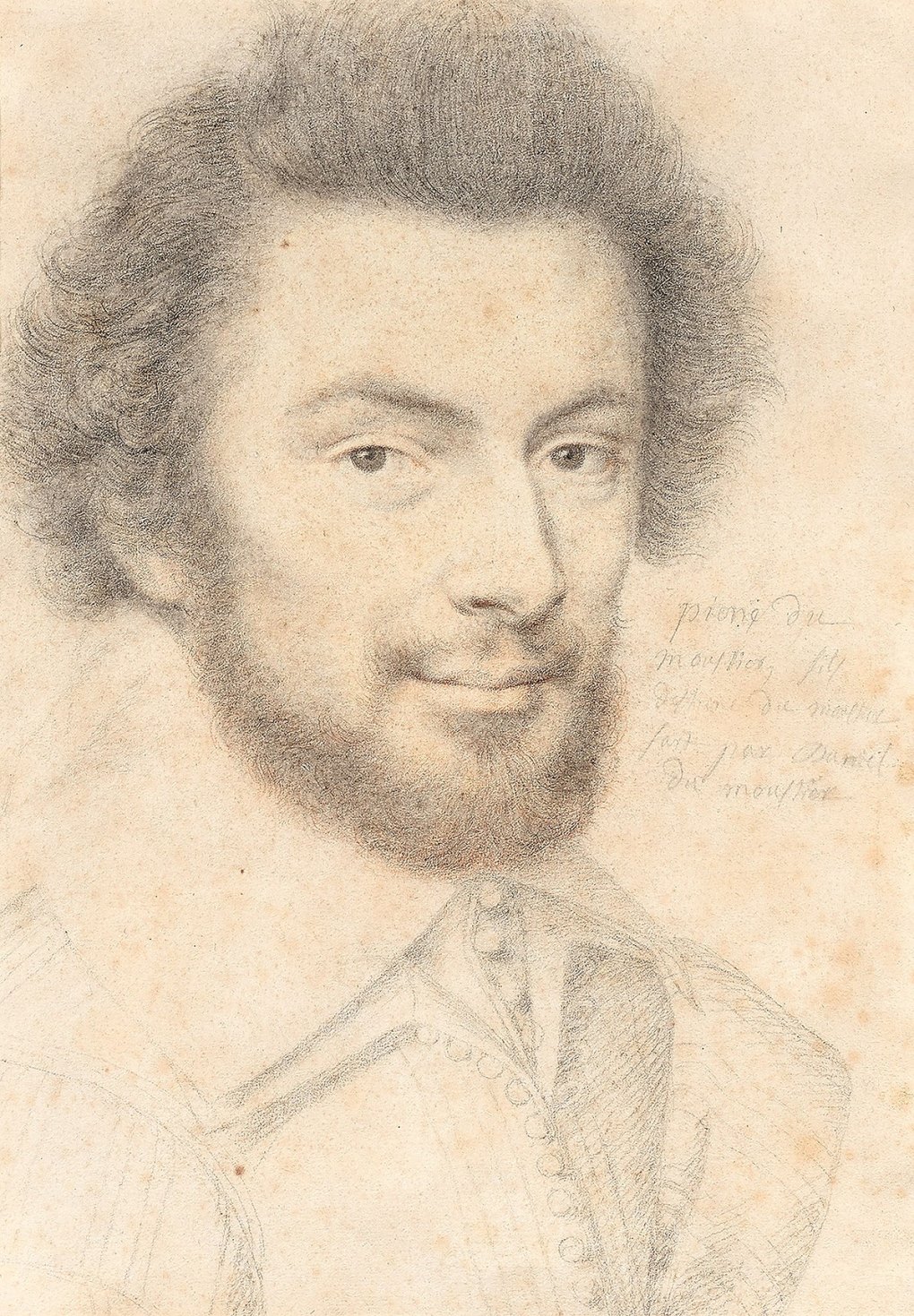
Luca Penni was an Italian painter, draughtsman and printmaker, nicknamed Romano (Roman).
Luca was the younger brother of Raphael's first assistant, Giovanni Francesco Penni (1488/1496-1528), and must have originally studied under his brother in the environment of Raphael's studio. After Raphael's death, Luca worked in Genoa, then traveled to England, in the service of King Henry VIII, before leaving for France around 1530.
At Fontainebleau, together with French painters, Penni worked on the decoration of the royal palace and became one of the most respected artists there. His work had a marked influence on sixteenth-century French painting and was reproduced by Italian engravers. Penni also produced many designs for engravers including Leon Davent, Etienne Delon and Giorgio Ghisi, as well as for tapestries and stained glass.
The work of the first generation of Italian masters in France, mostly pupils and followers of Raphael, is called the "first school of Fontainebleau", and Luca Penni is a prominent representative of it.
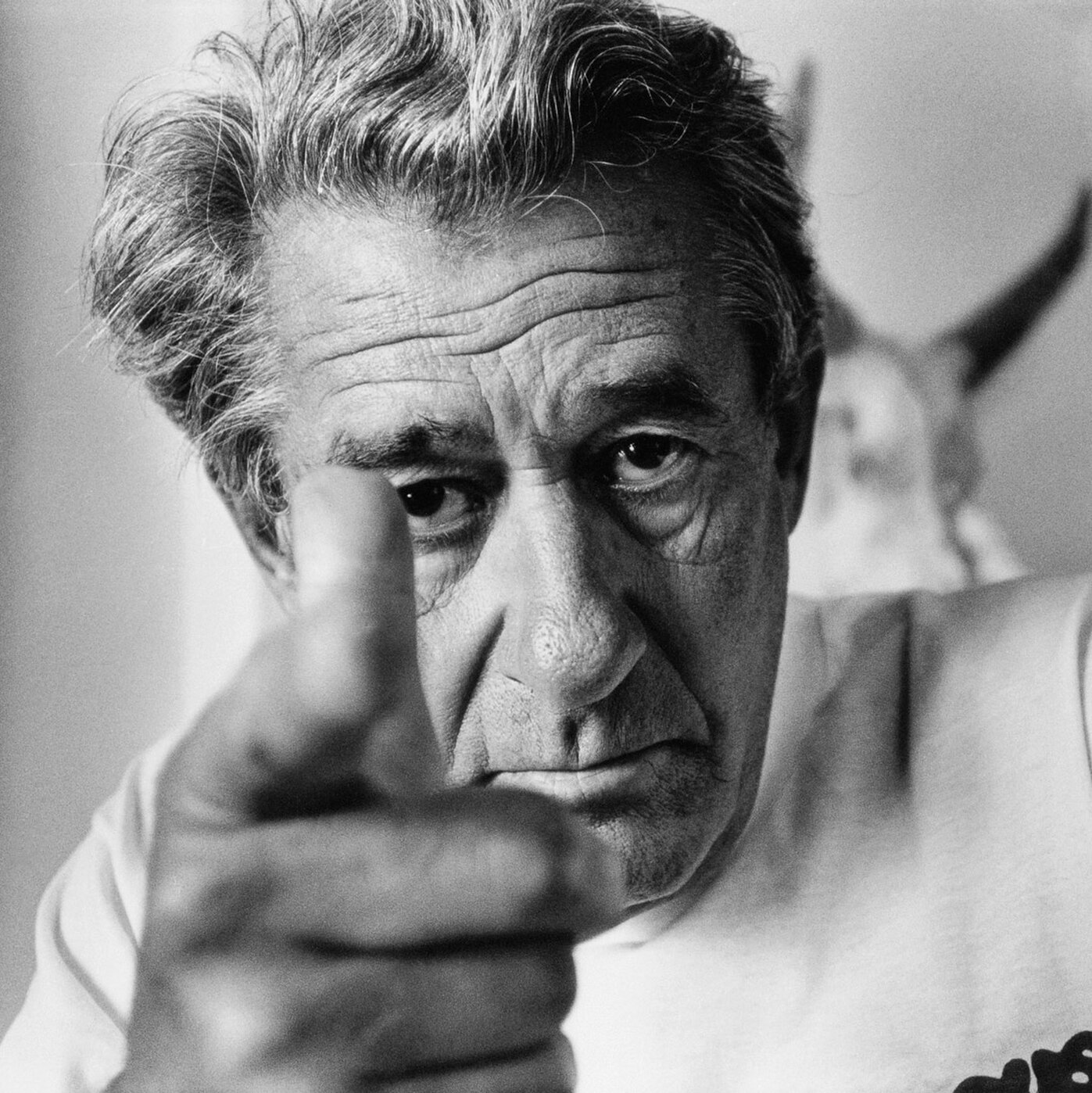

Helmut Newton (born Helmut Neustädter) was a German-Australian photographer. The New York Times described him as a "prolific, widely imitated fashion photographer whose provocative, erotically charged black-and-white photos were a mainstay of Vogue and other publications."
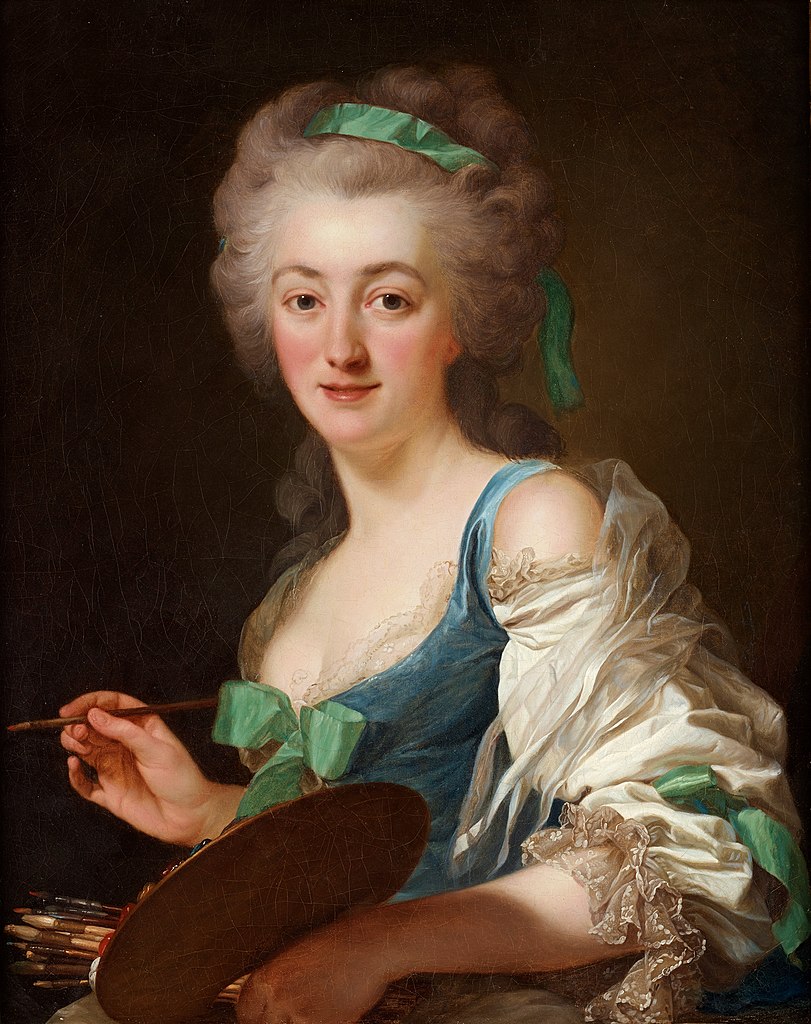


Anne Vallayer-Coster was a renowned French artist, celebrated for her exceptional still-life paintings that captivated 18th-century art enthusiasts, including the French Queen Marie Antoinette. Born into an artistic family in 1744, Vallayer-Coster's talent was evident early on, leading to her unanimous election into the prestigious Académie Royale at just 26 years old. Her works, characterized by their vibrant color, meticulous detail, and textural precision, often depicted bowls of fruit, game, shells, and flowers, showcasing the opulence of French aristocracy before the Revolution.
Vallayer-Coster's career was notable not only for her artistic achievements but also for her ability to navigate the male-dominated art world of her time. Despite the societal constraints on women artists, she gained the patronage of influential figures like Marie Antoinette and was one of the few women admitted to the Royal Academy of Painting and Sculpture. Her work received critical acclaim at the Salon, where she exhibited regularly from 1771 until 1817, and her still-lifes were praised for their sensuality, illusionistic perfection, and the rich, indulgent luxury they portrayed.
One of Vallayer-Coster's most ambitious works, Still Life with Flowers in an Alabaster Vase and Fruit (1783), exemplifies her unparalleled skill in capturing the soft textures of flowers and their harmonious arrangement. This masterpiece was hailed as such at the Salon of 1783 and is considered by Vallayer-Coster herself as her finest painting. Lost for nearly two centuries, it was recently rediscovered in an almost pristine state and is now part of the National Gallery of Art's collection, highlighting Vallayer-Coster's significant contributions to European art history.
Throughout her career, Vallayer-Coster produced more than 120 still lifes, always with a distinctive brilliance in color, earning her a place among the elite artists of her time. Despite facing challenges during the French Revolution due to her close association with the monarchy, she continued to exhibit her work and contribute to the art world until her death in 1818.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Anne Vallayer-Coster's legacy is a testament to her skill, resilience, and the impact of her work on the history of art. To stay updated on new product sales and auction events related to Anne Vallayer-Coster, sign up for updates that focus solely on this exceptional artist's contributions to the art world.

.jpg)
Jacint Rigau-Ros i Serra, known in French as Hyacinthe Rigaud, was a Catalan-French baroque painter most famous for his portraits of Louis XIV and other members of the French nobility.
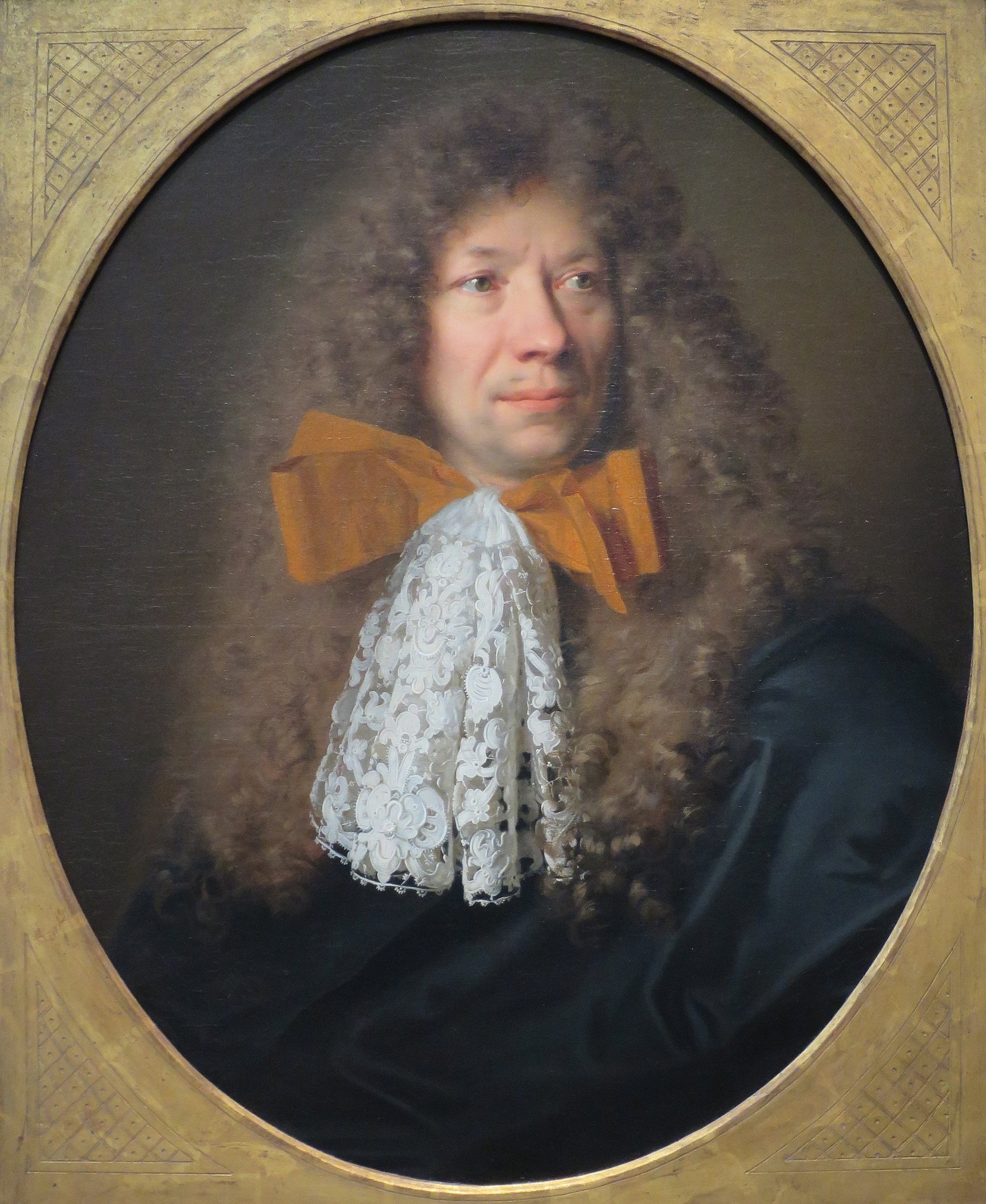


Adam Frans van der Meulen was a Flemish painter and draughtsman who was particularly known for his scenes of military campaigns and conquests. Van der Meulen also painted portraits, hunting scenes, paintings of chateaux and landscapes. He created designs for prints and cartoons for tapestries.
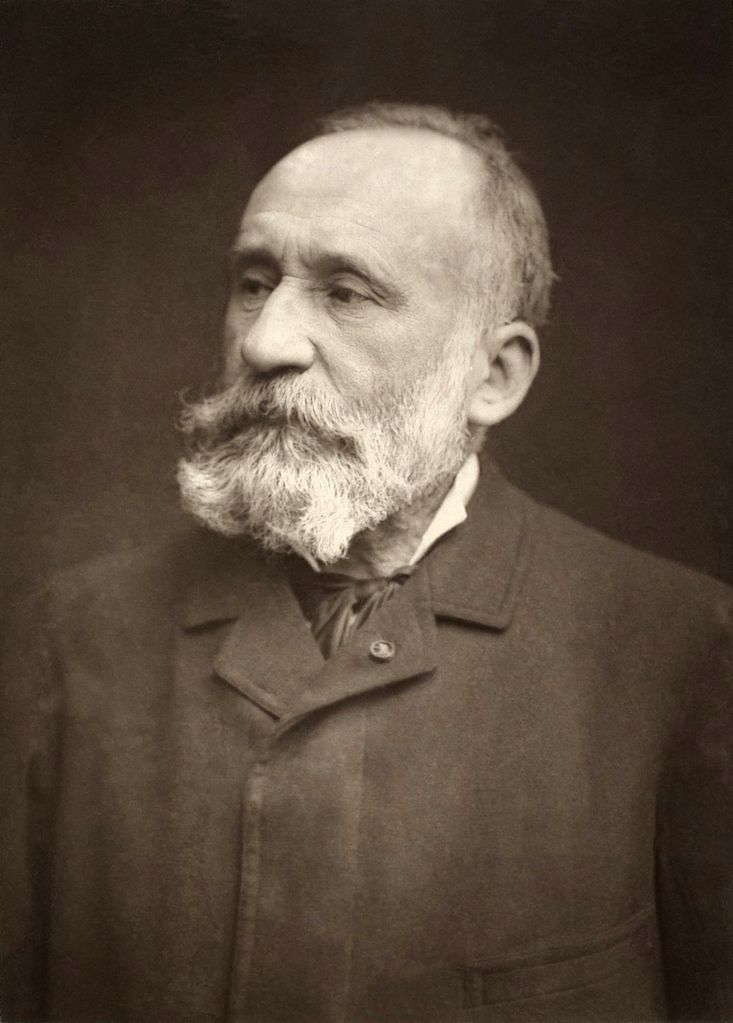


Pierre Cécile Puvis de Chavannes, a prominent French painter, was known as "the painter for France." His influential mural paintings showcased a classicizing style, often referencing visions of Hellenistic Greece.
Puvis received numerous commissions for public and private institutions across France, with significant works in Amiens, Marseille, Lyon, Poitiers, and Paris. His success as a 'painter for France' stemmed from his ability to appeal to various ideologies of the time. In addition to murals, Puvis created easel paintings, some of which can be found in galleries worldwide. Despite his significance, he was not fully appreciated during his lifetime, and his work remains a subject of ongoing art criticism.
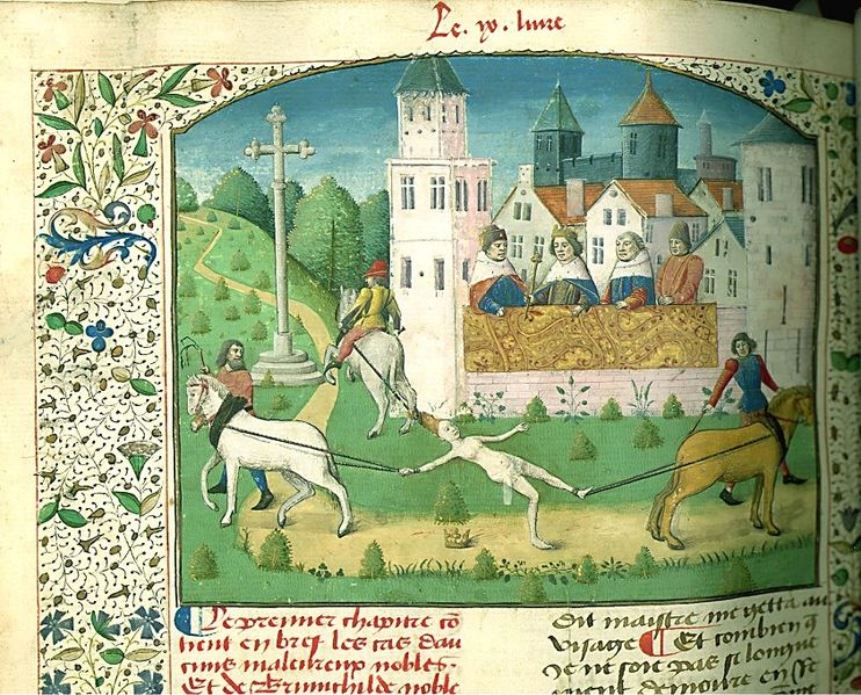


Maître François was a French illustrator who worked in Paris in the 1460s-1480s.
The identity of Maître François as an artist is first mentioned in a letter written by Robert Gauguin in 1473. Most of the prestigious commissions from the court and leading ecclesiastical figures of the time were carried out in François' studio. In Paris in the second half of the fifteenth century, one can trace the predominant style of illumination by the works of Master Jean Rolin, Maître François, and Master Jacques de Besançon. Bibliophiles close to the royal court encouraged the work of miniaturists through private commissions. In particular, Jacques d'Armagnac owned six manuscripts of Maitre Francois and his entourage.
Boccaccio's De casibus virorum illustrium was very popular in the 15th century, where the author retells the fates and downfalls of famous personalities from the Bible, antiquity and medieval history, ending with Boccaccio's own contemporaries in 14th-century Florence. For a long time this book was even more famous and successful than Boccaccio's Decameron. The text was translated into French in 1409 for Jean, Duke de Berry, by his secretary Laurent Premieffe. And the illustrations for the book were later created in the workshop of the then respected Maître François.















































































