éditions imprimées
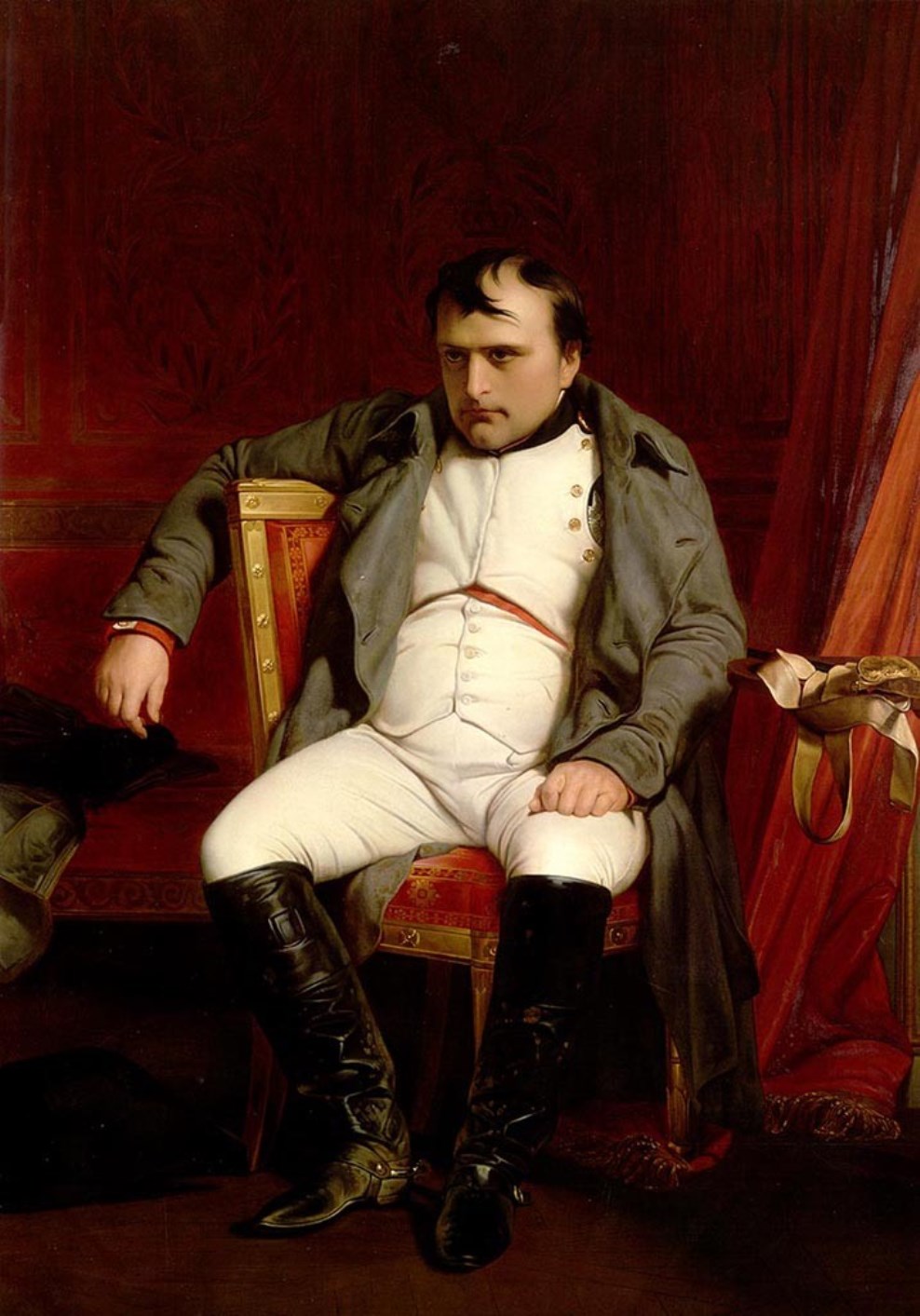







Napoleon I Bonaparte was a French statesman and military leader, Emperor of France (1804-1815).
Napoleon was born in the family of an ignorant Corsican nobleman, graduated from the Brienne military school, then the Paris military school. In 1785 he began military service in the rank of junior lieutenant of artillery in the Royal Army. From the first days of the Great French Revolution of 1789-1799 Bonaparte joined the political struggle on the island of Corsica, in 1792 in Valence joined the Jacobin Club and actively participated in all the turbulent political and military events.
In November 1799 Napoleon was at the head of a coup d'état: the government of the Directory was deposed, and the French Republic was headed by three consuls, the first of whom was Napoleon. In June 1804 Bonaparte was proclaimed Emperor Napoleon I of France, and in December a lavish coronation ceremony took place. After Italy recognized him as its king, in March 1805 he was also crowned in Milan.
With his rise to power, France entered a period of almost continuous warfare. Napoleon greatly expanded the territory of the empire, made most of the states of Western and Central Europe dependent on France. His brothers became kings: Joseph in Naples, Louis in Holland, and Jerome in Westphalia. In 1812, Napoleon made a campaign against Russia and even reached Moscow, but the Russian troops under the leadership of commander M.I. Kutuzov with the active support of all the people completely defeated the "invincible army". This military campaign was the beginning of the collapse of Napoleon's empire. The entry of the anti-French coalition troops into Paris in March 1814 forced Napoleon I to abdicate (April 6, 1814).
Napoleon retained the title of Emperor and was given possession of the island of Elba in the Mediterranean Sea. However, in March 1815, the deposed emperor at the head of a small detachment suddenly landed in the south of France and three weeks later, without a single shot entered Paris. But the emperor failed to live up to the hopes of the people of France, plus his defeat at the Battle of Waterloo all led to his second abdication. As a result, Napoleon Bonaparte was exiled to the island of St. Helena in the Atlantic Ocean, where he died on May 5, 1821.
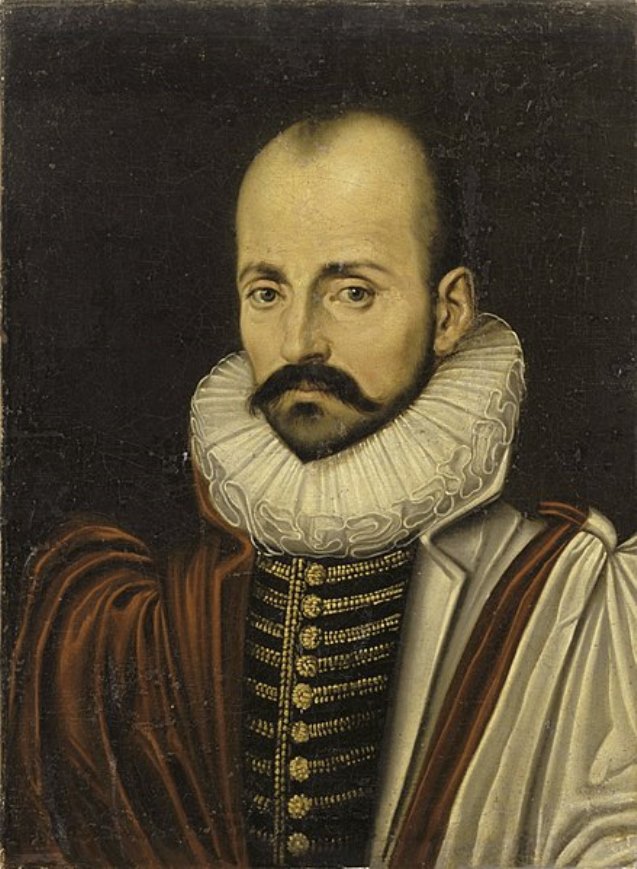
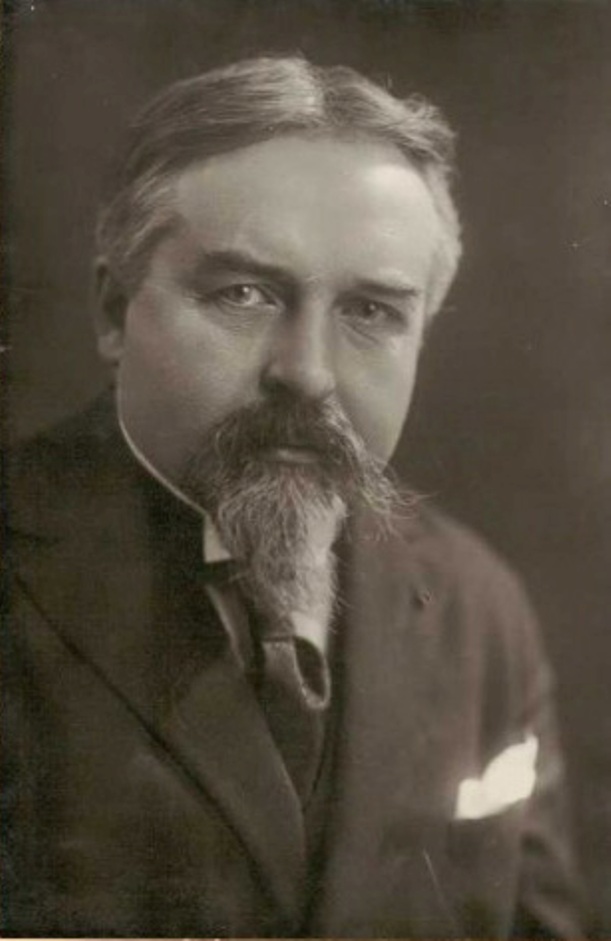









Maurice Denis, a French painter and writer, was an influential figure in the transition from impressionism to modern art. Born on November 25, 1870, in Granville, France, Denis's artistic journey began at the Académie Julian in Paris. Here, he met future collaborators like Paul Sérusier and Pierre Bonnard, with whom he later formed the Nabis group, a collective deriving its name from the Hebrew word "Nabi," meaning "Prophet".
Denis's style evolved from neoimpressionism, influenced by artists like Seurat, to a more decorative and colorful approach under the influence of Gauguin. This shift is evident in works like "Taches du soleil sur la terrace" (1890). He famously stated, "Art is no longer a visual sensation... it is a creation of our spirit," highlighting his belief in art as an idealistic expression, transcending mere imitation of nature.
Denis was also impacted by Japanese art, which influenced his compositions and styles, contributing to his unique and recognizable approach. His philosophy on art, encapsulated in his 1890 essay published in "Art et Critique," emphasized the importance of color and form in creating emotional depth, a notion that laid the groundwork for modernism. He argued that a painting's essence lies in its colors and composition, rather than its subject matter.
Throughout his career, Denis's work evolved towards a more classical approach. His involvement with the Ateliers d'Art Sacré, founded in 1919, demonstrated his interest in religious art and decoration. His notable works include "The Legend of Saint Hubert" (1897) and "The History of Music" for the Théâtre des Champs Elysées (1912-1913).
Tragically, Maurice Denis's life ended on November 13, 1943, when he was struck by a truck during the German occupation of Paris. However, his legacy endures through his contributions to modern art and symbolism, his influence on fellow artists, and his works displayed in various museums and galleries.
For collectors and art experts, Denis's work offers a unique glimpse into the evolution of modern art. His blend of symbolism, color, and form marks a significant shift in art history. To stay updated on new sales and auction events related to Maurice Denis's work, sign up for our newsletter. This subscription will keep you informed about the latest developments in the world of this remarkable artist.
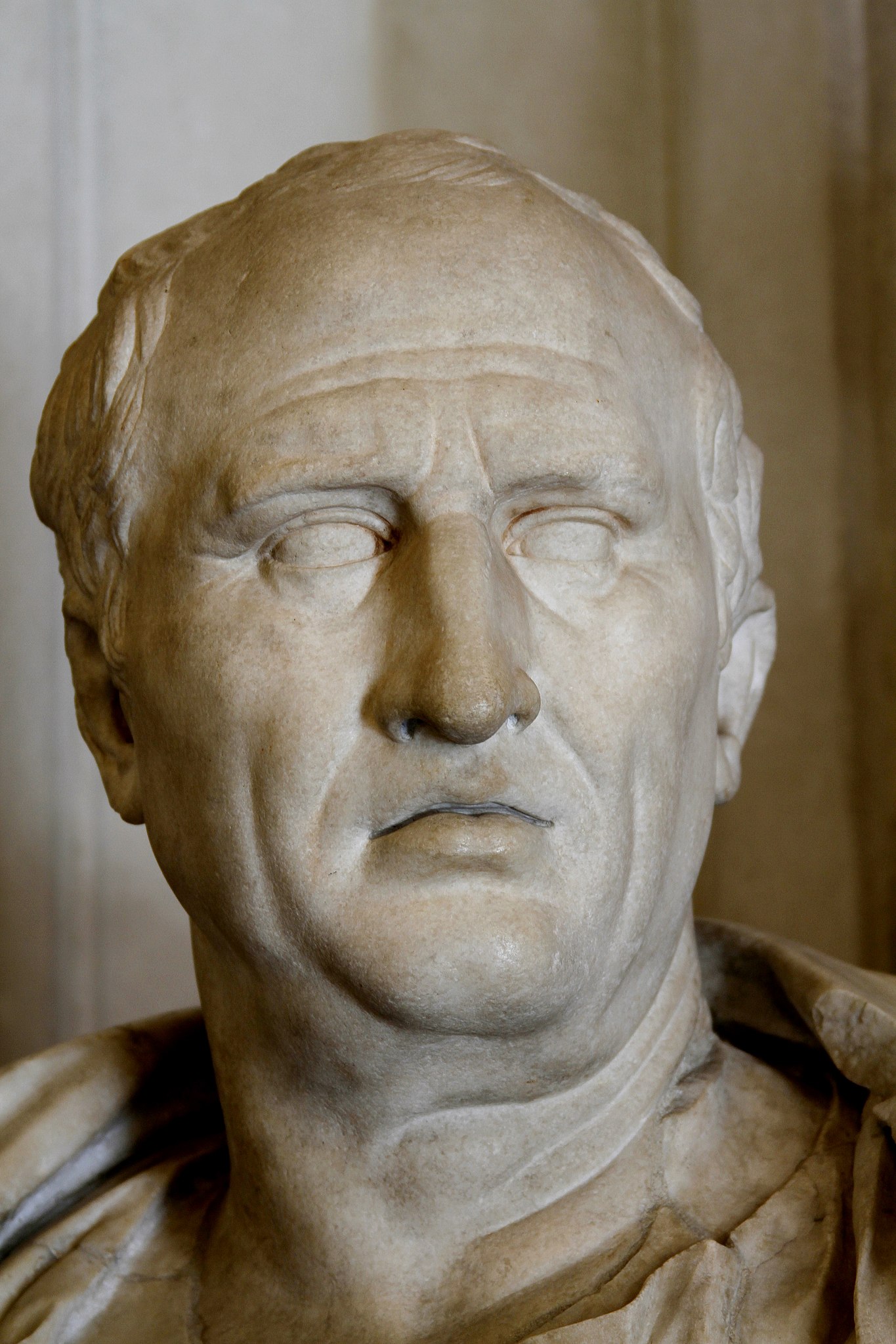




Marcus Tullius Cicero was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the establishment of the Roman Empire. His extensive writings include treatises on rhetoric, philosophy and politics. He is considered one of Rome's greatest orators and prose stylists. He came from a wealthy municipal family of the Roman equestrian order, and served as consul in 63 BC.
His influence on the Latin language was immense. He wrote more than three-quarters of extant Latin literature that is known to have existed in his lifetime, and it has been said that subsequent prose was either a reaction against or a return to his style, not only in Latin but in European languages up to the 19th century. Cicero introduced into Latin the arguments of the chief schools of Hellenistic philosophy and created a Latin philosophical vocabulary with neologisms such as evidentia, humanitas, qualitas, quantitas, and essentia, distinguishing himself as a translator and philosopher.
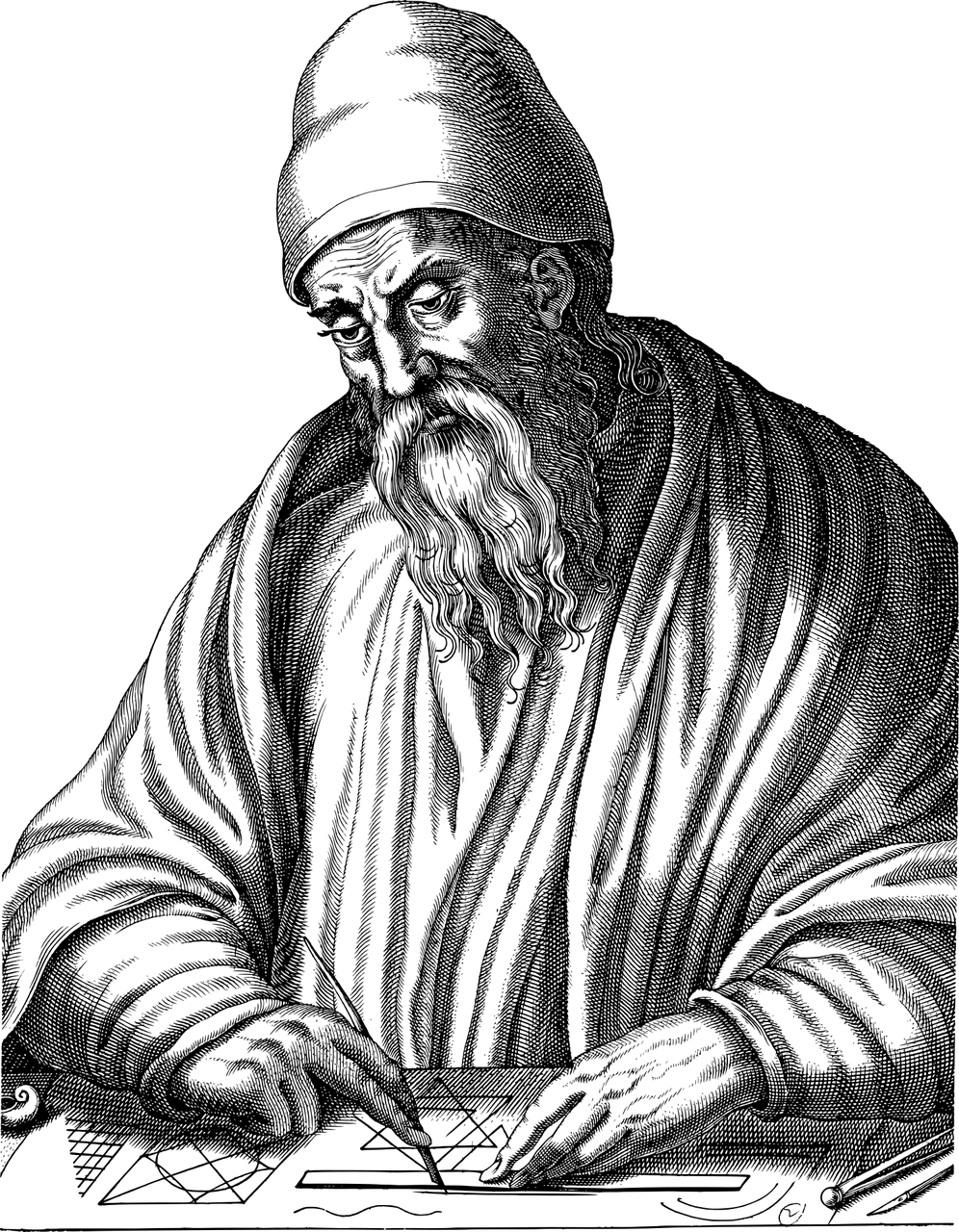


Euclid (Greek: Εὐκλείδης) was an ancient Greek mathematician active as a geometer and logician. Considered the "father of geometry", he is chiefly known for the Elements treatise, which established the foundations of geometry that largely dominated the field until the early 19th century. His system, now referred to as Euclidean geometry, involved new innovations in combination with a synthesis of theories from earlier Greek mathematicians, including Eudoxus of Cnidus, Hippocrates of Chios, Thales and Theaetetus. With Archimedes and Apollonius of Perga, Euclid is generally considered among the greatest mathematicians of antiquity, and one of the most influential in the history of mathematics.

![[Heures imprimées sur vélin]](/assets/image/picture_2500861/45a67/6206d49e01ac5af20632b782f954f2ed1667984400jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[Heures imprimées sur vélin]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_2500861/45a67/6206d49e01ac5af20632b782f954f2ed1667984400jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[ÉDITIONS DE MINUIT].](/assets/image/picture_2932390/62cb5/9ffda273d6df69a2796fa8e1f69cb4a31687420800jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[ÉDITIONS DE MINUIT].](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_2932390/62cb5/9ffda273d6df69a2796fa8e1f69cb4a31687420800jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)





![[AUBIGNÉ, Théodore Agrippa d' (1552-1630)]. Les Tragiques. Donnez au public par le larcin de Prométhée. Au Dezert par L.B.D.D, [château de Maillé : Jean Moussat], 1616.](/assets/image/picture_1320898/3976f/cbf089ad2351e04118152eab6351a58d1616454000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[AUBIGNÉ, Théodore Agrippa d' (1552-1630)]. Les Tragiques. Donnez au public par le larcin de Prométhée. Au Dezert par L.B.D.D, [château de Maillé : Jean Moussat], 1616.](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_1320898/3976f/cbf089ad2351e04118152eab6351a58d1616454000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![EXPÉDITION D'ÉGYPTE [LE PÈRE, Jacques-Marie (1763-1841) et Gratien LE PÈRE (1769-1826)]](/assets/image/picture_4260212/a4ba1/sjjzgn9bhgtpyrvctoiua2rrkb9kfnhzrsxisikusj5ylgnuffmmrf39-g1nespn1729545597jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![EXPÉDITION D'ÉGYPTE [LE PÈRE, Jacques-Marie (1763-1841) et Gratien LE PÈRE (1769-1826)]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_4260212/a4ba1/sjjzgn9bhgtpyrvctoiua2rrkb9kfnhzrsxisikusj5ylgnuffmmrf39-g1nespn1729545597jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![RONSARD, Pierre de (1524-1585). Epithalame d’Antoine de Bourbon, et Ianne de Navarre par Pierre de Ronsard Vandomois. Paris : Imprimerie de [Michel de] Vascosan, 1549.](/assets/image/picture_1320893/c0bc5/09942b4681cf81b13c892f174c27ecb71616454000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![RONSARD, Pierre de (1524-1585). Epithalame d’Antoine de Bourbon, et Ianne de Navarre par Pierre de Ronsard Vandomois. Paris : Imprimerie de [Michel de] Vascosan, 1549.](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_1320893/c0bc5/09942b4681cf81b13c892f174c27ecb71616454000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)


![[MUSSET, Alfred de (1810-1857)]](/assets/image/picture_3806738/a6dc8/3470724f96ccd1b2e87402872ad747681710234000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[MUSSET, Alfred de (1810-1857)]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3806738/a6dc8/3470724f96ccd1b2e87402872ad747681710234000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)








![CASTIGLIONE, Baldassare (1478-1529) Le premier [-quart] livr...](/assets/image/picture_1080045/4b2a1/pacp16g2aagwf75jcgczokbyev42tdh3zl0peqentfa6yivuelwtmujn-5in1602251660jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![CASTIGLIONE, Baldassare (1478-1529) Le premier [-quart] livr...](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_1080045/4b2a1/pacp16g2aagwf75jcgczokbyev42tdh3zl0peqentfa6yivuelwtmujn-5in1602251660jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)





![[MONTESQUIEU, Charles-Louis de Secondat, baron de (1689-1755)]](/assets/image/picture_4604831/df92d/4b24b13b4d61805b7d6ba9441053cc001747864800jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[MONTESQUIEU, Charles-Louis de Secondat, baron de (1689-1755)]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_4604831/df92d/4b24b13b4d61805b7d6ba9441053cc001747864800jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)