Scientists 18th century


Ivan Akimovich Akimov (Russian: Иван Акимович Акимов) was a Russian painter celebrated for his contributions to the Classical and Neoclassical styles of art. Born into a family of a typographer for the Governing Senate, Akimov's journey into the arts began early when, after his father's death, he penned a heartfelt letter to the Imperial Academy of Arts. This letter secured his admission, marking the start of his lifelong association with the Academy, where he evolved from a student to its director.
Akimov's education at the Academy was marked by numerous awards, including gold medals for his artworks, showcasing his burgeoning talent in painting. His artistic journey took him to Italy on a fellowship, where, despite initial challenges, he found mentorship under Pompeo Battoni and was inspired by the Venetian masters. This period was instrumental in shaping his skills and artistic outlook.
Throughout his career, Akimov was revered not just for his artistic output but also for his contributions to art education and historiography in Russia. He played a pivotal role at the St. Petersburg Academy of Arts, ultimately serving as its director. Akimov's legacy extends beyond his paintings, through his influence on future generations of artists and his foundational work in Russian art historiography. Among his notable works are "Prometheus Making a Statue at the Command of Minerva" and "The Baptism of Princess Olga in Constantinople", which reflect his classical influences and historical interests.
For those interested in exploring Ivan Akimovich Akimov's works and legacy, signing up for updates on new product sales and auction events related to Akimov could provide valuable insights and opportunities to connect with his art. This subscription ensures you stay informed about the latest discoveries and offerings in the world of Russian classical painting.


Eleazar Albin was a British naturalist and author of illustrated books on birds and insects.
Albin wrote and illustrated a number of books, including A Natural History of English Insects (1720), A Natural History of Birds (1731-38), and A Natural History of Spiders and Other Curious Insects (1736). His work was based on careful observation and artistic talent. Eleazar Albin has been called one of the "great illustrators of entomological books of the 18th century".
Some of the illustrations in these books are by Albin's daughter Elisabeth. Eleazar Albin himself proudly wrote of his drawings that they were all painted from life, with all the accuracy of a sketch, unlike the sketches of other scientists, who did them either from memory or from stories.


Jan Bleuland was a Dutch physician, medical scientist, educator and writer.
Bleuland was an intellectually advanced man, a sought-after physician, and a rich lover of the arts. Jan Bleuland taught anatomy, physiology and obstetrics for 31 years and was professor and rector of Utrecht University. His talents as a physician and medical researcher were recognized not only by his patients and the scientific community, but also by the highest authorities.
During his lifetime, Jan Bleuland amassed a large collection of medical specimens of the human body, which he used for research. Part of this significant collection is still on display in the original wooden Bleulandkabinet in the Utrecht University Museum. The Bleulandkabinet contains an extensive collection of skeletons, embryos in alcohol and wax preparations of body parts. His pioneering preparations were acquired by Utrecht University by royal decree of King Willem I in 1815 and are still used as teaching material.


Bernard Bolzano, full name Bernard Placidus Johann Nepomuk Bolzano, was an Italian-born Czech scientist, mathematician, logician, philosopher and theologian.
Bolzano graduated from the University of Prague and was immediately appointed professor of philosophy and religion at the university. Within a few years, however, Bolzano had already shown himself to be a free thinker with his teachings on the social costs of militarism and the needlessness of war. He called for a complete reform of the educational, social, and economic systems that would direct the nation's interests toward peace rather than armed conflict between states. In 1819, Bolzano was expelled from the university for his beliefs and thereafter turned his full attention to works on social, religious, philosophical, and mathematical issues.
Bolzano held advanced views on logic, mathematical quantities, limits, and continuity. He is the author of the first rigorous theory of real numbers and one of the founders of set theory. In his studies of the physical aspects of force, space, and time, he proposed theories opposed to those advanced by the German philosopher Immanuel Kant. His contributions to logic, in particular, established his reputation as the greatest logician of his time. Much of his work remained unpublished during his lifetime and was not widely disseminated until the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, when a number of his conclusions were reached independently.
Bolzano was multi-talented in various fields of science to which he made significant contributions. His published works include The Binomial Theorem (1816), A Purely Analytic Proof (1817), The Functional Model and the Scientific Model (1834), An Attempt at a New Statement of Logic (1837), and The Paradoxes of Infinity (1851).
Among other things, Bolzano was also a great philanthropist. Together with his friends and students, he supported the activities of almshouses, homes for the blind, loan banks for the working class, libraries, and elementary schools in rural areas.


Filippo Bonanni or Buonanni was an Italian Jesuit scholar. His many works included treatises on fields ranging from anatomy to music. He created the earliest practical illustrated guide for shell collectors in 1681, for which he is considered a founder of conchology. He also published a study of lacquer that has been of lasting value since his death.


Aimé Bonpland, born Aimé Jacques Alexandre Goujaud, was a French and Argentine natural scientist, traveler, physician, and botanist.
Bonpland became famous for his participation in an expedition to the Americas. Together with the explorer Alexander von Humboldt, he traveled through much of the American territory, from Cuman to the United States, passing through Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Mexico, and Cuba, in addition to Venezuela. In all these places he did a great deal of botanical work, describing and collecting six thousand species of American plants, many of which were new. The scientist made them known in Europe after his return in 1804, publishing several scientific papers. Four years later, Bonpland was appointed botanist of the Empress's Garden.
After more years, he returned to Buenos Aires and continued numerous botanical, zoological, and medical studies in various regions of South America. Bonpland sent plants to the Museum of Natural History in Paris and maintained correspondence with its naturalists.


Joachim Bouvet was a French Jesuit monk and missionary who worked in China.
Joachim Bouvet was one of six Jesuit mathematicians chosen by Louis XIV to travel to China as his envoys and work as missionaries and scholars. In 1687 in Beijing, Bouvet began this work, especially in mathematics and astronomy, and in 1697 the Chinese emperor Kangxi (1654-1722) sent him as ambassador to the French king. Kangxi expressed his wish that Bouvet should bring more missionary scientists with him. Thus, in addition to his scholarly work, Bouvet was also an accomplished diplomat and served as a liaison between the Chinese Emperor Kangxi and King Louis XIV of France.
Bouvet brought to France a manuscript describing Kangxi's life with an eye for diplomatic subtleties, as well as a collection of drawings depicting graceful Chinese figures in traditional and ceremonial dress. The first French edition of The Historical Portrait of the Emperor of China was published in Paris in 1697, and was subsequently translated and published in other languages. And Bouvet returned to China in 1699 with ten new missionaries and a collection of King Louis XIV's engravings for Emperor Kangxi. He remained in China for the rest of his life.


Mathurin Jacques Brisson was a French zoologist, ornithologist, naturalist and physicist, a member of the Academy of Sciences.
He is known for his published works in natural history: Le Règne animal ("The Kingdom of Animals", 1756) and Ornithologie ("Ornithology", 1760), in which he described 1,500 species of birds grouped into 115 genera, twenty-six orders, and two classes. Brisson was one of the first to come close to the concept of "type" in zoology, although he does not use the term, but his classification was used for about 100 years. He translated a number of important books on zoology for his time into French.
Brisson's works in physics are related to the measurement of specific gravity of various bodies, the study of gases and refraction of light, mirrors, magnetism, atmospheric electricity, and barometers.


Giovanni Battista Brocchi was an Italian mineralogist, geologist and paleontologist.
Brocchi studied law at the University of Padua, but was seriously interested in natural sciences and mineralogy. In 1802, Brocchi became a teacher of natural history at the Brescia Gymnasium. Appointment in 1808 as inspector of mines in Milan gave him the opportunity to travel extensively in Italy, making extensive notes and collecting numerous samples. The fruits of these labors appeared in various publications, notably his "Treatise mineralogical and chemical on the iron mines of the department of Mella" (1808). He then obtained a position as inspector of mining in the newly created kingdom of Italy.
In 1811 Brocchi wrote a valuable essay entitled "Mineralogical Memoirs on the Fassa Valley in the Tyrol." He made his first extensive exploration of central Italy in 1811-1812, witnessed the eruption of Vesuvius, and was able to compare the condition of its crater before and after the eruption. But his most important work is Fossils of the Sub-Apennines with geological observations on the Apennines and adjacent soil (1814), which contains precise details of the structure of the Apennine ridge and an account of the fossilization of Italian Tertiary strata in comparison with existing species. Brocchi also wrote several significant works on biology.
In the fall of 1822 he sailed from Trieste to Egypt, whence he made excursions up the Nile and into Syria and Palestine. In 1826 he contracted the bubonic plague, of which he died. His last journals and collections are preserved at the Museo Civico in Bassano. In all, Brocchi published five voluminous books and about seventy articles in various journals.


Edward Browne was a British physician, president of the College of Physicians, traveler, historian and writer.
Edward was the eldest son of the famous British scientist Sir Thomas Browne (1605-1682), received a Bachelor of Medicine degree from Cambridge later and a Doctor of Medicine degree from Oxford, and became a member of the Royal Society. In addition to medicine, his subjects of study included botany, literature, and theology. He lived in London and traveled throughout Europe visiting museums, churches, and libraries (Italy, France, the Netherlands, and Germany). In 1673 he published an account of his travels in Eastern Europe, notable for its scrupulous accuracy.
Edward Browne also published two other works: a historical treatise and biographies of Themistocles and Sertorius. He was physician to King Charles II of England and left many manuscript notes on medicine. The chronicle of his journey through Thessaly is a unique and valuable source of information about the region in the second half of the 17th century. He was admitted to the College of Physicians in 1675 and served as its president from 1704 to 1708.


Patrick Browne was an Irish physician and historian, traveler, naturalist and botanist.
Patrick Browne studied medicine in Paris, graduated from the University of Reims, continued his studies in Leiden, and then worked as a doctor at St. Thomas' Hospital in London. Subsequently, he lived for many years in the Caribbean, in Antigua, Santa Cruz, Montserrat and Jamaica, where he practiced medicine. He devoted all his spare time to the study of the natural history of the island. In 1771, Brown returned to Mayo County.
In 1756, Brown published A Civil and Natural History of Jamaica, his most significant work in terms of Carl Linnaeus's botanical nomenclature, which included new names for 104 genera.


Caspar Commelin was a Dutch botanist and mycologist.
Caspar Commelin was trained as a medical doctor, practiced botanical science and worked on books that were left unfinished due to the death of his uncle, botanist Jan Commelin. Caspar was mainly interested in exotic plants.


William Curtis was a British botanist and entomologist, editor of the oldest botanical publication in Great Britain.
Curtis became interested in natural history in his youth, and at the age of 25 had already published "Instructions for the Collection and Preservation of Insects", particularly butterflies. In 1779 he founded his own London botanical garden at Lambeth and published Flora Londinensis (1777-1798), a 6-volume work on urban nature.
In 1787 Curtis began publishing the later popular Botanical Magazine, which also featured hand-colored plates by artists. This magazine has changed its name several times over time, but is still continued by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, as a publication for those interested in horticulture, ecology or botanical illustration. Interestingly, the magazine was entirely hand-colored until 1948.


Joao de Souza Freire de Araujo Borges Da Veiga was a Portuguese astronomer and climatologist.
This scientist is one of the authors of the manuscript Dialogo epistolar astronomico sobre o cometa apparecido em Lamego as da Abril e observado aze o dia 9. dao anno de 1766. The second author who signed this manuscript is Joze de Araujo Souza Freire Borges Da Veiga.
It is a Portuguese treatise on the 1766 comet (D/1766 G1 Helfenzrieder), which appeared in April of that year and was discovered on April 1 by Helfenzrieder, and independently by Messier, Cassini de Turi, and others. The treatise gives a detailed account of the observations made by the authors from an observatory located on Mount Queimada near Lamego, Portugal. The authors also provide a chronological catalog of previous observations of comets since 1500 and cite their numerous authors.
The authors of this treatise were the first known climatologists, as well as experienced astronomers in continental Portugal who made meteorological observations.


John Dalton was a British scientist, chemist and physicist, naturalist, and pioneer in the development of modern atomic theory.
In the 1800s, he was the first scientist to explain the behavior of atoms in terms of weight measurements. Some of the tenets of Dalton's atomic theory proved to be false, but most of the conclusions remain valid to this day.
Problems with his own eyesight led Dalton to research and describe the visual defect he himself suffered from in 1794 - color blindness, later named color blindness in his honor.


Nicolas-Louis De la Caille was a French astronomer, abbot and educator.
He studied philosophy and theology, became an abbot, but the craving for science overpowered everything, and he studied astronomy on his own. In 1736, la Caille received a place at the Paris Observatory, in 1739 was appointed professor of mathematics at Mazarini-College in Paris and built his own observatory, where he conducted astronomical observations. In 1741 Lacaille was admitted to the Académie des Sciences.
La Caille was an outstanding astronomer: he observed more than 10,000 stars in the Southern Hemisphere and named 14 of the 88 constellations. In 1752, he made an astronomical expedition to the Cape of Good Hope, where he built an observatory and conducted a huge series of observations, including the discovery and cataloging of 42 nebulae. These studies led to la Caille being called "the father of southern astronomy," and his observations from South Africa of the Moon, Venus, and Mars, combined with similar observations already made in the Northern Hemisphere, led to the calculation of more accurate values for the distances to these bodies.
On his return to Paris two years later, in 1754, he resumed his post and taught at the school of Mazarin, continuing his work at the observatory of the College of Mazarini. Among his pupils was the great chemist Antoine Lavoisier. La Caille was a foreign honorary member of the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences and a member of the Royal Society of London. His Coelum Australe Stelliferum ("Star Catalog of the Southern Sky") was published in 1763.


Denis Dodart was a French botanist, naturalist and physician.
Dodart studied at the University of Paris, received a doctorate in medicine and was already in his youth known for his erudition, eloquence and open-mindedness. In 1673 he was elected to the French Academy of Sciences.
He is known for his early studies of plant respiration and growth. Dodart collaborated with the French engraver Nicolas Robert to illustrate his botanical works.


Dru Drury was a British entomologist and collector.
Dru Drury was an avid collector and his entomological collection totals 11,000 specimens. Drury corresponded extensively with entomologists from all over the world, from India to Jamaica to America, and bought any insects for 60 cents from officers of merchant ships arriving from afar. He even supplied travelers with a pamphlet of collecting instructions. It was through this work that Drury amassed most of his collection. From 1770 to 1787 he published three volumes on entomology, Illustrations of Natural History, with over 240 drawings of exotic insects.
Drury was president of the Society of Entomologists of London from 1780 to 1782, and a member of the Linnaean Society.


Leonhard Euler was the greatest mathematician of the 18th century and history in general.
Euler brilliantly graduated from the University of Basel and entered the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences, then began to work at the Berlin Academy, and later to lead it. In 1766, the scientist received an invitation from the Russian Empress Catherine II and again came to St. Petersburg to continue his scientific work.
Here he published about 470 works in a wide variety of fields. One of them is a large-scale work "Mechanics" - an in-depth study of this science, including celestial mechanics. Euler by that time was practically blind, but continued to be actively engaged in science, in the records he was helped by his son Johann Albrecht and stenographers. Leonhard Euler made many fundamental discoveries that brought great benefit to mankind.
His massive contribution to the development of mathematics, mechanics, physics and astronomy cannot be overestimated, and his knowledge in the most diverse branches of science is admirable. During his lifetime, he published more than 850 works that contain in-depth studies of botany, chemistry, medicine, ancient languages, and music. Euler held membership in many academies of science around the world.


Joseph Fourier, full name Jean-Baptiste Joseph Fourier, was a French mathematician and physicist and historical Egyptologist.
Fourier famously accompanied Napoleon Bonaparte on his Egyptian expedition in 1798 as a scientific advisor and was appointed secretary of the Institute of Egypt. During the occupation of Egypt, Fourier worked in the French administration, supervised archaeological excavations, and worked to shape the educational system.
But the main thing in Fourier's life was science. Back in France, he studied the mathematical theory of heat conduction, established the partial differential equation governing heat diffusion, and solved it using an infinite series of trigonometric functions. Fourier showed that heat diffusion obeyed simple observable physical constants that could be expressed mathematically. His work The Analytic Theory of Heat (1822) had a great influence on the development of physics and pure mathematics.
Joseph Fourier was a member of the Paris Academy of Sciences, the French Academy, a foreign honorary member of the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences, and a member of the Royal Society of London.


Johann Gottfried Gruber was a German critic and literary historian.
A graduate of the University of Leipzig, Gruber was later appointed professor at the University of Wittenberg, and in 1815 he became professor of philosophy at Halle. Gruber is the author of numerous historical and philosophical works.


Johann Anton Güldenstädt was a Russian scientist, naturalist and traveler born of Baltic Germans.
Born in Riga, then part of the Russian Empire, Güldenstädt studied pharmacy, botany and natural history in Berlin from 1763. At the age of 22, he earned a doctorate in medicine from the University of Frankfurt. The following year he became a member of an expedition of the Russian Imperial Academy of Sciences sent by Catherine the Great to explore the southern borders of the Russian Empire.
Güldenstädt traveled through Ukraine and the Astrakhan region, as well as the North Caucasus and Georgia. In March 1775 the scientist returned to St. Petersburg. The results of this expedition were published after his premature death from typhoid fever at the age of 36.
This expedition made a great contribution in the fields of biology, geology, geography and especially linguistics. Guldenstedt made detailed notes on the languages of the region. Güldenstädt's materials are still constantly consulted by linguists. Dictionaries of one and a half dozen languages and dialects of the Caucasian peoples compiled by him 250 years ago serve as a valuable basis for research in linguistics and toponymy. He was one of the first European scholars to study the life and culture of the Kumyks, Ingush, Ossetians, Chechens and other North Caucasian peoples.
Güldenstädt was also the first to describe and characterize the soils, vegetation and fauna of the South Russian steppes, and one of the first to explain the origin of black soil.


Adrian Hardy Haworth was a British scientist of entomology, botany and carcinology, and a Fellow of the Linnean Society.
Haworth made significant contributions to botany and entomology, describing many species of plants and insects. He summarized and published the results of his entomological collections in the extensive Lepidoptera Britannica (1803-1828), which was the first major monograph on the scales of Britain and one of the most authoritative works of the 19th century. Haworth was also a carcinologist and specialized in shrimps.


Martinus Houttuyn (Dutch: Maarten Houttuyn) was a Dutch botanist, zoologist and physician.
In addition to his medical practice, Houttuyn practiced science and published many scientific works on natural history, including minerals, fossils, botany and zoology. He was also a keen student of ferns, mosses and seed plants.


Christian Friedrich Carl Kleemann was a German artist, entomologist, and publisher.
He is known for his work on the continuation of the voluminous work on entomology by August Johann Rösel (1740-1761). Due to ill health, Rösel was unable to complete his series, so his work was continued by his son-in-law Christian Friedrich Karl Kleemann with the help of his daughter Katharina Barbara Kleemann. The second edition as well as the 6th part of this work did not appear until after Kleemann's death under the direction of Christian Schwarz. Most of the descriptions are devoted to butterflies, but other invertebrates, such as crabs, spiders, mollusks, and polyps, are depicted in addition to insects.


Georg Wolfgang Knorr was a German engraver, naturalist, and one of the first paleontologists of the 18th century.
Knorr was first apprenticed to his father as a lathe operator, and at the age of eighteen became a copper engraver for Leongard Blank, working with Martin Tiroff on the illustrations for Jacob Scheuchzer's Physica Sacra (1731). This work and his acquaintance with J.A. Beurer, a mineralogist and correspondent of the Royal Society, awakened Knorr's interest in natural history.
In the 1750s Knorr began publishing his own sumptuous folios. One of the most beautiful books of the eighteenth century is devoted to sea shells.


Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz was a German philosopher and a prominent polymath in many fields of science.
Leibniz was a universal genius; he showed his talents in logic, mathematics, mechanics, physics, law, history, diplomacy, and linguistics, and in each of the disciplines he has serious scientific achievements. As a philosopher, he was a leading exponent of 17th-century rationalism and idealism.
Leibniz was a tireless worker and the greatest scholar of his time. In the fate of Leibniz, among other things, there is one interesting page: in 1697, he accidentally met the Russian Tsar Peter I during his trip to Europe. Their further meetings led to the realization of several grandiose projects in Russia, one of which was the establishment of the Academy of Sciences in St. Petersburg.
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz was also the founder and first president of the Berlin Academy of Sciences and a member of the Royal Society of London.


Carl Linnaeus was a Swedish naturalist, botanist and physician.
Carl Linnaeus created a unified system of classification of flora and fauna, in which he summarized and organized the knowledge of the entire previous period of development of biological science. He was the first to formulate the principles of definition of living beings of natural nature and created a unified system of their names, binary nomenclature. Linnaeus' book "The System of Nature", first published in 1735, is one of the most important books in the history of science and practically opened the classification of plants and animals.
Linnaeus was a professor at Uppsala University for many years, and he is also valued in Sweden as one of the creators of the literary Swedish language in its modern form. In addition to his work in botany and scientific classification, Linnaeus led many activities for the betterment of his native country. He was also involved in the establishment of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences.


Martin Lister was a British naturalist and physician.
It could be argued that Lister founded two fields of natural history: arachnology (the study of spiders) and conchology (the study of the shells of organisms). He wrote more than 60 articles in the Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, published several volumes on natural history, speculated on the mysterious nature of fossils, and was successful as a physician.
Lister employed his artist daughters to illustrate his books on insects and molluscs - the names of Susanna and Anne appear on the title pages of the volumes. The Lister family published Historiæ Conchyliorum between 1685 and 1692.


Isaac Newton was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the greatest mathematicians and physicists and among the most influential scientists of all time. He was a key figure in the philosophical revolution known as the Enlightenment. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), first published in 1687, established classical mechanics. Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and shares credit with German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for developing infinitesimal calculus.
In the Principia, Newton formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation that formed the dominant scientific viewpoint until it was superseded by the theory of relativity. Newton used his mathematical description of gravity to derive Kepler's laws of planetary motion, account for tides, the trajectories of comets, the precession of the equinoxes and other phenomena, eradicating doubt about the Solar System's heliocentricity. He demonstrated that the motion of objects on Earth and celestial bodies could be accounted for by the same principles. Newton's inference that the Earth is an oblate spheroid was later confirmed by the geodetic measurements of Maupertuis, La Condamine, and others, convincing most European scientists of the superiority of Newtonian mechanics over earlier systems.


Peter Simon Pállas was a German and Russian scientist-encyclopedist, naturalist and traveler, who gave almost all his life to the service of Russia.
The breadth of his scientific interests made him a true encyclopedist, but he was particularly interested in natural sciences. By the age of 25, Pallas had already acquired European fame as a major scientist-naturalist. At the same time he received an invitation from the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences, where he was offered a professorship. In 1767, Pallas arrived in St. Petersburg with his wife and soon led several important expeditions to Siberia and southern Russia. In his numerous ethnographic descriptions, the scientist was the first to report in detail on the Kalmyks, Tatars, Mordvins, Chuvashs, Nagaians, Tungus (Evenks), Votyaks (Udmurts), and Cheremis (Mari). In addition, he brought with him large natural-scientific collections. Later he traveled with scientific expeditions to Kamchatka, the Kuril Islands, Crimea and other previously unexplored lands.
In 1785 Catherine II attracted Pallas to the collection and comparative analysis of the languages of the peoples inhabiting America, Asia, Europe and Russia, and he compiled and published a comparative dictionary in two parts (1787-1789), in which more than 200 languages and dialects of the peoples of Asia and Europe were presented. In the last years of his life, among other things, Pallas was engaged in the preparation of a fundamental three-volume work on the fauna of Russia, Zoographia rosso-asiatica ("Russian-Asiatic Zoology"), in which more than 900 species of vertebrates, including 151 species of mammals, of which about 50 new species were introduced. This work was so extensive, and the descriptions of the animals were so thorough and detailed, that until the early 20th century the book remained the main source of knowledge about the fauna of Russia. In 1810. Peter Pallas went to Berlin to prepare illustrations for this work, but a year later the famous scientist died and was buried in Berlin.
A volcano in the Kuril Islands, a reef off New Guinea, and many animals and plants are named after Pallas.


Giuseppe Piazzi was an Italian astronomer, mathematician and priest.
Around 1764 Piazzi became a Theatine priest, in 1779 he was appointed professor of theology in Rome, and in 1780 - professor of higher mathematics at the Academy of Palermo. Later, with the assistance of the Viceroy of Sicily, he founded an observatory in Palermo. There he compiled his great catalog of the positions of 7,646 stars and showed that most stars move relative to the Sun. There, on January 1, 1801, Piazzi also discovered the asteroid Ceres.
Giuseppe Piazzi's merits were appreciated: he was a member of the Royal Society of London, a foreign honorary member of the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences and a foreign member of the Paris Academy of Sciences. A crater on the Moon is named in his honor.
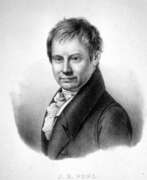

Johann Baptist Emanuel Pohl was an Austrian and Czech scientist, botanist, naturalist, and traveler.
Pohl studied in Prague, earned a doctorate in medicine and practiced science, becoming one of the most prominent botanists in Bohemia. Consequently, he was invited on an expedition to Brazil. Johann Pohl arrived in Brazil in 1817 with the Italian botanist Giuseppe Raddi as part of a large scientific expedition sent by Francis I of Austria, and spent four years traveling through the states of Minas Gerais, Goias, Bahia, and Rio de Janeiro, including some 30 rivers in the country. He collected thousands of plant specimens, as well as studying minerals and zoology, exploring gold and diamond mines, caves, and villages of local people.
After his return to Europe, Pohl served as curator of the Vienna Museum of Natural History and the Museum of Brazil in Vienna until his death. His extensive collections, including some 4,000 plant specimens, were housed here along with the expedition's other scientific collections.


John Ray was a British clergyman, naturalist, botanist and zoologist, and a Fellow of the Royal Society of London.
He came from a poor family, but through his persistence in acquiring knowledge he achieved recognition as a scientist. Ray published important works on botany, zoology, and natural history. His classification of plants in Historia Plantarum was an important step toward modern taxonomy (the scientific study of naming, defining, and classifying groups of biological organisms based on common characteristics). John Ray was the first to provide a biological definition of the term "species."


Michele Rosa was an Italian chemist and professor.
Rosa graduated from the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Bologna, then practiced in Venice and Rome. In 1766 he published An Essay on Clinical Observations, a pioneering work that brought him fame and earned him a professorship at the University of Pavia. In 1782 Rosa was appointed professor of practical medicine and president of the medical faculty of the new University of Modena. At Este he was elected president of the medical college and was in charge of sanitation.
In 1783 he published Letters on some physiological curiosities. In addition to physiology, epidemiology and public hygiene, Michele Rosa wrote works on natural science, antiquarianism and dietetics. Among these are the memoirs On Pores and Substances in Antiquity (1786) and On Gianda and Quercia (1801). In 1796 Rosa returned to Rimini, where he continued to teach and held some public offices.


Jacob Christian Schäffer was a German inventor, naturalist, entomologist and mycologist.
Schäffer was a very versatile scientist. He is best known for his work in mycology (the study of fungi), but his most important publication was undoubtedly a book on daphnia or water fleas.
Schäffer also published reference books on pharmaceuticals and medicinal herbs. He conducted experiments on electricity, colors, and optics, and invented the manufacture of prisms and lenses. He invented the washing machine, designs for which he published in 1767, and studied ways to improve paper production.
Schäffer was a professor at the Universities of Wittenberg and Tübingen, a member of the Royal Society of London, and a correspondent of the French Academy of Sciences.


Johann Jakob Scheuchzer was a Swiss naturalist and geologist, paleontologist and fossil collector.
Scheuchzer studied at the University of Altdorf near Nuremberg, earned a doctorate in medicine at Utrecht University, and studied astronomy. He worked as a teacher, physician, and corresponded extensively with many scientists, writing several papers, including those on Swiss research, weather, geology, and fossils. Scheuchzer collected fossils during his extensive travels. And, as a proponent of diluvialism, he believed that all fossils and layers of the earth were formed by the Flood.
Between 1731 and 1735, Scheuchzer published a massive four-volume work called Physica Sacra, which is essentially a commentary on the Bible. It presented the facts of natural history along with passages of scripture. Thus Physcia Sacra attempted to reconcile the Bible with science.
This book is also called the "Copper Bible" because it contains over 750 magnificent color engravings on copper plates. These engravings are in themselves the pinnacle of engraving from the Baroque period. The illustrations depict scenes with biblical and scientific motifs. They were based on his own cabinet of natural history and other famous European cabinets of rare specimens. The engravings were produced by highly skilled engravers, including Georg Daniel Heumann and Johann August Corwin.
During his lifetime, Johann Jakob Scheuchzer wrote 34 scientific papers and many articles, and he was a member of the Royal Society.


Heinrich Jacob Sivers was a German Evangelical Lutheran theologian and scholar, poet and writer, naturalist and collector.
Sifers studied law and theology at the University of Kiel, and received his doctorate at the University of Rostock, where he lectured and wrote various works. He wrote many poems, sermons and ceremonial speeches in German, Swedish and Latin.
Heinrich Sivers also studied geology, traveled extensively in Scandinavia, and compiled his own mineral collection. In 1737 he sold many of his minerals, as well as a cabinet of Roman coins to Count Carl Gillenborg, today they can be seen at Lund University.


Antonio Vallisneri the Elder was an Italian naturalist, physician and geologist, collector, and member of the Royal Society of London.
He studied in Bologna, Venice, Padua and Parma and headed the chair first of practical medicine and then of theoretical medicine at the University of Padua. In addition to medicine, Vallisneri conducted important research in the natural sciences. In particular, in the field of geology, he is credited with recognizing the organic nature of fossils unrelated to the Great Flood, which contributed to the end of centuries-old disputes. His observations on the water cycle, thermal waters and some mines in the Apennines were also important.
Vallisneri was interested in all branches of the natural sciences, collecting numerous collections of animals, minerals, and other natural objects during his lifetime. The scientist compiled a brief catalog of his collection, which was published in 1733 by his son, Antonio Vallisneri, Jr. The Vallisneri Museum included naturalistic finds, anatomical preparations, medical and scientific instruments, antiques, and exotics from various cultures and eras as well as geographical origins. In 1734, his son donated this museum to the University of Padua, initiating the creation of a general museum for the university.
Antonio Vallisneri Jr. followed in his father's footsteps and for many years held the position of professor of natural history at the University of Padua. He devoted his life to collecting and processing his father's writings and tidying up his library, which contained about a thousand volumes. These were donated to the University Library in Padua.


Etienne-Pierre Ventenat was a French botanist, mycologist and writer.
Etienne-Pierre Ventenat was one of the greatest botanists in France. Empress Josephine Bonaparte hired him to describe and catalog rare plants at her castle of Malmaison. Josephine enlisted eminent botanists such as Claes and Blaikie to collect plants on a grand scale. Ventenat was commissioned to write the text of the work on the Malmaison collection, and the illustrations were created by the talented artist Pierre-Joseph Redoute, nicknamed the "Raphael of Flowers." As a result, a sumptuous book entitled Jardin de la Malmaison (The Garden of Malmaison) was published in 1803.


Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, a German polymath and writer, is celebrated as one of the most influential figures in the German language and Western culture. His vast array of works spans poetry, novels, plays, and scientific writings, reflecting his diverse interests and profound impact on various fields.
Goethe's early life in Frankfurt laid the foundation for his diverse interests. After studying law, he gained fame with "The Sorrows of Young Werther," which led to an invitation to the Weimar court. His contributions there were significant, including roles in the ducal council, mining supervision, and cultural endeavors like theater management and the botanical park's planning.
His literary achievements are vast, with notable works like "Faust" and "Wilhelm Meister's Apprenticeship," which delve into human nature and societal reflections. Goethe's "Sturm und Drang" period was marked by intense emotion and a break from traditional forms, influencing subsequent cultural movements.
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe's interest in science is equally noteworthy. He made contributions to biology, zoology, and color theory, advocating for a holistic view of nature and expressing skepticism toward restrictive scientific methodologies. His works in these areas reflect a deep desire to understand and articulate the natural world's interconnectedness.
For art collectors and experts, Goethe's influence extends beyond his literary and scientific contributions. His role in Weimar Classicism and his artistic endeavors offer rich insights into the period's cultural landscape, providing a multifaceted perspective on his legacy.
To stay informed about developments and events related to Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, consider signing up for updates. This subscription will keep you informed about new product sales and auction events related to Goethe's works and influence, offering exclusive insights for enthusiasts and collectors.


Nikolaus von Jacquin, full name Nikolaus Joseph Freiherr von Jacquin, also Baron Nikolaus von Jacquin, was an Austrian and Dutch scientist, professor of chemistry and botany, and director of the Vienna Botanical Garden.
Jacquin is considered a pioneer of scientific botany in Austria. He wrote fundamental works in botany, was the first to describe many plants, fungi, and animals, introduced experimental methods in chemistry, and successfully campaigned for the introduction of Linnaeus' system of plants in Austria. On behalf of Emperor Franz I, von Jacquin was in charge of the imperial gardens (including Schoenbrunn) and also led a scientific expedition to Central America from 1754 to 1759, from which he returned with an extensive collection of plants.
In 1768, Nikolaus von Jacquin was appointed professor of botany and chemistry at the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Vienna and director of the newly founded botanical garden, which he reorganized according to scientific principles. Nikolaus von Jacquin was a member of the Royal Society of London, a foreign honorary member of the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences, and a correspondent of the Paris Academy of Sciences.


Franz Xaver Freiherr (from 1801) von Zach, Baron (Hungarian: Zách János Ferenc) was an Austro-German astronomer, surveyor, mathematician, science historian and officer of Hungarian origin. He rendered outstanding services in the exploration of the solar system and the organization of international astronomy, after whom a lunar crater (Zach) and an asteroid ((999) Zachia) were named, among others. He was also the founder of the first scientific journals and organised the first astronomical congress in 1798.


Johann Zahn (German: Johann or Johannes Zahn) was a German scientist and philosopher, optician and astronomer, mathematician and inventor.
Zahn studied mathematics and physics at the University of Würzburg, was professor of mathematics at the University of Würzburg, and served as a canon of the Order of Regular Canon Premonstratensians. His other activities were optics as well as astronomical observations.
In 1686 Johann Zahn invented and designed a portable camera obscura with fixed lenses and an adjustable mirror, which is the prototype of the camera. In his treatise on optics, Oculus Artificialis Teledioptricus (1702), Zahn gives a complete picture of the state of optical science of his time. He begins with basic information about the eye and then moves on to optical instruments. The book is aimed at eighteenth-century microscope and telescope enthusiasts and includes all the necessary details of construction, from lens grinding to drawings.