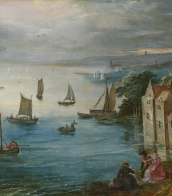lombard school
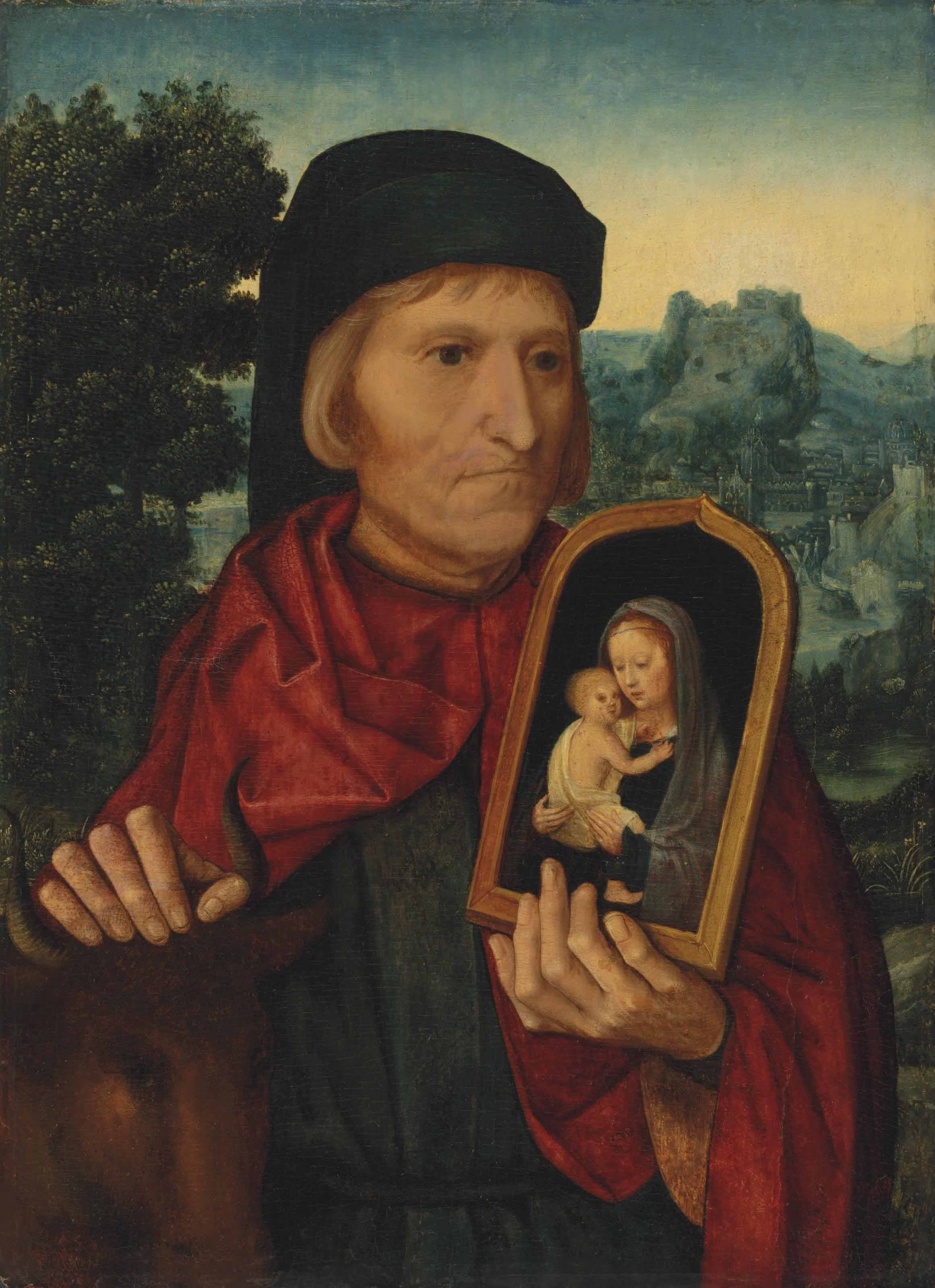

Ambrosius Benson was an Italian painter who became a part of the Northern Renaissance.
While many surviving paintings have been attributed, there is very little known of him from records, and he tended not to sign his work. He is believed to be responsible for mainly religious art, but also painted portraits on commission. He sometime painted from classical sources, often setting the figures in modern-dress, or a contemporary domestic setting. In his lifetime he was successful; he had a large workshop, his work was sold internationally and he was especially popular in Spain.


Ambrosius Benson was an Italian painter who became a part of the Northern Renaissance.
While many surviving paintings have been attributed, there is very little known of him from records, and he tended not to sign his work. He is believed to be responsible for mainly religious art, but also painted portraits on commission. He sometime painted from classical sources, often setting the figures in modern-dress, or a contemporary domestic setting. In his lifetime he was successful; he had a large workshop, his work was sold internationally and he was especially popular in Spain.



Pierre Bersuire, also known as Petrus Berchorius, was a French medieval writer, Benedictine monk, translator, and encyclopedist.
He was the leading French scholar of his time and friend of Petrarch, author of encyclopedic works on morality, and the first French translator of Titus Livy's History from the Foundation of the City. Very interesting for researchers is Pierre Bersuir's text Ovidius Moralisatus - written in Avignon in 1340 and spreading rapidly, it is a systematic allegorical analysis of the Metamorphoses, aimed at the current situation in church and society.
Bersuire was also an eloquent preacher and author of voluminous sermons.
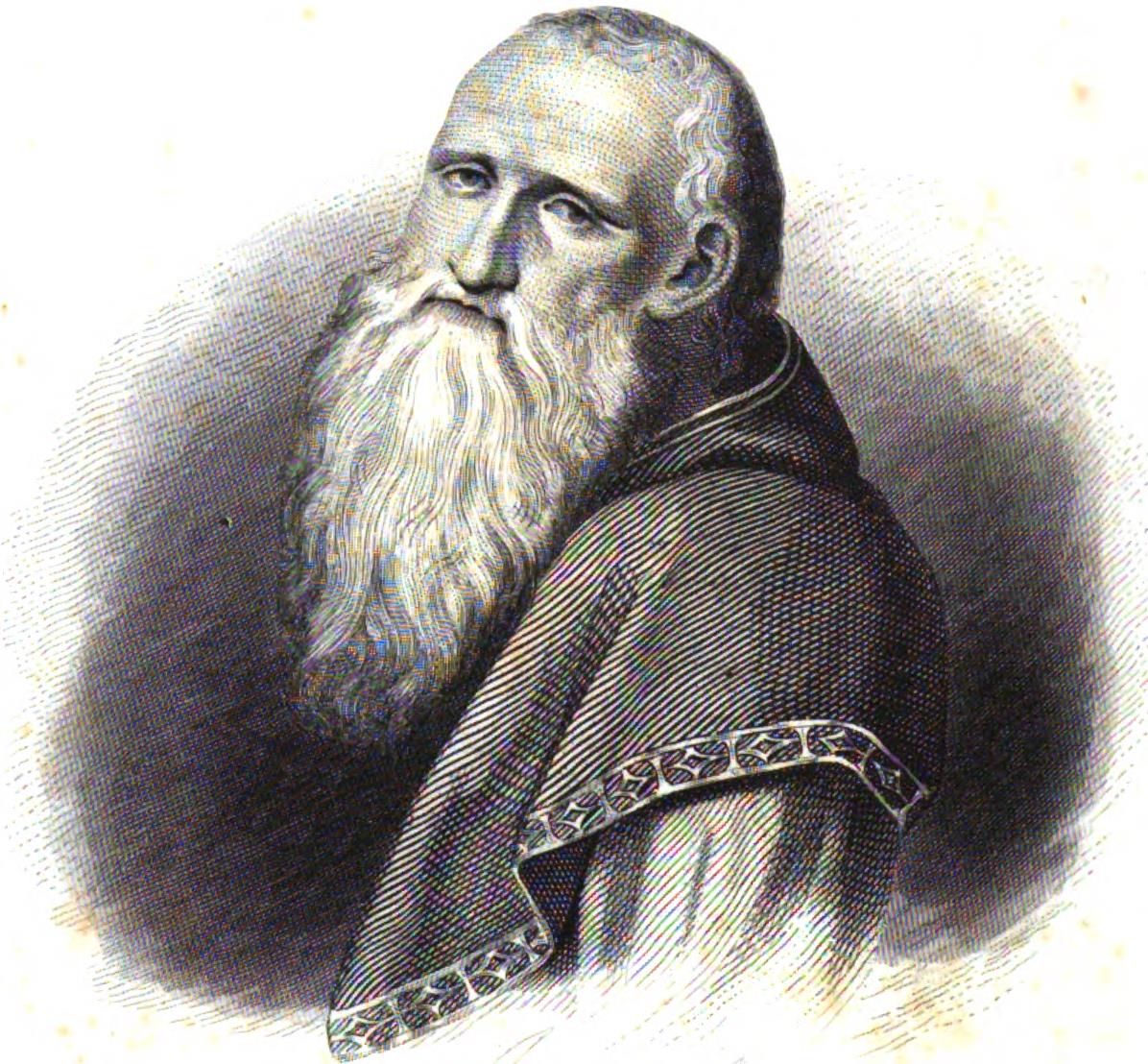


Bernardino Luini, born in Runo, Lombardy around 1481, remains a significant figure in the 16th-century Lombard school of painting. A key member of the Milanese second Leonardo movement, he, along with Cesare da Sesto and Giampietrino Francesco Melzi, contributed to the essence of this artistic era. Luini's journey into art was accompanied by his marriage to Margherita Lomazzo in 1510. Among their four sons, Giovan Pietro and Aurelio followed their father's footsteps, becoming painters themselves. Influenced profoundly by Raphael's work, Melozzo da Forlì, and Leonardo da Vinci, Luini skillfully blended Leonardo's techniques with his own innovations. His Salome with the Beheading of John the Baptist (Uffizi) draws inspiration from Leonardo's La Scapigliata, while his Holy Family with the Infant John (Prado) echoes Leonardo's lost original sketch of affectionate children.
Luini's artistic journey began with the disputed but noteworthy Madonna with the Child and Two Saints (1507), now exhibited in Paris's Musée Jacquemart-André. One of his remarkable works, Madonna della Buonanotte, can be found in the Chiaravalle Milanese monastery. This painting held a unique purpose – after evening prayers, passing monks would be greeted by the artwork, offering them a peaceful night's rest. In later years, Luini's focus shifted to fresco painting. Notably, his captivating depictions of the Crucifixion in Lugano's Santa Maria degli Angioli church and the small-scale Crucifixion in San Nazario in Dino, a subdivision of Sonvico, are celebrated masterpieces that showcase his skill.
Bernardino Luini's legacy endures as a testament to his mastery of Lombard Renaissance art. His fusion of Leonardo's influence with his own creative brilliance left an indelible mark on the artistic landscape of the 16th century, making him an integral part of the Milanese second Leonardo movement.