Physicists


Jack W. Aeby is an American environmental physicist and photographer.
Aeby attended the University of Nebraska and was one of the first civilian employees of the Manhattan Project beginning in 1942. He worked on the project in many areas, starting with human transportation, then he was assigned as the chemical warehouse superintendent.
On July 16, 1945, while at base camp with all the official photographic equipment, Aeby took the only well-exposed color photograph of the first detonation of a nuclear weapon at the Trinity Nuclear Test Site in New Mexico, for which he became famous. The rest of the film was destroyed by the explosion. At the time of the photograph, Aeby was a civilian working in the health physics group with Emilio Segre.
Jack Aeby continued to work at Los Alamos during the Crossroads tests and eventually witnessed nearly 100 nuclear explosions. He then returned to work at Los Alamos National Laboratory in the Department of Health Physics.


Bernard Bolzano, full name Bernard Placidus Johann Nepomuk Bolzano, was an Italian-born Czech scientist, mathematician, logician, philosopher and theologian.
Bolzano graduated from the University of Prague and was immediately appointed professor of philosophy and religion at the university. Within a few years, however, Bolzano had already shown himself to be a free thinker with his teachings on the social costs of militarism and the needlessness of war. He called for a complete reform of the educational, social, and economic systems that would direct the nation's interests toward peace rather than armed conflict between states. In 1819, Bolzano was expelled from the university for his beliefs and thereafter turned his full attention to works on social, religious, philosophical, and mathematical issues.
Bolzano held advanced views on logic, mathematical quantities, limits, and continuity. He is the author of the first rigorous theory of real numbers and one of the founders of set theory. In his studies of the physical aspects of force, space, and time, he proposed theories opposed to those advanced by the German philosopher Immanuel Kant. His contributions to logic, in particular, established his reputation as the greatest logician of his time. Much of his work remained unpublished during his lifetime and was not widely disseminated until the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, when a number of his conclusions were reached independently.
Bolzano was multi-talented in various fields of science to which he made significant contributions. His published works include The Binomial Theorem (1816), A Purely Analytic Proof (1817), The Functional Model and the Scientific Model (1834), An Attempt at a New Statement of Logic (1837), and The Paradoxes of Infinity (1851).
Among other things, Bolzano was also a great philanthropist. Together with his friends and students, he supported the activities of almshouses, homes for the blind, loan banks for the working class, libraries, and elementary schools in rural areas.


Giovanni Alfonso Borelli was an Italian universalist scientist of the 17th century Scientific Revolution, the founder of biomechanics.
He studied mathematics under Benedetto Castelli (1577-1644) in Rome. In the 1640s Borelli was appointed to the chair of mathematics at the University of Messina and at Pisa in 1656. After 12 years at Pisa and numerous disputes with colleagues, Borelli left the university. In 1667 Borelli returned to the University of Messina, where he engaged in literary and historical studies, studied the eruption of the volcano Etna, and continued to work on the problem of muscular movement of animals and other bodily functions according to the laws of statics and dynamics. In 1674 he was accused of participating in a conspiracy to liberate Sicily from Spain and fled to Rome.
Borelli is known primarily for his attempts to explain muscular movement and other bodily functions according to the laws of statics and dynamics. His best-known work is De Motu Animalium (1680-81; "On the Motion of Animals"). Borelli calculated the forces required for balance in the various joints of the human body, long before Newton published his Laws of Motion. Borelli was the first to realize that musculoskeletal levers increase motion, not force, so muscles must produce much greater forces than those that resist motion. He was also one of the first microscopists: he made microscopic studies of blood circulation, nematodes, textile fibers, and spider eggs. Borelli also authored works on physics, medicine, astronomy, geology, mathematics, and mechanics.


Mathurin Jacques Brisson was a French zoologist, ornithologist, naturalist and physicist, a member of the Academy of Sciences.
He is known for his published works in natural history: Le Règne animal ("The Kingdom of Animals", 1756) and Ornithologie ("Ornithology", 1760), in which he described 1,500 species of birds grouped into 115 genera, twenty-six orders, and two classes. Brisson was one of the first to come close to the concept of "type" in zoology, although he does not use the term, but his classification was used for about 100 years. He translated a number of important books on zoology for his time into French.
Brisson's works in physics are related to the measurement of specific gravity of various bodies, the study of gases and refraction of light, mirrors, magnetism, atmospheric electricity, and barometers.


Augustin Louis Cauchy was a French mathematician and mechanic, military engineer, and founder of mathematical analysis.
Cauchy studied at the École Polytechnique and at the Paris School of Bridges and Roads. After becoming a military engineer, he went to Cherbourg in 1810 to work on harbors and fortifications for Napoleon's English invasion. Here he began independent mathematical research. Cauchy returned to Paris in 1813, and Lagrange and Laplace convinced him to devote himself entirely to mathematics. The following year he published a memoir on definite integrals, which formed the basis of the theory of complex functions. From 1816, Cauchy held professorships at the Faculty of Natural Sciences, the Collège de France, and the École Polytechnique in Paris.
Cauchy developed the foundation of mathematical analysis, and made enormous contributions to analysis, algebra, mathematical physics, and many other areas of mathematics. He almost single-handedly founded the theory of functions of a complex variable, which has extensive applications in physics. Cauchy's greatest contributions to mathematics are published primarily in three of his treatises, "Courses in Analysis at the Royal Polytechnic School" (1821), "Summary of Lessons on Infinitesimal Calculus" (1823), and "Lessons on the Application of Infinitesimal Values in Geometry" (1826-28). In all, Augustin Louis Cauchy wrote about 800 scientific articles.
Cauchy was a member of the Paris Academy of Sciences, the Royal Society of London, the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences, and other academies.


Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1962.
During World War II he had to work on developments for the military, and in 1947 he turned to biology at the Strangeways Research Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1949 he moved to the University Medical Research Council at Cavendish Laboratories. Using X-ray diffraction studies of DNA by biophysicist Maurice Wilkins (1916-2004) and X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin, biophysicist James Watson and Crick were able to construct a molecular model consistent with the known physical and chemical properties of DNA.
This achievement became a cornerstone of genetics and was regarded as one of the most important discoveries of 20th century biology. In 1962, Francis Crick, along with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for determining the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the chemical ultimately responsible for the hereditary control of life functions.
From 1977 until the end of his life, Crick served as professor emeritus at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego, California, where he conducted research on the neurological basis of consciousness. He also wrote several books. In 1991, Francis Crick received the Order of Merit.


John Dalton was a British scientist, chemist and physicist, naturalist, and pioneer in the development of modern atomic theory.
In the 1800s, he was the first scientist to explain the behavior of atoms in terms of weight measurements. Some of the tenets of Dalton's atomic theory proved to be false, but most of the conclusions remain valid to this day.
Problems with his own eyesight led Dalton to research and describe the visual defect he himself suffered from in 1794 - color blindness, later named color blindness in his honor.
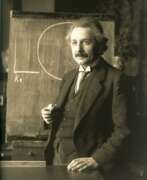

Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are together the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius".


Leonhard Euler was the greatest mathematician of the 18th century and history in general.
Euler brilliantly graduated from the University of Basel and entered the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences, then began to work at the Berlin Academy, and later to lead it. In 1766, the scientist received an invitation from the Russian Empress Catherine II and again came to St. Petersburg to continue his scientific work.
Here he published about 470 works in a wide variety of fields. One of them is a large-scale work "Mechanics" - an in-depth study of this science, including celestial mechanics. Euler by that time was practically blind, but continued to be actively engaged in science, in the records he was helped by his son Johann Albrecht and stenographers. Leonhard Euler made many fundamental discoveries that brought great benefit to mankind.
His massive contribution to the development of mathematics, mechanics, physics and astronomy cannot be overestimated, and his knowledge in the most diverse branches of science is admirable. During his lifetime, he published more than 850 works that contain in-depth studies of botany, chemistry, medicine, ancient languages, and music. Euler held membership in many academies of science around the world.


Michael Faraday was a British physicist and chemist, explorer and experimenter.
Faraday, because of his family's poverty, was unable to receive a formal education, but at the bookbinding shop in London where he worked, he read many books, including encyclopedias and textbooks on chemistry and physics. He persevered in self-education, attending hearings at the City Philosophical Society and later lectures by Sir Humphry Davy at the Royal Institution, who as a result took the able student on as an apprentice. In 1825 he replaced the seriously ill Davy in the management of the laboratory of the Royal Institution.
In 1833 Faraday was appointed to a research chair of chemistry created especially for him, where, among other achievements, the scientist liquefied various gases, including chlorine and carbon dioxide. His study of heating and lighting oils led to the discovery of benzene and other hydrocarbons, and he experimented extensively with various steel alloys and optical glasses. Faraday was an excellent experimentalist who presented his ideas in simple language. He is best known for his contributions to the understanding of electricity and electrochemistry. The concepts behind electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism, and electrolysis were some of his most important discoveries. His electromagnetic research formed the basis of the electromagnetic equations that James Clerk Maxwell developed in the 1850s and 1860s.
Between 1831 and 1855, Faraday read a series of 30 papers before the Royal Society, which were published in his three-volume Experimental Investigations in Electricity. His bibliography numbers some 500 printed articles. By 1844 he had been elected a member of some 70 scientific societies, including the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences.


Joseph Fourier, full name Jean-Baptiste Joseph Fourier, was a French mathematician and physicist and historical Egyptologist.
Fourier famously accompanied Napoleon Bonaparte on his Egyptian expedition in 1798 as a scientific advisor and was appointed secretary of the Institute of Egypt. During the occupation of Egypt, Fourier worked in the French administration, supervised archaeological excavations, and worked to shape the educational system.
But the main thing in Fourier's life was science. Back in France, he studied the mathematical theory of heat conduction, established the partial differential equation governing heat diffusion, and solved it using an infinite series of trigonometric functions. Fourier showed that heat diffusion obeyed simple observable physical constants that could be expressed mathematically. His work The Analytic Theory of Heat (1822) had a great influence on the development of physics and pure mathematics.
Joseph Fourier was a member of the Paris Academy of Sciences, the French Academy, a foreign honorary member of the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences, and a member of the Royal Society of London.


Galileo Galilei was an Italian naturalist, physicist, mechanic, astronomer, philosopher, and mathematician.
Using his own improved telescopes, Galileo Galilei observed the movements of the Moon, Earth's satellites, and the stars, making several breakthrough discoveries in astronomy. He was the first to see craters on the Moon, discovered sunspots and the rings of Saturn, and traced the phases of Venus. Galileo was a consistent and convinced supporter of the teachings of Copernicus and the heliocentric system of the world, for which he was subjected to the trial of the Inquisition.
Galileo is considered the founder of experimental and theoretical physics. He is also one of the founders of the principle of relativity in classical mechanics. Overall, the scientist had such a significant impact on the science of his time that he cannot be overemphasized.


Pierre Gassendi was a French Catholic priest, Epicurean philosopher, mathematician, astronomer and researcher of ancient texts.
He taught rhetoric at Diné and philosophy at Aix-en-Provence. Gassendi's Syntagma philosophicum, the result of his historical research and philosophical reflections, is a well-known work. Several of his works on astronomy, physics and mechanics were also published in the 17th century.


William Gilbert was a British physicist and medical scientist famous for pioneering the study of magnetic and electrical phenomena.
After receiving a medical degree, Gilbert settled in London and began his research. In his major work De Magnete, Magneticisque Corporibus, et de Magno Magnete Tellure (On Magnetic Stones and Magnetic Bodies and the Great Magnet of the Earth), published in 1600, the scientist describes in detail his studies of magnetic bodies and electric attraction.
After years of experimentation, he came to the conclusion that the compass arrow points north-south and downward because the Earth acts as a rod magnet. He was the first to use the terms electric attraction, electric force, and magnetic pole. Gilbert came to believe that the Earth rotates on its axis and that the fixed stars are not all the same distance from the Earth, and believed that the planets are held in their orbits by magnetism.


Sir John Frederick William Herschel, 1st Baronet was a British astronomer and son of the Uranus discoverer Wilhelm Herschel. He is credited with the first double star and nebula catalogues of the southern starry sky, which he observed during a five-year stay near Cape Town.


Heinrich Rudolf Hertz was a German physicist and inventor of radio waves.
Hertz graduated from the University of Berlin, studying under Hermann von Helmholtz and Gustav Kirchhoff, then was a professor of physics at the University of Karlsruhe, and from 1889 became a professor of physics at the University of Bonn.
A tireless experimenter, Hertz conducted various experiments with electric waves. Hertz reported his first discovery at the end of 1887 in a treatise "On the electromagnetic effects caused by electrical perturbations in insulators," which he sent to the Berlin Academy. For a time the waves he discovered were called Hertzian waves, but today they are known as radio waves. Hertz's discovery was a confirmation of James Clerk Maxwell's electromagnetic theory and paved the way for numerous advances in communication technology.
Hertz is also known for the discovery of the photoelectric effect, which occurred during his research on electromagnetic waves. Hertz was only 37 years old at the time of his death and many of his experiments and work remained unfinished, but his discovery of radio waves had a huge impact on the world in the 20th century, paving the way for the development of radio, television and radar.


Christiaan Huygens van Zeelhem was a Dutch mechanic, physicist, mathematician, inventor and astronomer who formulated the wave theory of light.
An admirer of Descartes, Huygens preferred to conduct new experiments himself to observe and formulate laws. In physics, he contributed to the development of the crucial Huygens-Fresnel principle, which applies to wave propagation. He also extensively investigated free fall. He experimentally proved the law of conservation of momentum. He derived the law of centrifugal force for uniform circular motion.
He also invented the pendulum clock, discovered centrifugal force and the true shape of Saturn's rings as well as its moon Titan. Huygens is considered the first theoretical physicist to use formulas in physics and one of the founders of theoretical mechanics and probability theory.


Hendrik Anthony Kramers was a Dutch theoretical physicist and a member of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Sciences.
Kramers studied mathematics and physics at Leiden University before being recruited in Copenhagen by future Nobel Prize-winning physicist Niels Bohr (1885-1962). He tried to understand how electromagnetic waves interact with matter and made important contributions to quantum mechanics and statistical physics. Under Bohr's supervision, Kramers prepared his dissertation.
In 1926, Kramers left Denmark and became a professor of theoretical physics at Utrecht University, and from 1931 he also worked at Delft University of Technology. After the end of World War II, the scientist was active in Europe and taught in the United States.
Kramers' scientific works are devoted to atomic physics, quantum mechanics, solid-state physics, low-temperature physics, physical optics, and the kinetic theory of gases. Together with Ralph de Laer Kronig, he derived important equations relating absorption to the dispersion of light. Kramers' research on X-rays led to the development of equations for determining the efficiency and intensity of X-ray production.
In the 1930s, Kramers worked as an editor of a literary magazine, wrote and translated poetry into Dutch, and was an expert on the works of Shakespeare.


Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz was a German philosopher and a prominent polymath in many fields of science.
Leibniz was a universal genius; he showed his talents in logic, mathematics, mechanics, physics, law, history, diplomacy, and linguistics, and in each of the disciplines he has serious scientific achievements. As a philosopher, he was a leading exponent of 17th-century rationalism and idealism.
Leibniz was a tireless worker and the greatest scholar of his time. In the fate of Leibniz, among other things, there is one interesting page: in 1697, he accidentally met the Russian Tsar Peter I during his trip to Europe. Their further meetings led to the realization of several grandiose projects in Russia, one of which was the establishment of the Academy of Sciences in St. Petersburg.
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz was also the founder and first president of the Berlin Academy of Sciences and a member of the Royal Society of London.


James Clerk Maxwell was a British physicist, mathematician and mechanic, and a Fellow of the Royal Society of London.
James Clerk Maxwell was one of the most influential scientists of the nineteenth century. His theoretical work on electromagnetism and light largely determined the direction physics would take in the early 20th century. Maxwell conducted research in a number of areas, but was particularly preoccupied with the nature of Saturn's rings. In 1860 he obtained a professorship at King's College, London, and it was his years there that were most fruitful. For his electromagnetic theory,
Maxwell is most often credited with fundamentally changing the course of physics. Maxwell saw electricity not just as another branch of physics, but "as an aid to the interpretation of nature." He showed the importance of electricity to physics as a whole by advancing "the important hypothesis that light and electricity are the same in their ultimate nature." This theory, one of the most important discoveries in nineteenth-century physics, was Maxwell's greatest achievement and laid the foundation for Einstein's theory of relativity.


Marin Mersenne (also Marinus Mersennus or le Père Mersenne) was a French mathematician, physicist, philosopher and theologian, and music theorist.
Mersenne was educated at the Jesuit college of La Fleche and went on to study theology in Paris. He also became a member of the Order of the Minims and taught philosophy and theology at Nevers. He developed his ideas about the essence of the world and knowledge, insisting on the importance of experimentation and observation, and contrasted the rational natural world with human reason.
Beginning in 1635, Mersenne founded the Académie Parisienne, the forerunner of the French Academy of Sciences, where France's leading mathematicians and natural philosophers gathered. It provided a forum for the exchange of ideas among scientists and promoted the works of René Descartes and Galileo. The scientist's most famous achievement in mathematics was finding a formula for generating prime numbers, known today as Mersenne's Numbers. In 1644, Mersenne published his studies of Mersenne numbers and their relationship to prime numbers. His work in number theory and arithmetic proved pivotal to the development of mathematics in the seventeenth century.
He corresponded with many other scientists of the era, such as René Descartes, Blaise Pascal, and Pierre Fermat. However, his contributions extend much further, through his role in disseminating the work of the outstanding minds of his time. Mersenne traveled extensively throughout Europe, bringing new scientific ideas to France. He was an important mediator in the exchange of knowledge and contributed to the advancement of science in his era.


Isaac Newton was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the greatest mathematicians and physicists and among the most influential scientists of all time. He was a key figure in the philosophical revolution known as the Enlightenment. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), first published in 1687, established classical mechanics. Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and shares credit with German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for developing infinitesimal calculus.
In the Principia, Newton formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation that formed the dominant scientific viewpoint until it was superseded by the theory of relativity. Newton used his mathematical description of gravity to derive Kepler's laws of planetary motion, account for tides, the trajectories of comets, the precession of the equinoxes and other phenomena, eradicating doubt about the Solar System's heliocentricity. He demonstrated that the motion of objects on Earth and celestial bodies could be accounted for by the same principles. Newton's inference that the Earth is an oblate spheroid was later confirmed by the geodetic measurements of Maupertuis, La Condamine, and others, convincing most European scientists of the superiority of Newtonian mechanics over earlier systems.


Chérubin of Orleans (French: Chérubin d'Orleans), born François or Michel Lasseré, was a French monk of the Order of the Friars Minor Capuchin, physicist, and optical instrument maker.
Cherubin was engaged in the study of optics and problems related to vision. He designed the first binocular telescope, as well as a special type of spectacle in which the lens was replaced by a short perforated tube. Many of his binoculars, binocular microscopes and telescopes survive today. Cheruben is also credited with modeling the eyeball to study the functioning of the ocular lens.
About his research and work, Cherubin of Orléans published in Paris the works La dioptrique oculaire (Dioptrique oculaire, 1671) and La vision parfaite (Perfect Vision, 1677).


Giovanni Vincenzo Petrini was an Italian priest and theologian, philosopher, mathematician, and expert in mineralogy.
Along with Scipio Breislacus, Petrini was one of the founders of Italian volcanology. He taught philosophy and mathematics, theology, but specialized in mineralogy and created the Mineralogical Cabinet in Nazareth. This museum was famous in Europe and was visited, among others, by Emperor Joseph II, who gave him rare specimens from the lands of the Empire and especially from Hungary.
Giovanni Petrini was the author of the catalog Gabinetto mineralogico del Collegio Nazareno ("The Mineralogical Cabinet of the Nazarene Collegium, described by external features and distributed by component parts" (Rome, 1791-1792). The specimens in it are classified according to a standard structure: salts, earths, bitumens, combustibles, and metals. There is also a section on gemstones.


Max Planck, full name Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck, is a German theoretical physicist and the founder of quantum theory, which won him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1918.
Planck made many discoveries in theoretical physics, but his quantum theory revolutionized our understanding of atomic and subatomic processes, just as Albert Einstein's theory of relativity revolutionized our understanding of space and time. Together they represent the fundamental theories of 20th-century physics. They forced humanity to reconsider some philosophical beliefs and began to be applied to industry, including the military, affecting all aspects of modern human life.
Planck was one of the first scientists to realize the importance of Einstein's special theory of relativity, and his influence played a crucial role in its acceptance in Germany. As dean of the University of Berlin, he personally visited Einstein in Zurich in 1913 to persuade him to move to Berlin, which became his base for the next 20 years. Einstein's 1905 work on the photoelectric effect (for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize) is based on Planck's constant (h), the fundamental unit of quantum theory.


Henry DeWolf Smyth was an American scientist, nuclear physicist, and diplomat.
Smyth studied at Princeton and Cambridge Universities, taught in Princeton's physics department from 1924 to 1966, and chaired the department for many years. At first he investigated the ionization of gases, but from the mid-1930s he turned his attention to nuclear physics. During World War II, Smith was a member of the uranium section of the National Defense Research Committee. He also proposed electromagnetic techniques that were used to enrich the first samples of U-235 during the Manhattan Project. Smith worked as a consultant on this project from 1943 to 1945 and served as deputy director of the Metallurgical Laboratory at the University of Chicago.
In 1944, General Leslie Groves appointed Henry Smith to the Committee on Postwar Policy to propose a public policy for research and development of atomic energy after the war. He wrote the official public report on the bomb, which became known as the Smith Report and was widely distributed throughout the country.
After the war, Henry DeWolf Smith served as commissioner of the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission and as the U.S. representative to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). In 1953, he was President Eisenhower's chief advisor on Ike's "Atoms for Peace" speech and received the Atoms for Peace Award in 1968.


Otto Guericke, from 1666 von Guericke (pronunciation and original spelling: Gericke) was a German politician, jurist, physicist and inventor. He is best known for his experiments on air pressure with the Magdeburg hemispheres. He is considered the founder of vacuum technology.









































































