Publishers 19th century


Rudolph Ackermann the Elder was a German and British inventor and publisher, founder of Ackermann & Co.
He was the son of a master saddler, learned the craft and in time achieved a high art in carriage making, designing carriages and coaches. In 1794 Ackermann opened a printing and picture store in London, which quickly became popular. The following year he opened a printing shop at 96 Strand - thus began the printing business of the Ackermann dynasty, which lasted for over two hundred years.
Between 1808 and 1810. Ackermann published the first of his sumptuous plate books, The Microcosm of London, with beautiful hand-colored aquatints. This work established his reputation as a book publisher, and he subsequently published many more elaborate illustrated books. Ackermann also gained widespread fame for the periodical he founded in 1809, the Repository of Art, Literature, Commerce, Manufactures, Fashion, and Politics. This popular journal, published monthly until 1828, contained articles and illustrations of various kinds, especially on fashion, social and literary news.
Ackermann's business flourished, and by the end of 1820 he had established offices in Central and South America. Continuators of the Ackermann dynasty were in the printing business until the end of the twentieth centur


Platon Petrovich Beketov (Russian: Платон Петрович Бекетов) was a Russian publisher, book printer, historian and collector.
Platon Beketov was born into an old Russian landowning family, from 1798 he lived in Moscow, where he became interested in collecting and in 1801 opened his own printing house, which was considered one of the best in Moscow. Beketov raised the national printing industry to a worthy level. His books were made with great artistic taste and elegance, more than a hundred beautiful editions in all. A number of editions of Russian authors were printed here, among them Vasily Andreyevich Zhukovsky, Alexander Nikolayevich Radishchev, Mikhail Matveyevich Kheraskov and others. The printing house also printed the magazines "Friend of Enlightenment" (1805) and "Inventory of Books Printed at the Dependence of Platon Beketov's Printing House" (1806).
Beketov was passionate about old manuscripts, especially with portrait miniatures and autographs, and portraits of famous contemporaries. He collected an entire picture gallery, which formed the basis of two of his major projects - the publication "Pantheon of Russian Authors" (1801-1802) and the collection "Collection of Portraits of Russians, famous..." (1821-1824). (1821-1824). The texts for them were written by the publisher's friend and distant relative N.M. Karamzin.
Platon Petrovich Beketov was widely known in the circles of the Russian intellectual elite of the first half of the XIX century. In 1811 he was elected chairman of the Moscow Society of Russian History and Antiquities, a position he held until 1823.


Johann Ludwig Bleuler, sometimes called Louis Bleuler, was a Swiss landscape painter, engraver and publisher.
He studied painting under his father, the painter Johann Heinrich Bleuler the Elder (1758-1823), and his older brother, the painter Johann Heinrich Bleuler the Younger (1787-1857). He traveled extensively in the picturesque Rhine region, painting landscapes and making sketches, and made study trips to Brussels, Amsterdam, and Paris.
In 1824 Bleuler founded his own publishing company in Schaffhausen and from 1827 he worked on a series of engravings of landscapes of the Rhine from its source in the glaciers of the Alps, eventually publishing a complete set of engravings by about 1843. All of the aquatints were hand-colored using the gouache technique, giving them the appearance of the work of old masters.


Désiré-Magloire Bourneville was a French physician, neurologist, innovator and educator, and statesman.
Born into a modest family, Bourneville began his medical education in 1860 and for about ten years worked as an assistant to Jean-Martin Charcot, where, together with Paul Régnard, he supervised the publication of "Photographic Iconography of Salpetriere". During the Franco-Prussian War, he served as both surgeon and physician's assistant. Appointed physician at Bissetre, Borneville devoted himself to the medical and educational care of "idiots and epileptics" for whom he organized a service, and later directed the Fondation Vallée in Gentilly until his death. He is considered one of the earliest child psychiatrists.
In 1876, Bourneville was elected a municipal councilor of Paris, three years later he became a general councilor of the Seine, and then a deputy. In this capacity, Bourneville carried out several health reforms: he became the rapporteur for the public assistance budget and the budget for psychiatric asylums, achieved the creation of the first special classes for mentally retarded children, and the first municipal nursing school in Salpêtrière.
Bourneville had many very different talents. Very early on he became interested in medical journalism, where he made a name for himself through the vividness of his articles. In 1873, he founded the journal Progrès Médical, which promoted the tenets of avant-garde medicine, open to pioneering scientific developments (Bourneville published Charcot's lessons) and social issues. He fully developed the theoretical and practical foundations of teaching for the nursing profession. Outraged by the lack of practitioners' professional knowledge of obstetrics, he worked to create a new medical specialty, gynecology. But his main purpose in life was to educate and nurture those who were labeled "idiots" and mentally retarded.


Vincent Brooks, full name Vincent Robert Alfred Brooks, was a British etcher, lithographer and publisher.
Brooks began working for Day & Son, and in 1862 founded his own firm called Vincent Brooks, Day & Sons. He worked for the Arundel Society from 1856 to 1897. Brooks was for many years London's leading lithographer, with many important commissions printed in his publishing house.


William Cullen Bryant is an American poet, journalist, and editor-in-chief of the New York Post.
He began his education at Williams College, then studied law and worked as a lawyer, but a very different fate awaited him. In 1825, he moved to New York City and became co-editor of the New York Review. In 1827 he became editor of the New York Evening Post, and in 1829 he became its editor-in-chief and co-owner.
Bryant remained in this position until his death, for 50 years. He made the Post a voice for free trade, workers' rights, free speech, and abolition of the death penalty, and he was a founding member of the Republican Party.
Bryant wrote poetry from his early youth and announced himself by publishing a book of Poems (1821). His main theme was nature, and his best-known poems are "Thanatopsis" and "To a Waterfowl." In later years he devoted much time to translations and was an active patron of art and literature.


Lydia Maria Child, née Francis, is an American writer and journalist, women's rights and Indian rights activist, and a prominent abolitionist.
Lydia Francis was born into a family of abolitionists, which shaped her worldview. From the age of 18, she taught, wrote historical novels and in 1826 founded a periodical for children "Juvenile Miscellany".
Her first novel, Hobomock, was published in 1824 - set in colonial New England and based on the marriage of a white woman, Mary Conant, and a Native American named Hobomock. In 1833, Lydia Child published An Appeal in Favor of the Class of Americans Called Africans, which recounted the history of slavery and decried the educational and employment inequalities of the black population in the United States. As a result, she was expectedly publicly condemned and her magazine collapsed. But this book united and empowered like-minded people in the abolitionist movement.
On the subject of inequality, Lydia Child wrote throughout her life, and she also spoke out on behalf of Native American peoples. In 1861, "Incidents in the Life of a Slave Girl" was published. Her many books also include Flowers for Children (1844-47), Facts and Fictions (1846), The Freedmen's Book (1865), and An Address to the Indians (1868).


Sir James Crichton-Browne was a British and Scottish psychiatrist, neurologist, and MD.
James studied medicine at the University of Edinburgh, where his interest in psychiatry soon developed. After receiving his MD degree, he worked in hospitals in Derby, Devon and Newcastle. At the age of 26 he was appointed medical superintendent of the Lunatic Asylum in Wakefield and within nine years had transformed the hospital into a leading center for research and treatment.
Crichton-Browne initiated a scientific approach to the brain and its diseases. In 1871 he started the West Riding Asylum Medical Reports, which were published annually for six years. He was a pioneer in combating the common belief at the time that mental asylums could not produce original research and useful science. The persuasive scientist attracted many talented young people to collaborate in his research. Among them were David Ferrier (1843-1928) and Hughlings Jackson, who worked on cerebral localization and epilepsy. In 1878 they together founded what became the famous neurological journal Brain, the first journal devoted to what is now called neurobiology.
Crichton-Browne corresponded extensively with Charles Darwin, providing him with drawings and photographs for his book The Expression of Emotion in Man and Animals. Darwin valued his co-author so much that in 1883 he proposed that he be elected a Fellow of the Royal Society.
Crichton-Browne was also active in the development of public health policy regarding mental health. He worked prolifically into old age, writing monographs and autobiographical material, but in recent years he became involved in the controversial science of eugenics.


Francesco de Bourcard was a Swiss-born Italian scholar, historian and publisher.
De Bourcard devoted about twenty years, from 1847 to 1866, to the production of a voluminous work, The Uses and Customs of Naples, to which he engaged a large number of contributors, both writers, artists, and engravers.
The first of the two volumes was published in 1853. The books depict the customs of the time, the typical characters of the people, their daily lives, and a wide range of popular and religious festivals. Hundreds of lithographs are accompanied by explanatory texts.


Adam Friedel or Adam Friedel von Friedelsburg was a Danish soldier and pirate, painter and actor.
Having the character of an adventurer, Friedel became a participant in the War of Liberation in Greece 1821-1829. He was granted the title of Baron Friedel von Friedelsburg, but the information about his aristocratic origin was found to be false and he was expelled from the Greek army. He was eventually forced to leave Greece for London, where his talents as an actor, musician, and painter became apparent.
In London, Adam Friedel opened his own lithographic studio. He became best known for his portraits of the heroes and leaders of the Greek Revolution, first produced between 1824 and 1826. The series of 24 portraits sold in large editions throughout Europe. He also created several famous portraits of Lord Byron.


Joseph Dennie was an American writer, journalist, and major literary figure of the early 19th century.
Dennie graduated from Harvard College, became a lawyer, but became active in writing. In 1801, he founded a periodical called The Port Folio, which became the most prominent literary weekly of its time in America. It was also the first important political and literary journal in the United States.
As founder of the Tuesday Club, Dennie was the center of Philadelphia's aristocratic literary circle in the early 19th century and for a time was the leading literary critic in the country. He ridiculed the simplistic and crude nature of Native Americans and opposed democratic innovations. He also encouraged talented young writers.


Pierre Duflos the Younger was a French painter, engraver and publisher.
Duflos was a renowned copper engraver and created works based on paintings by popular artists of his time. Of special note is a large work entitled "A Collection of Engravings representing the Degrees, Ranks, and Dignities, corresponding to the Costumes of all existing Nations; with Historical Explanations and Abridged Lives of Great Men, which illustrated the Dignities with which they were adorned," published in Paris in 1780. It is a veritable encyclopedia of the costume of many cultures of the world. It depicts real people such as Confucius, Montezuma, Mohammed II, Ahmet IV, Cortes, Jacques-Auguste de Thou, Thomas More, Marie Antoinette, as well as types from Africa, Asia, the Americas and Europe, including indigenous peoples. Pierre Duflos created it in collaboration with Marie-Elisabeth Thibault and Clément-Pierre Marillier.


Philip Morin Freneau was an American publicist, editor, and known as the "poet of the American Revolution".
After graduating from Princeton University, Freneau taught school and studied to become a minister. With the outbreak of the American Revolution, he began writing scathing satire on the British and the Tories. During a two-year voyage to the Caribbean islands, he created the poems "The Beauties of Santa Cruz" and "The House of Night," and in 1778 he became involved in the war. After his release from British captivity, Freneau wrote a book in verse, "The British Prison Ship" (1781).
After serving as a sea captain for several years, Freneau took up journalism. In his National Gazette newspaper in Philadelphia, he sharply criticized George Washington.
Freneau's poetry, which accompanied him throughout his life, covers a variety of subjects, including political situations, American Indians, nature, the sea, and naval battles. His political poems are often satirical, but his nature poems are very lyrical.


Sarah Josepha Buell Hale, born Sarah Josepha Buell, was an American writer, magazine editor, and civic activist.
Sarah Buell received a good home education and married David Hale in 1813, but, finding herself in financial difficulty after her husband's death, she turned to literary work in the 1820s. Her poems were published in local journals and in the collection The Genius of Oblivion (1823). Sarah also wrote several novels during her lifetime.
In 1828, she became editor of the new Boston edition of Ladies' Magazine (from 1834, American Ladies' Magazine). Hale herself wrote much of the wide variety of material for each issue-literary criticism, essays on American life, essays, and poetry, and she supported patriotic and humanitarian organizations, notably the Boston Ladies' Peace Society and the Sailors' Aid Society, which she founded in 1833. She was a lifelong advocate of women's education. During this period she also published Poems for Our Children (1830), containing her most famous work, Mary Had a Little Lamb.
In 1837, in Philadelphia, Hale became editor of Lady's Book, soon to be known as Godey's Lady's Book. During her years as editor, this publication became the most influential and circulating women's magazine published in the country at the time. Hale encouraged American writers: Edgar Allan Poe, Nathaniel Hawthorne, Ralph Waldo Emerson, Harriet Beecher Stowe, and other women writers published in the magazine.
Hale's major accomplishment was Woman's Record; or, Sketches of Distinguished Women, published in 1853, 1869, and 1876. For this project, she produced some 36 volumes describing biographies of women, emphasizing their influence in history on social organization and literature.
Sarah Hale is considered one of the main organizers of the Thanksgiving holiday, and she helped shape the worldview of women of her time.


Edward Everett Hale was an American clergyman, preacher and writer, abolitionist and pacifist.
Hale demonstrated outstanding literary ability from an early age. He went to Harvard College and became a minister and preacher. Grandnephew of Revolutionary hero Nathan Hale and nephew of orator Edward Everett, Hale worked for his father's newspaper, the Boston Daily Advertiser. And for 70 years he never stopped writing newspaper articles, historical essays, short stories, pamphlets, and sermons for the North American Review, The Atlantic Monthly, and the Christian Examiner. From 1870 to 1875 he published and edited the Unitarian magazine Old and New.
Hale wrote several novels, of which the most popular were East and West (1892) and In His Name (1873). Hale's most famous novel, A Man Without a Country, first published in The Atlantic Monthly in 1863, was written to evoke patriotism during the Civil War. It is a political fable about a man who renounces his American citizenship and greatly regrets it.
Many of Hale's 150 books and pamphlets were tracts in support of the ideas of Negro education, worker's housing, and world peace. The moralistic novel Ten Times One is Ten (1871) was the impetus for the organization of several youth groups.
In 1847, Hale was elected a member of the American Antiquarian Society and remained a member for the rest of his life. A 10-volume collection of Edward Hale's writings was published between 1898 and 1900. In 1903 he was appointed chaplain of the United States Senate and joined the Literary Society of Washington. The following year he was elected a member of the Academy of Arts and Sciences.


Nicolaus Heideloff, full name Nikolaus Innocentius Wilhelm Clemens van Heideloff, was a German painter and copperplate engraver and publisher.
Heideloff came from a respected family in Germany that included prominent painters and sculptors. He studied and worked in Paris, but had to flee to London during the French Revolution, where he spent 30 years of his life. Here he worked as a publisher for the most luxurious fashion magazine of the time, The Fashion Gallery, which published elaborate color copperplate prints, aquatints, and etchings. Heideloff drew many outfits for the publication for all occasions of high society.
Nikolaus Heideloff also depicted historical scenes, battles, the British navy, and caricatures for Rudolf Ackermann while he was working in London until 1814, often as hand-colored etchings.
In 1815, William I, King of the Netherlands, appointed him director of an art gallery in The Hague.


John Camden Hotten was a British publisher, writer, linguist and bibliophile.
By mid-1855, Hotten had opened a small bookstore in London and then established his own publishing business, which after his death became Chatto & Windus. Hotten's publishing house published many works by classic and contemporary writers. After spending about six years in America, he was the first to introduce a number of American writers to the British public, including James Russell Lowell, Oliver Wendell Holmes, and Bret Harte.
Hotten compiled The Dictionary of Modern Slang, Slang, and Vulgar Words, first published in 1859 and reprinted many times thereafter. His other major work is A Handbook of Topography and Family History of England and Wales (1863). Hotten also wrote and edited literary and biographical material in various periodicals.
Hotten was a collector, author, and secret publisher of erotic works, which were illustrated, among others, by the famous caricaturist Thomas Rowlandson (1757-1827).

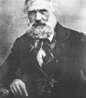
Johann Baptist Isenring was a Swiss landscape painter and printmaker, one of the first photographers in 19th-century Switzerland.
Johann studied painting and aquatint at the Munich Academy of Fine Arts, opened an art studio in St. Gallen in 1828 and soon began publishing his lithographic collection of picturesque views of Switzerland's most remarkable cities and towns.
In 1839, Isenring, fascinated by the discoveries of Niépce and Daguerre, bought equipment for "daguerreotype" and a year later organized an exhibition in his studio in Multtertor, which was probably the first photographic exhibition in the world. Isenring even gave up painting for a while and worked as a photographer for two years, settling in Munich. He made portraits, photographs of architecture, reproductions of paintings and developed a coloring method for his prints, which he patented in America.


William Jardine was a Scottish naturalist, ornithologist, ichthyologist, artist and publisher of works on zoology.
Jardine studied medicine at the University of Edinburgh and was an excellent sportsman. Although his main passion was ornithology, he also studied ichthyology, botany and geology. Sir William Jardine was a prominent Scottish Victorian naturalist, author and publisher of 40 volumes of the popular Naturalist's Library (1833-43). Of these, 14 volumes were devoted to ornithology, 13 volumes to mammals, 7 volumes to entomology, and 6 volumes to ichthyology.
A series in four volumes, Illustrations on Ornithology, co-written with Prideaux John Selby, was published between 1825 and 1843. His book on burrows and fossil tracks, The Ichnology of Annandale, includes fossils from his ancestral estate. Jardine was a leading expert on salmon and trout in the British Isles. His outstanding knowledge of the species was profound that in 1860 he was appointed a member of the Royal Commission on the Salmon Fisheries of England and Wales. His research culminated in the best and most comprehensive monograph on these fish, "British Salmonids," with the remarkable illustrations by Jardine himself. William Jardine's private natural history museum and library are considered the finest in Britain.


Paul Jerrard was a British artist, illustrator, cartographer and publisher.
His publishing house, Jerrard & Son, Paul & Son, produced Shakespearean paintings, ornithological, entomological and botanical publications, species, sheet music, gift books, almanacs etc.


Theophilus Johnson was a British artist, amateur naturalist and publisher.
He trained as a clerical worker and then started his own printing business. Johnson had a passion for the natural sciences and spent much time in the gardens of the Zoological Society of London. His drawings and books cover a wide range of topics, from molluscs to mammals, but his main interest was entomology.
Theophilus Johnson's publications on entomology depict the various species of moths found in the British Isles on beautifully colored watercolor sheets, and include illustrations of their larvae as well as the plants they feed on. During his lifetime he illustrated more than 46 volumes with original watercolors.


René Kieffer was a French bookbinder, publisher and bookseller.
A pupil of Henri Marius Michel, he worked for ten years as a gilder at the Chambolle-Douroux bookbinding factory. In 1903 René Kieffer opened his studio in Paris, and in the same year his work was first shown at the Salon de la Société des Artistes-Decorators.
Over time, his work shifted from classical forms to Art Nouveau motifs. René Kieffer was known for using bright colors in elaborate designs, creating luxurious bindings for unique publications. Between 1917 and 1923, he created Pierre Legrain's designs for Jacques Doucet's library. As a bookbinder and publisher, René Kieffer was vice-president of the book department of the 1925 Paris International Exhibition of Decorative Arts and Modern Industry. He also participated in the International Exhibition of Arts and Technology in Modern Life in Paris in 1937.


August Köllner (German: Augustus Koellner or Köllner), full name Augustus Theorore Frederick Adam Kollner, was a German and American painter and illustrator, engraver, and publisher.
August Köllner studied painting and lithography in Frankfurt, moved from Germany to the United States, and settled in Philadelphia in 1839. He soon took a job with Huddy and Duvall's U.S. Military Journal. In the 1840s he worked on a series of watercolors, fifty-four of which were published in 1848-51 by the Paris firm of Goupil, Vibert & Co. under the title Views of American Cities.
August Köllner worked on book illustrations, designed various merchandise, and worked for other lithographic firms in Philadelphia until he went into business for himself as a printer and lithographer. He exhibited his drawings at the Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts in Philadelphia in 1865 and 1868.


Jan Kops is a Dutch agronomist, botanist and publisher of thematic journals.
In his youth, Kops was interested in botany, but had to study to become a priest. He soon became disillusioned with a career as a preacher and took up his favorite occupation. The fruit of his botanical research was the first volume of the Flora of Batavia, published in 1800. He was engaged in the task of converting the dunes into agricultural land.
Kops great importance to the country's agriculture lies mainly in his work as the first Dutch agricultural official. He possessed great efficiency and great perseverance. On Kops's initiative, the first Dutch agricultural journal, Magazijn van Vaderlandschen Landbouw, appeared between 1803 and 1814, which he himself edited.


Gustav Kraus, also known as Gustav Friedrich or Gustav Wilhelm, was a Bavarian painter and lithographer.
He studied at the Munich Academy of Fine Arts and was admitted as a member of the Munich Art Society, and is considered a representative of the Biedermeier. In 1836 he founded his own lithographic publishing house. In his landscape works, Kraus combined topographical precision with artistic quality.
His urban and architectural vedute, depictions of historical events, including maneuvers, parades, processions, inauguration ceremonies, portraits of noble contemporaries, sketches of costumes and uniforms were published by many publishing houses. One of the most valuable of Kraus's works today is the depiction of the Oktoberfest procession of 1835 with 24 colorful lithographs.


Evert Maaskamp was a Dutch artist and engraver, publisher and print dealer.
In addition to publishing geographical publications, topographical maps and engravings, Maaskamp produced very high quality illustrated works on sheet metal. Throughout his career he collaborated with the English artist Charles Howard Hodges, whose influence is evident in many of Maaskamp's engravings.


Ardaseer Framjee Moos was a 19th-century Indian politician.
Ardaseer Framjee Moos was educated and later taught at Elphinstone Institute, and was the secretary of the Bombay Native Common Library from 1860 for more than two decades. An active participant in Parsi reform movements and Mumbai political life, he became treasurer of the Bombay Association in 1876. Moos prepared and published A Journal of Travels in India (1871), the illustrations in which are various views of the principal buildings of Lucknow, Agra, Dehli, and Calcutta. He also published dictionaries of English and Gujarati.


John Neal is an American writer, editor, and community activist.
Neal served for many years as editor of the Yankee and Boston Literary Gazette periodicals, publishing critical essays and always striving to promote American literature. While living in England in the 1820s, he wrote a long series of articles published in Blackwood's Edinburgh Magazine, essentially telling the story of American literature, which helped change the perception of American art in Britain.
Back in America, he used his popularity and influence to support young writers such as Poe and Whittier. In particular, it was Neale who put Edgar Allan Poe's very name in print and the very first words of encouragement to his work.
Neal's early recognition of Poe's genius was crucial to the budding talented writer's career. John Neel also wrote long adventure novels with complex plots, of which "Rachel Dyer" is considered the best, and "Bag Otter, Chief of the Oneida" and "David Whicher" are his best stories.
John Neal was also a very active social and political activist. In his literary work and lectures, he constantly addressed issues such as feminism and women's rights, slavery, the rights of free black Americans and American Indians, temperance, sports, and many others.


Edward Orme was a British artist, engraver and publisher of illustrated books.
He was engraver to King George III from 1799 to 1820 and to the Prince of Wales, painting portraits and landscapes. Edward Orme was a successful publisher, publishing many illustrated books. He had several stores in London.
Edward Orme is the younger brother of the painter and engraver Daniel Orme.


Pierre Paul Alexandre Joseph Pluchart was a French and Russian artist, printer, lithographer and publisher.
In 1805 he came to Russia to manage the printing house at the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, then served in the Senate Printing House. Plushar was a good draughtsman and lithographer, he mastered the publishing business to such an extent that by 1813 he opened his own printing house in St. Petersburg. It soon gained fame as one of the best printing houses in Russia, where books in Russian and European languages were printed, and it even opened its own bookstore.
After Alexandre Plushar's death, his widow Henrietta and his son Adolf Plushar (1806-1865), a publisher, took over the printing house. Another of his sons, Eugene Plushar (1809-1880), became a famous artist.


Bruce Rogers, born Albert Bruce Rogers, was an American typographer and book designer who had a major influence on the development of book design in the United States in the early 20th century.
Trained as an artist, Rogers began working as an illustrator for an Indianapolis newspaper. In 1895 he moved to Boston, where he met masters in book publishing, including George Mifflin of Houghton Mifflin, who offered him a job at the Riverside Press. When the publishing house opened a limited edition department in 1900, Rogers was appointed its manager and was responsible for the design and printing of unique books. Over the next 12 years, he developed several new typefaces and produced more than 100 Riverside Press editions, which are highly regarded.
From 1916 he worked as an advisor to Cambridge University Press in England, where he supervised the preparation of the monumental Oxford Lectionary Bible, and then served as an advisor to Harvard University Press in the United States until 1934. Bruce Rogers also designed outstanding books for the William E. Rudge Printing Company in Mount Vernon, New York. His other bibliophile books and limited editions include The Odyssey, an edition of Shakespeare, the Boswell Papers, and the American Folio Lectern Bible. Bruce Rogers is considered one of the preeminent book designers of the twentieth century.


Anne Royall, née Newport, was an American writer, newspaper editor and traveler, one of the first women journalists in the United States.
After the death of her husband William Royall in 1813, Anne was left destitute, but she did not despair and completely changed her life. She was about 50 years old when she set out to travel the country and describe what she saw. She visited Baltimore, Philadelphia, New York City, Albany, Springfield, Hartford, Worcester, Boston, and New Haven. In each city, she asked respected citizens for interviews and subscriptions to her future books. She made detailed notes on each town's population, industry, physical description, local transportation, regional dialects, fashions, and the character of its inhabitants.
In all, Anne Royall wrote ten volumes of travel books. She was 57 years old when she published under a pseudonym her first book, The Traveler: Sketches of History, Life, and Manners in the United States (1826), which provides a unique look at American life in the early nineteenth century. His first novel, The Tennessean, was published in 1827, followed by several others.
At the age of 62, in her home in Washington, D.C., Royall began publishing her own newspaper, Paul Pry (1831-1836) and then The Huntress (1836-1854). She exposed bribery and corruption and made many powerful enemies. Nevertheless, it is known that the intrepid journalist during her life met and talked with every man who occupied the presidential chair, from George Washington to Abraham Lincoln.


François-Louis Schmied was a French painter, illustrator, wood engraver, printmaker, editor and Art Deco binder.
François-Louis studied wood engraving at the École des Arts industriels in Geneva and painting at the École des Beaux-Arts de Genève. A Swiss, Schmied settled and naturalized in France in 1895. In 1910, he was commissioned to engrave and print Paul Jouve's illustrations for Rudyard Kipling's The Life of the Jungle, which was not published until 1919. For this book, now considered a masterpiece, the master produced about 90 color illustrations. Thanks to the success of this publication, Schmied was able to expand his activity and hire a group of craftsmen to execute his most famous and innovative works.
François-Louis Schmied is considered one of the greatest Art Deco artists and became particularly famous for his beautiful rare books for bibliophiles. Schmied's unique books were very expensive to produce, which required a lot of time and effort, and were always printed in very limited editions, from 20 to 200 copies. During the Great Depression, Schmied's expensive projects could not withstand the competition: the master was forced to sell off almost all his assets and close his workshop and store, and around 1932 he left for Morocco, where he died.
François-Louis Schmied's works are not only aesthetically pleasing, but also express his desire to combine art and literature. The talented artist conveyed with passion and precision the essence of the Art Deco style contemporary to him. Today, Schmied's works, reissued as fine art reproductions, not only convey the aesthetics and precision inherent in each of his originals, but also add a new dimension to them. His son, Theo Schmied, took over François-Louis Schmied's workshop in 1924, reviving its former glory and revitalizing it over time.


Jan Christiaan Sepp was a Dutch book publisher, printmaker and illustrator.
Jan Christiaan Sepp belonged to a dynasty of collectors, publishers and traders in printed books founded by his father, Christian Sepp (c. 1700-1775) in Goslar, Germany. Jan Christian Sepp is known for being the chief illustrator, creating the magnificent engravings for Cornelius Nozeman's highly prized work entitled Nederlandsche Vogelen (Birds of the Netherlands, 1770-1829). These copperplate engravings, superbly composed, meticulously engraved and hand-colored are of great value.
After Christian Sepp's death, the work of illustrating the five volumes was completed by his son, Jan Sepp. Each volume of this five-volume work of science and art contains 50 images of bird species, and each species is described on several pages.


Cornelius Suhr was a German painter, lithographer and publisher.
Cornelius is a member of the Suhr family of painters from Hamburg, the younger brother of Christoffer Suhr (1771-1842) and the older brother of Peter Suhr (1788-1857).
After 1805, he and his older brother Christoffer began painting panoramic views of their hometown in gouache, creating landscape paintings from all over Hamburg. Cornelius was also responsible for their distribution. Later, Peter Suhr joined the family business, forming a general lithographic company that also printed books and playing cards. Together they produced several hundred lithographs, engravings and etchings.


Peter Suhr was a German painter, lithographer and publisher.
Peter is a member of the Suhr family of painters from Hamburg, the younger brother of Christoffer Suhr (1771-1842) and Cornelius Suhr (1781-1857). The brothers were already producing panoramic views of Hamburg when Peter joined them around 1819, forming a general lithographic company that also printed books and playing cards.


Georg Wilhelm Timm (Russian: Василий Фёдорович Тимм, Вильгельм Фридрихович) was a Russian painter and lithographer originally from the Baltic Germans.
The son of a Riga burgomaster, Timm first studied art in Riga, then moved to St. Petersburg and entered the Imperial Academy of Arts. After graduating, he moved to Paris, where he worked under Horace Vernet. He traveled extensively in Russia, visited the Caucasus, where there was still a struggle with the mountaineers, and during the Crimean campaign accompanied Russian commanders. In 1852 he accompanied Tsar Nicholas I on his visit to Finland.
Timm was the author of battle, historical and genre paintings, he was an academician of the Academy of Arts and a professor at the Prussian Academy of Arts, and published the Russian Art Bulletin.
In 1867 Timm moved to Berlin, where he painted panels and ceramics. In 1876 he was appointed professor at the Prussian Academy of Arts and since then worked at the Royal Porcelain Manufactory in Berlin.


Julia Ward Howe is an American writer and poet, philosopher, abolitionist, and feminist.
Born into a well-to-do family and privately educated, Julia Ward married educator Samuel Gridley Howe and settled in Boston. She published her first collection of poems, Passionate Flowers, in 1854.Julia's early poems were praised by Hawthorne, Whittier, and Longfellow for their intellectual intensity. For a time Howe published the abolitionist newspaper Commonwealth with her husband. And in February 1862, The Atlantic Monthly published her poem "Battle Hymn of the Republic," which became the semi-official Civil War song of the Union Army, and Howe gained fame.
After the war, Howe began fighting for women's rights. In 1868, she was elected the first president of the New England Women's Suffrage Association. In 1868, she helped found the New England Woman's Club and became its president in 1871, the same year she became the first president of the American branch of the International Women's Peace Association. She was later active in the International Federation of Women's Clubs. Howe continued to write throughout her life, publishing travel books, poems, collections of essays, and biographies.
In 1870, she co-founded Woman's Journal and then served as its editor for 20 years. She traveled extensively until her advanced old age. In 1908, she became the first woman elected to the American Academy of Arts and Letters.


Walt Whitman was an American poet and essayist.
For some time in his youth Whitman worked as a journalist and even published his own newspaper, where he raised issues of slavery. In 1855, he self-published a collection of his poems, Leaves of Grass. This book is now a milestone in American literature, although at the time of publication it was considered highly controversial. In the early 1860s, Whitman volunteered in hospitals for the Civil War, resulting in a collection of new poems.
During his lifetime, his first collection, Leaves of Grass, underwent many editions and grew to 300 poems. It was only towards the end of his life that Whitman found fame as the first national poet of the United States. Whitman was translated into Russian by K. Balmont, I. Kashkin, and K. Chukovsky.


John Young was a British engraver, illustrator and publisher, and a curator of the British Institution.
Young worked exclusively in mezzotint and was a master of this technique; he executed some eighty portraits of contemporary characters from paintings by famous artists. In 1789 he was appointed mezzotint engraver to the Prince of Wales.
In 1815. Young published an album, Portraits of the Emperors of Turkey from the Founding of the Monarchy to 1808, consisting of thirty color plates with text in English and French. It is interesting that this series of portraits of Turkish emperors based on the album of miniatures of the XIX century was commissioned by the 28th Sultan Selim III, who ruled from 1789 to 1807, and after his death under Sultan Mahmud II the work was continued, which testifies to the high interest of the Ottoman Empire in European art.

















































