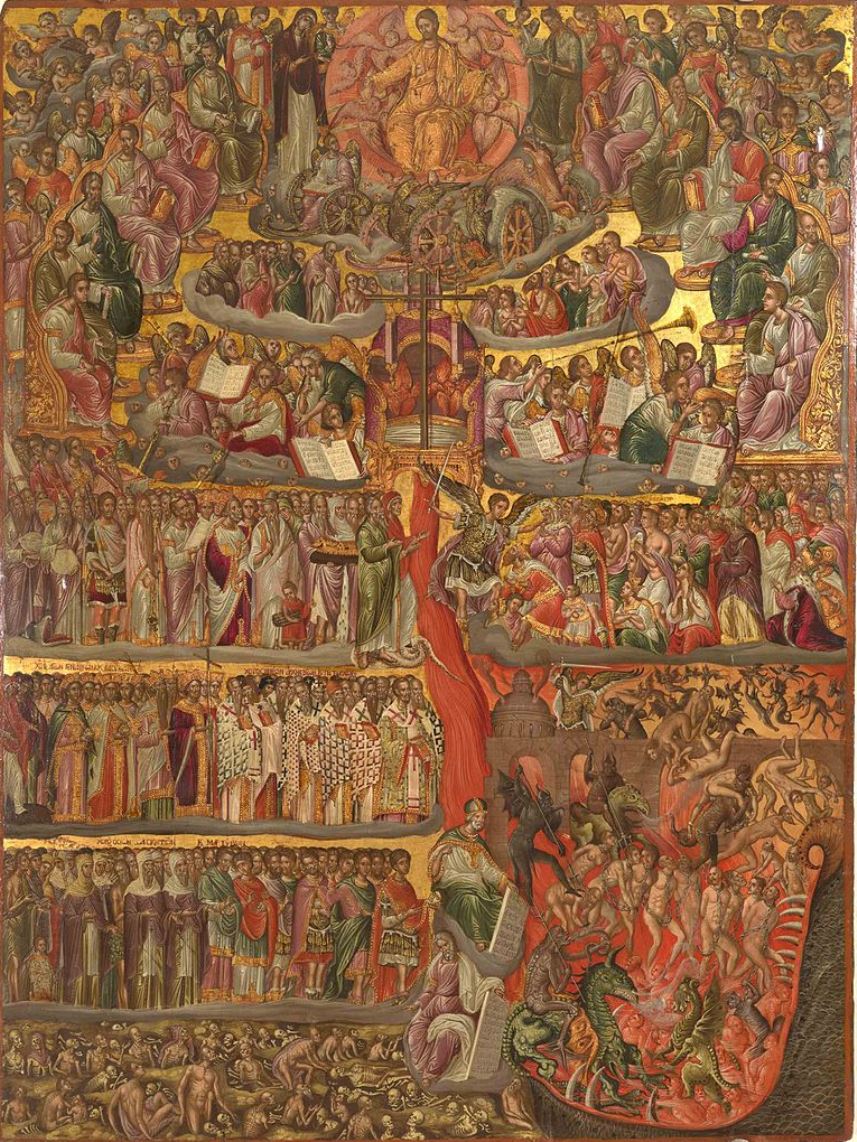
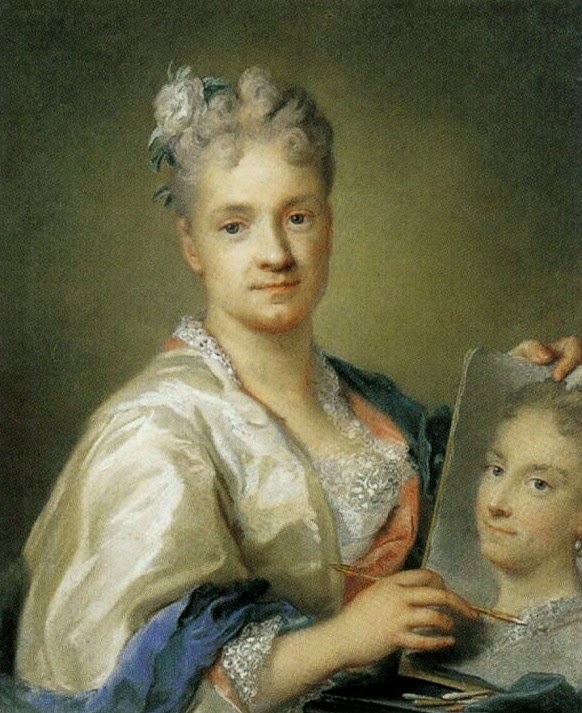
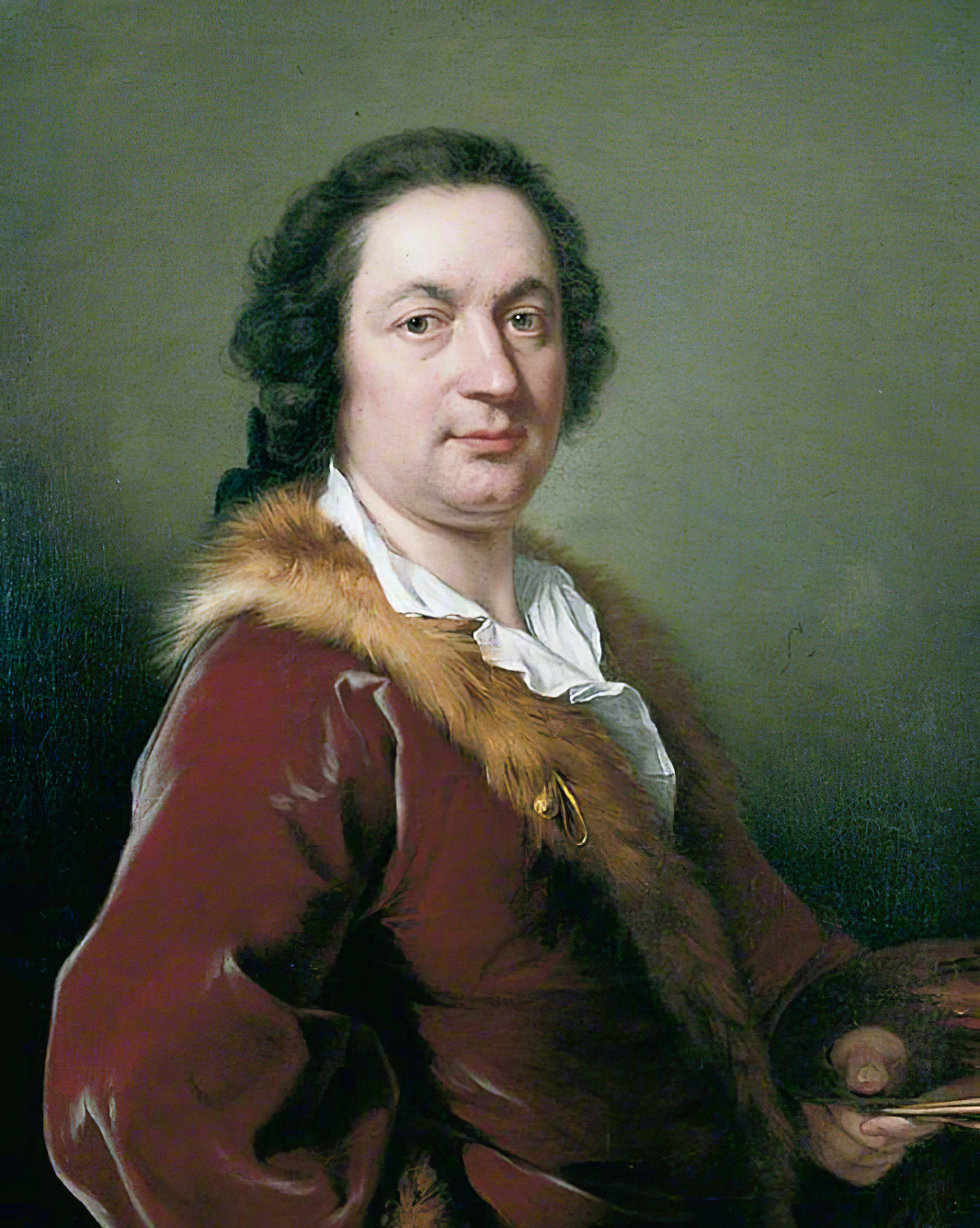
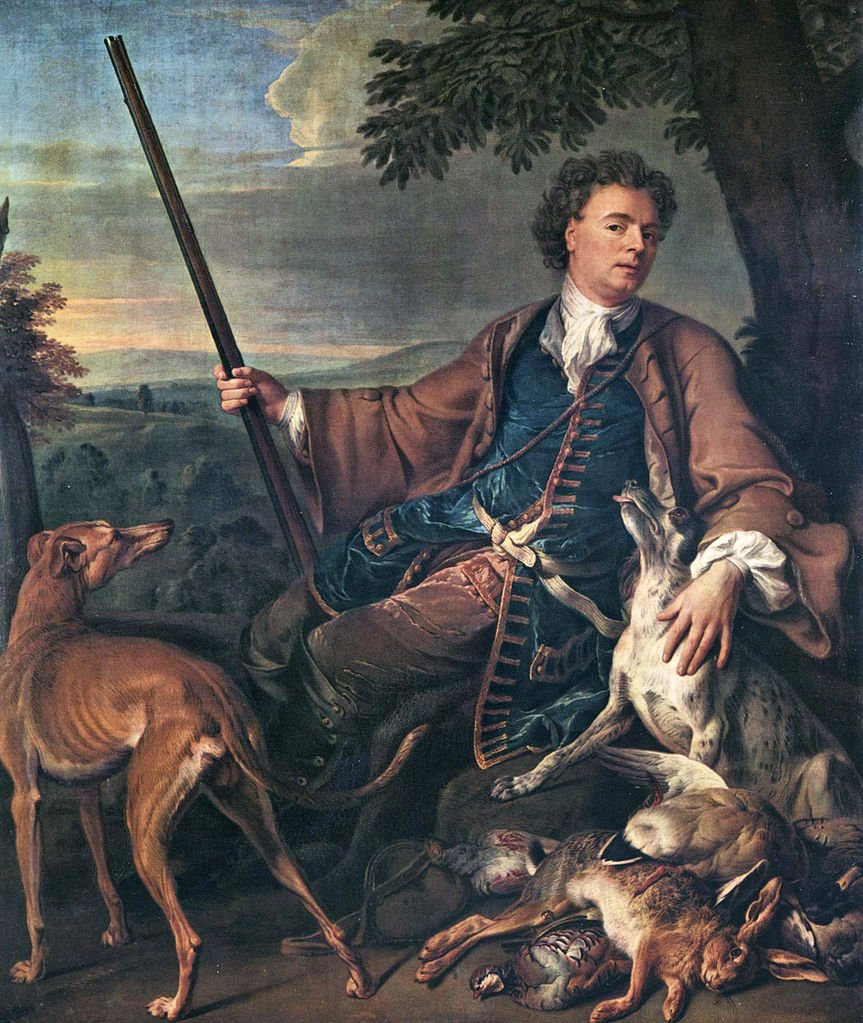
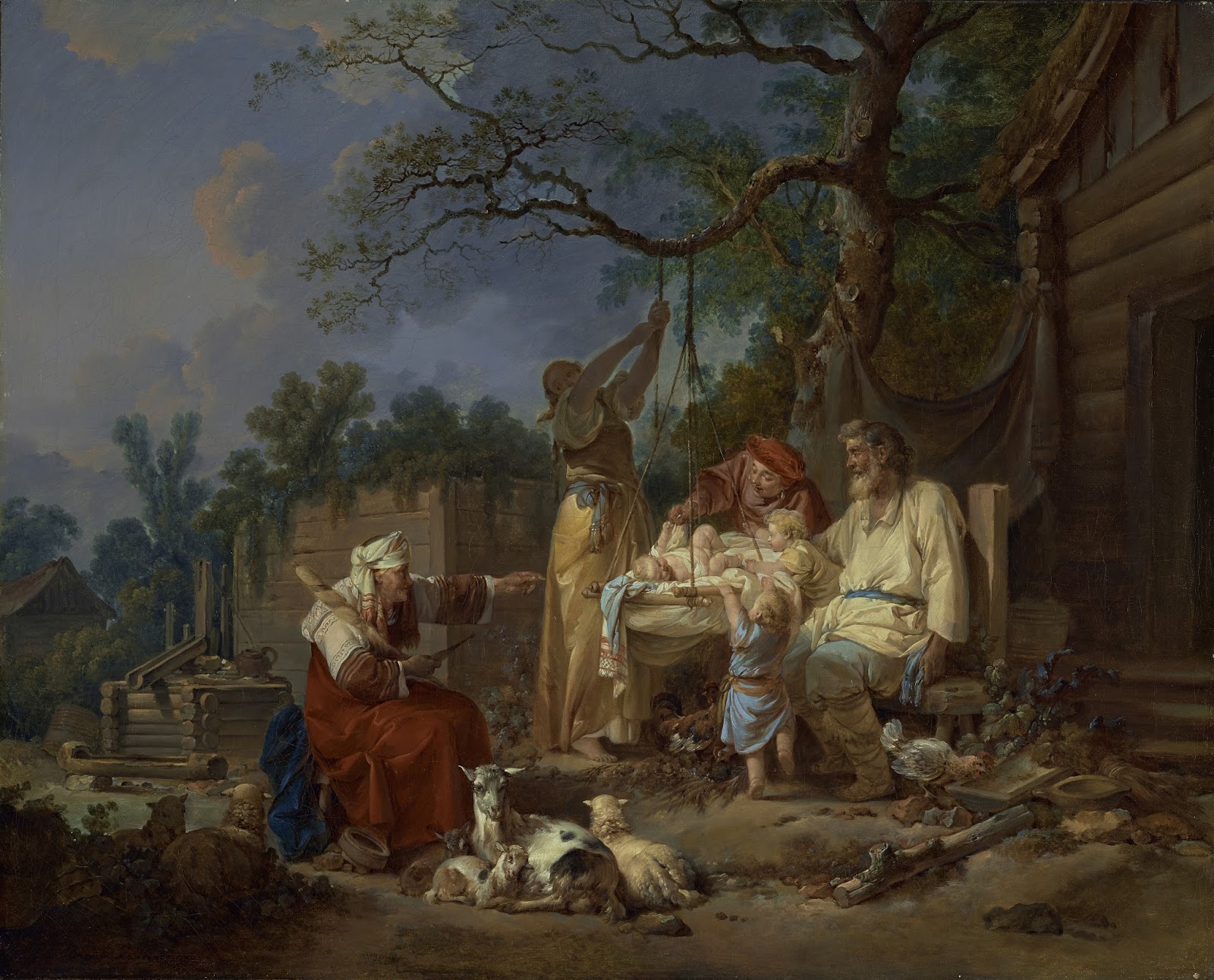
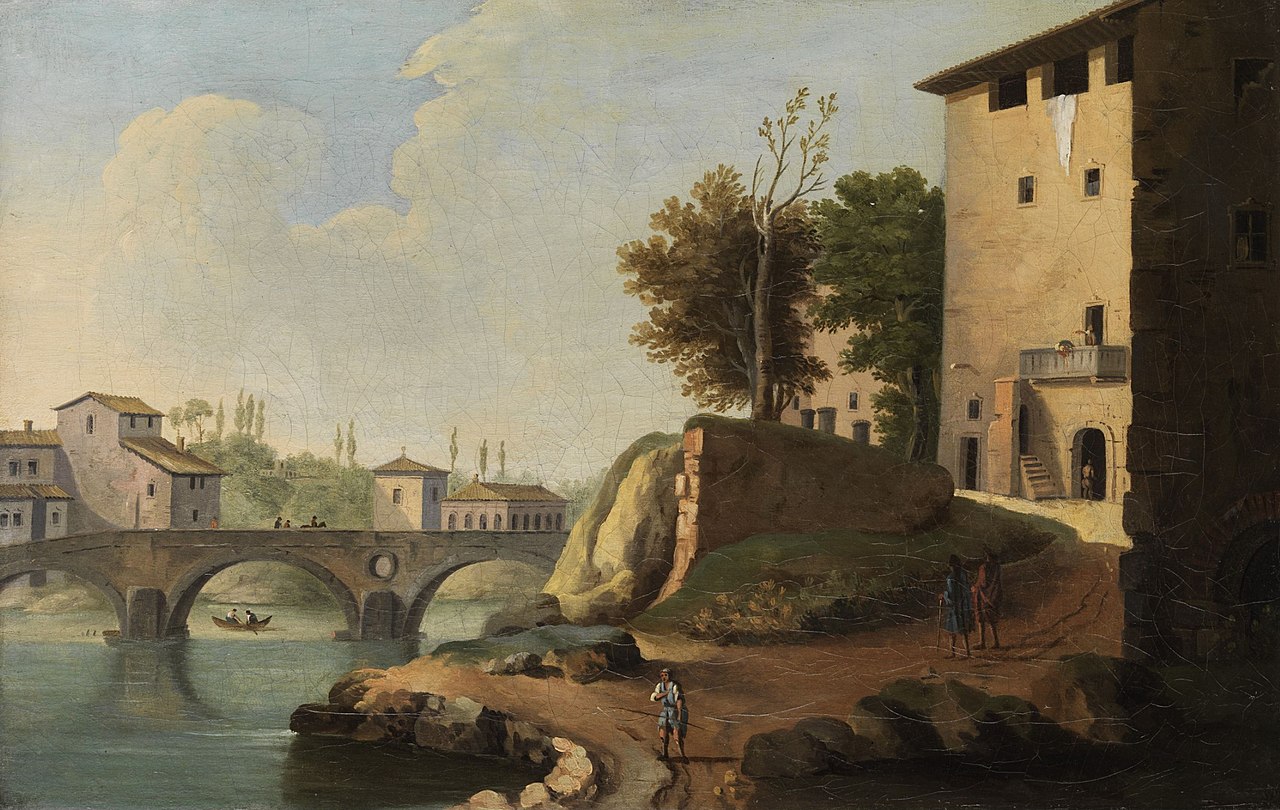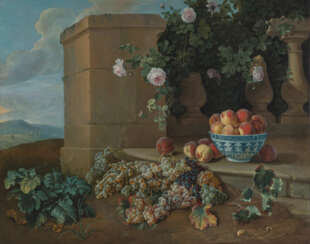Maîtres Anciens : Peintures - Sculptures - Dessins
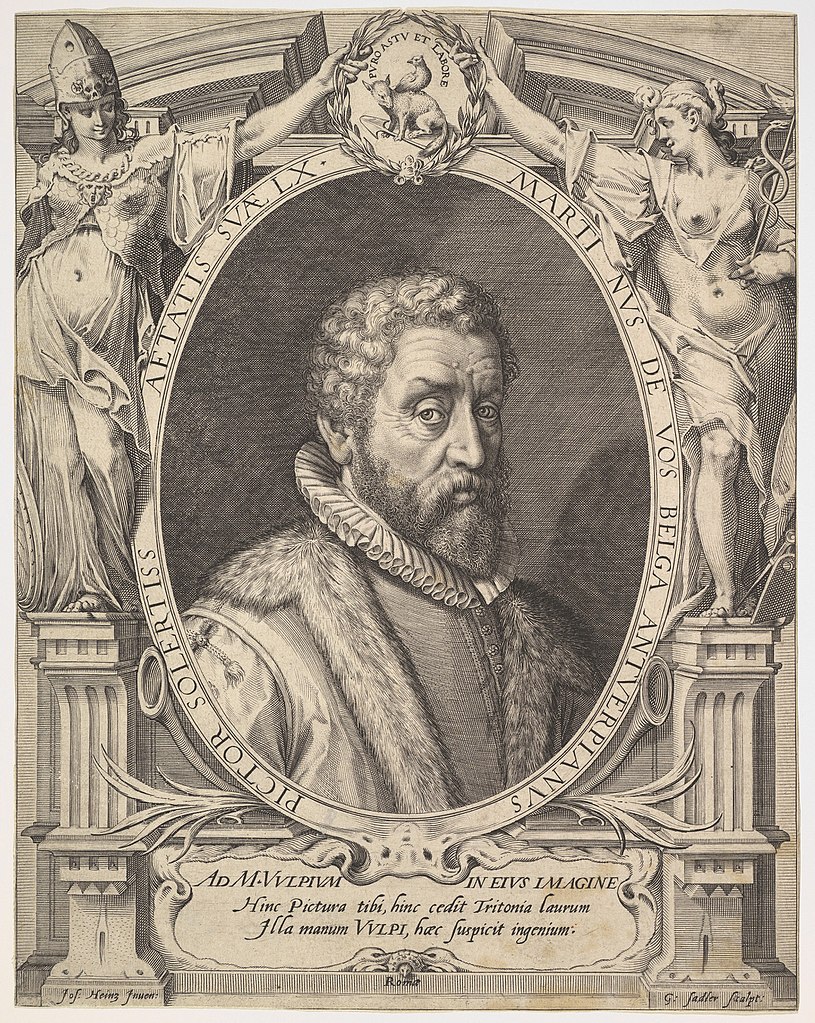

Marten de Vos (or Maarten de Vos, or Maerten de Vos) was a Dutch painter, draughtsman and graphic artist, dean of the Antwerp Guild.
After studying in Rome and Venice, de Vos returned to his native Antwerp in 1558 and became one of the city's leading artists. He created altarpiece images for many of Antwerp's churches. Many of his religious and historical paintings were later engraved, making him known throughout Flanders.
De Vos was also the founder of the Society of Romanists, whose members were famous artists and humanists of the time who appreciated the humanistic culture of Rome.
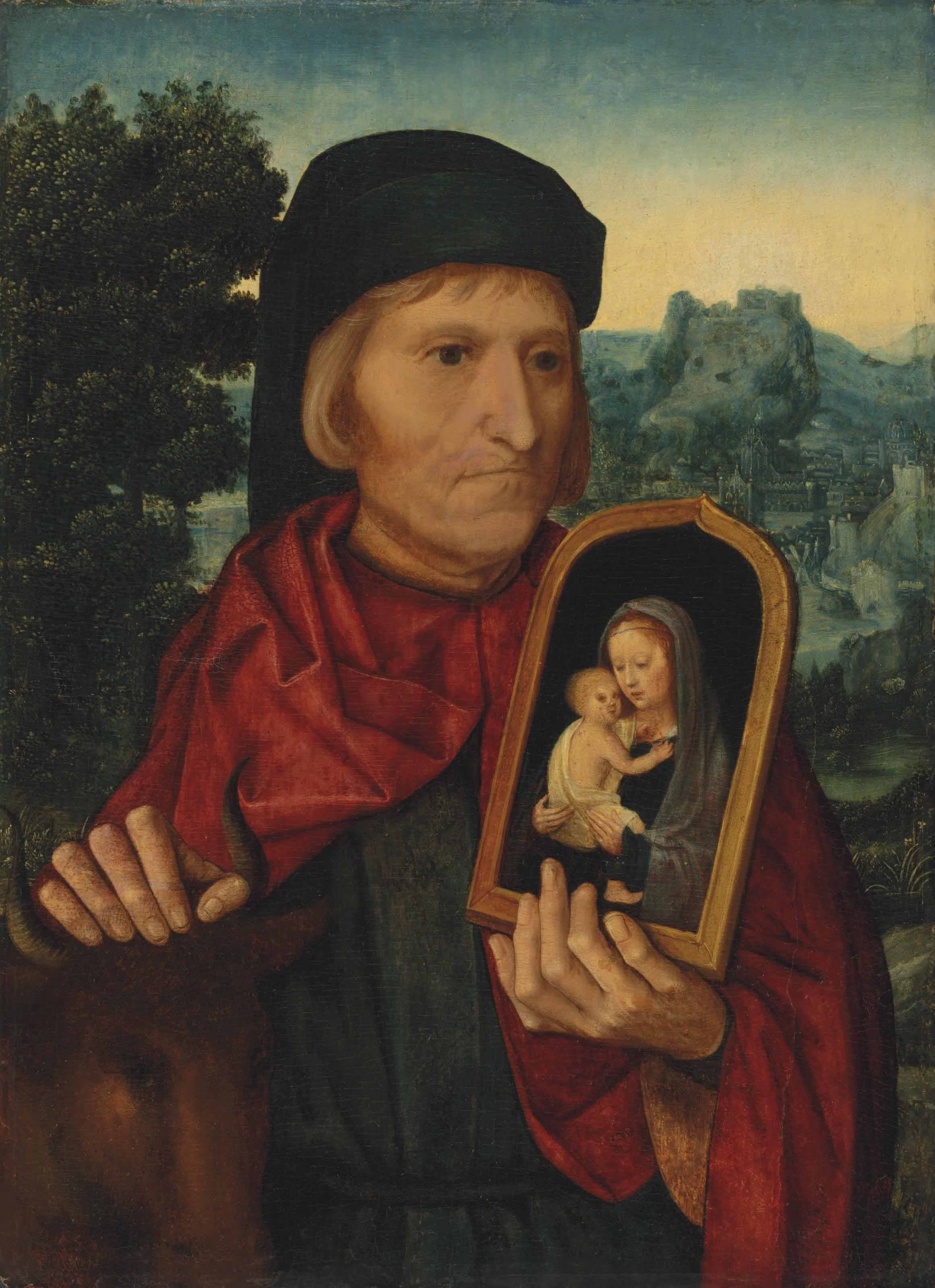

Ambrosius Benson was an Italian painter who became a part of the Northern Renaissance.
While many surviving paintings have been attributed, there is very little known of him from records, and he tended not to sign his work. He is believed to be responsible for mainly religious art, but also painted portraits on commission. He sometime painted from classical sources, often setting the figures in modern-dress, or a contemporary domestic setting. In his lifetime he was successful; he had a large workshop, his work was sold internationally and he was especially popular in Spain.
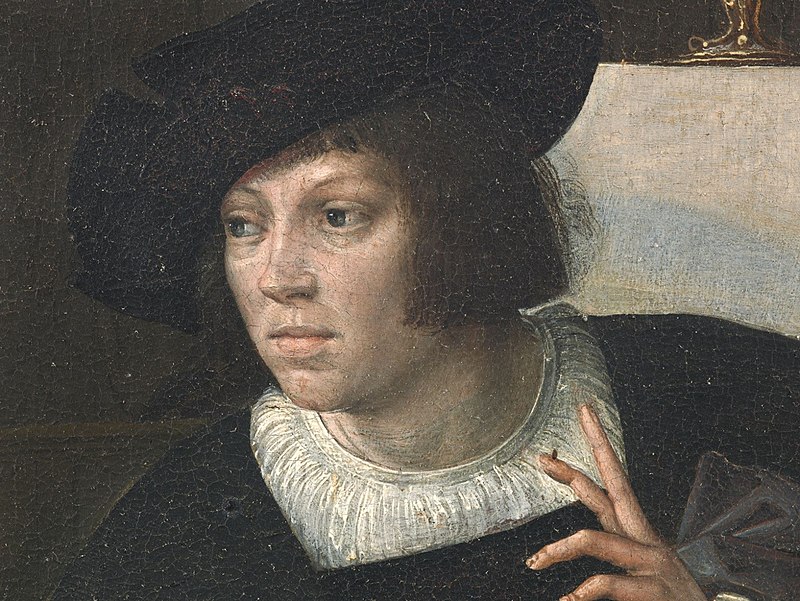

Bernard van Orley was a versatile Flemish artist and representative of Dutch and Flemish Renaissance painting, who was equally active as a designer of tapestries and, at the end of his life, stained glass. Although he never visited Italy, he belongs to the group of Italianizing Flemish painters called the Romanists, who were influenced by Italian Renaissance painting, in his case especially by Raphael.
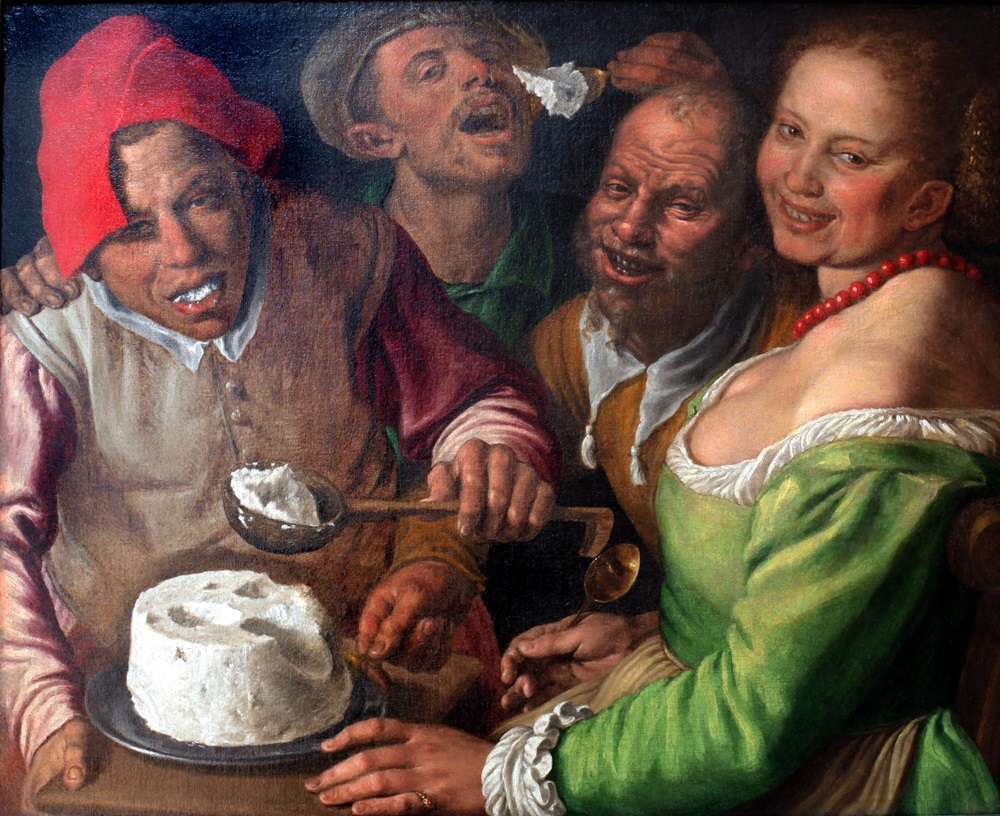

Vincenzo Campi was a notable painter of the 16th century, widely recognized for his unique style that combined traditional subjects with everyday life. Campi's journey in the world of art was influenced by his family background, as he trained under his brother Giulio and was part of a family of Italian painters known for their contributions to Mannerist painting.
Vincenzo Campi's paintings stood out for their vivid depictions of market scenes and kitchen tableaux, focusing on everyday objects and food with an extraordinary level of realism. This approach was quite innovative for his time. His works like "Pescivendoli" (The Fishmongers, 1579) and "The Ricotta Eaters" (1580) are emblematic of his style, combining elements of still life and genre painting. In "The Ricotta Eaters," for instance, Campi artistically weaves together themes of food and sensuality, presenting a scene that is both a hymn to life and pleasure and a subtle commentary on social classes and morality.
Vincenzo Campi's paintings were not just mere representations of daily life; they often carried deeper social and cultural meanings. For instance, in his depiction of the lower working classes in "Fishmongers," he illustrated contemporary beliefs regarding food's appropriateness based on social hierarchy. The paintings of commoners consuming foods like beans, dark bread, and cheese, as shown in "The Ricotta Eaters," reflected the societal norms of the time regarding class and diet.
Vincenzo Campi's work did not only portray the peasants in a crude or humorous light, but also carried a sophisticated blend of comedy and criticism, reflecting a deeper understanding of the human condition and social structures of his time.
Campi's style and themes influenced other artists in Cremona and contributed to the development of genre painting in northern Italy. His work, in some ways, served as a precursor to Caravaggio’s realism that emerged in the subsequent decade.
For collectors and connoisseurs of art and antiques, Vincenzo Campi's paintings offer a unique window into the societal and cultural aspects of 16th-century Italy, blending everyday life with deeper social commentaries. His work continues to be an important part of the conversation in the history of art.
To stay updated on the latest insights and collections of Vincenzo Campi's works, consider subscribing to our updates. This service will ensure you are informed about new sales, exhibitions, and auction events related to this influential Italian artist.
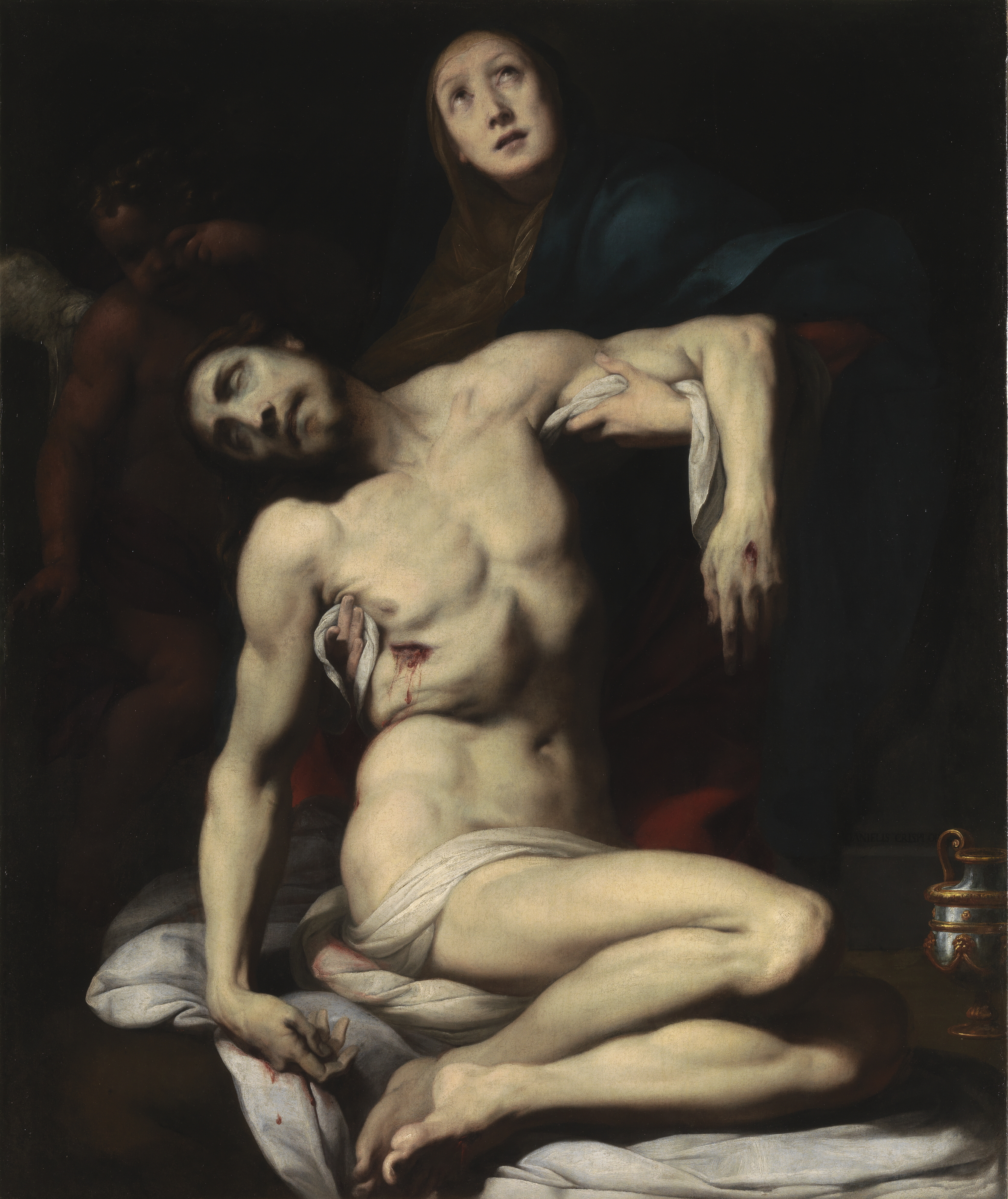

Daniele Crespi was an Italian painter and draughtsman. He is regarded as one of the most original artists working in Milan in the 1620s. He broke away from the exaggerated manner of Lombard Mannerism in favour of an early Baroque style, distinguished by clarity of form and content. A prolific history painter, he was also known for his portraits.
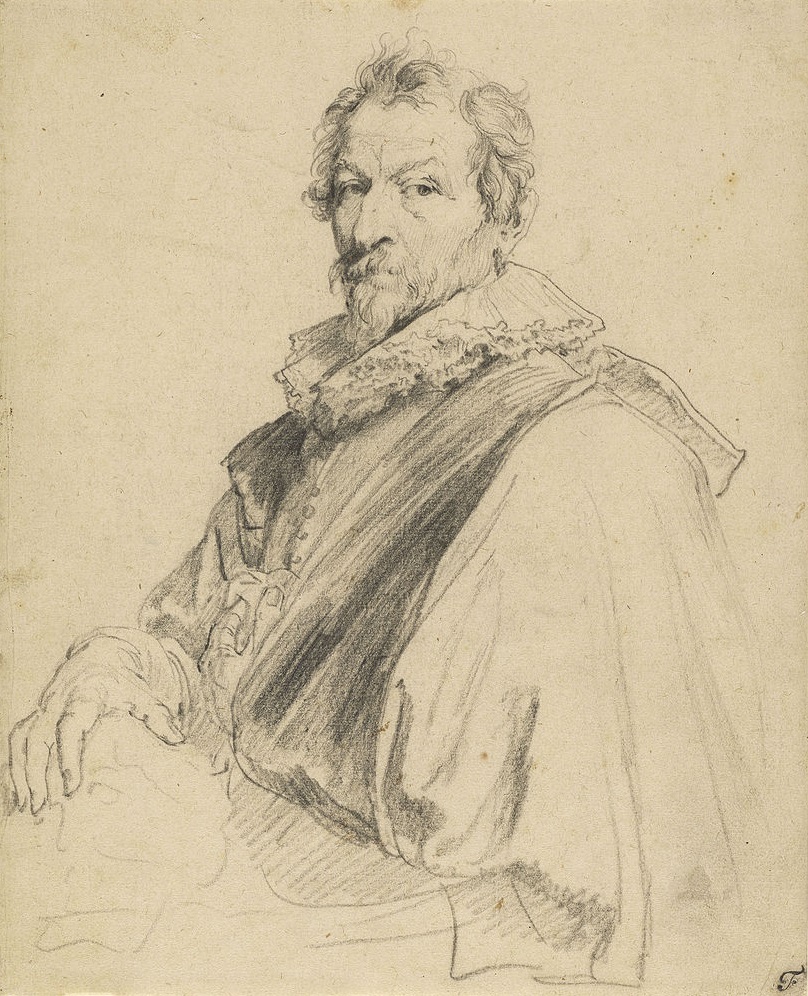

Hendrik van Balen the Elder was a Flemish Baroque painter and stained glass artist, member of the Guild of Saint Luke in Antwerp.
Hendrik van Balen specialized in small cabinet paintings, often painted on copperplate. The artist's work was inspired by mythological and allegorical as well as religious subjects. The artist played an important role in the renewal of Flemish painting at the beginning of the 17th century and was one of Antoni van Dyck's teachers.
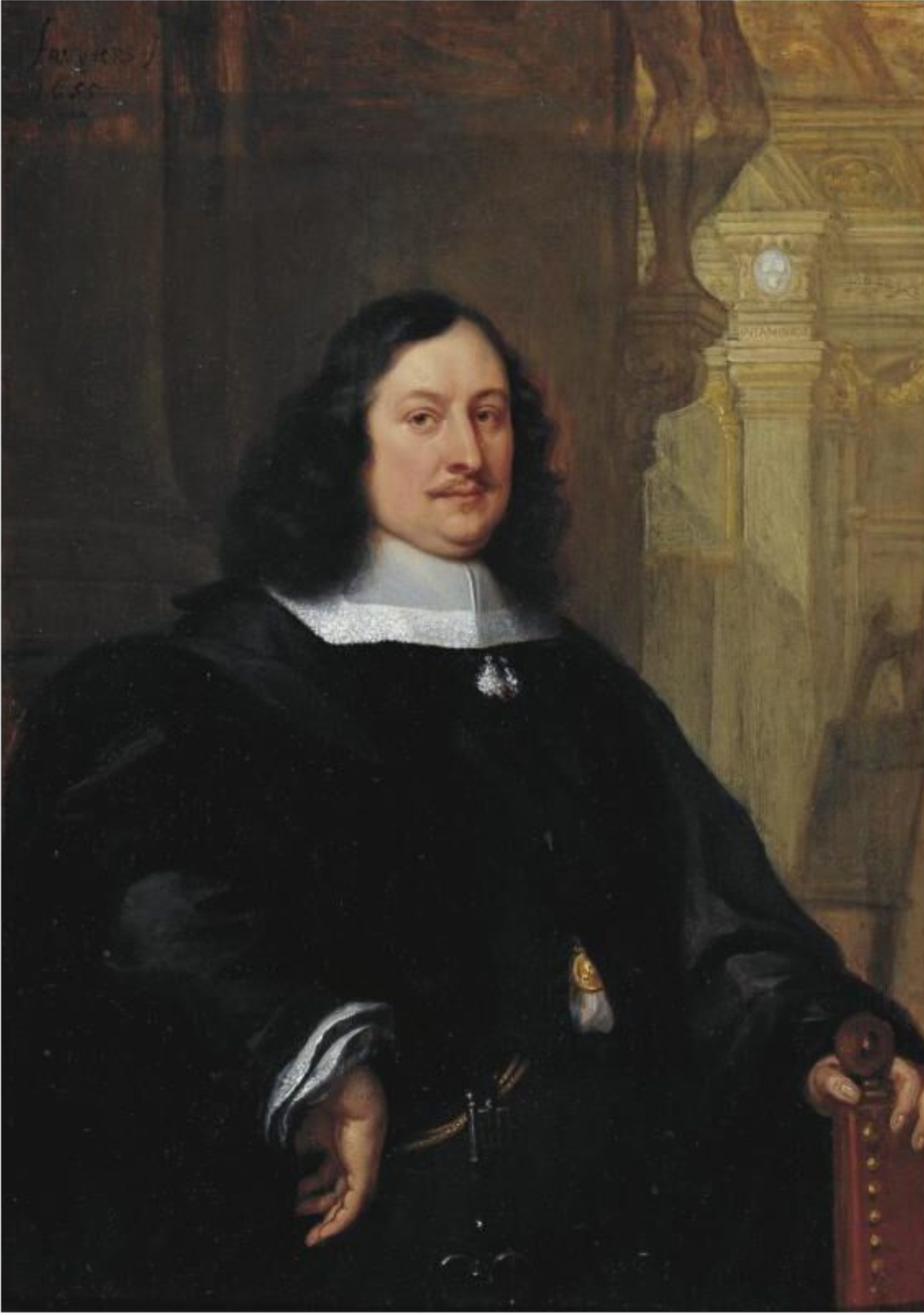

David Teniers the Younger was a Flemish Baroque painter, printmaker, draughtsman, miniaturist painter, staffage painter, copyist and art curator. He was an extremely versatile artist known for his prolific output. He was an innovator in a wide range of genres such as history painting, genre painting, landscape painting, portrait and still life. He is now best remembered as the leading Flemish genre painter of his day. Teniers is particularly known for developing the peasant genre, the tavern scene, pictures of collections and scenes with alchemists and physicians.
He was court painter and the curator of the collection of Archduke Leopold Wilhelm, the art-loving Governor General of the Habsburg Netherlands. He created a printed catalogue of the collections of the Archduke. He was the founder of the Antwerp Academy, where young artists were trained to draw and sculpt in the hope of reviving Flemish art after its decline following the death of the leading Flemish artists Rubens and Anthony van Dyck in the early 1640s. He influenced the next generation of Northern genre painters as well as French Rococo painters such as Antoine Watteau.
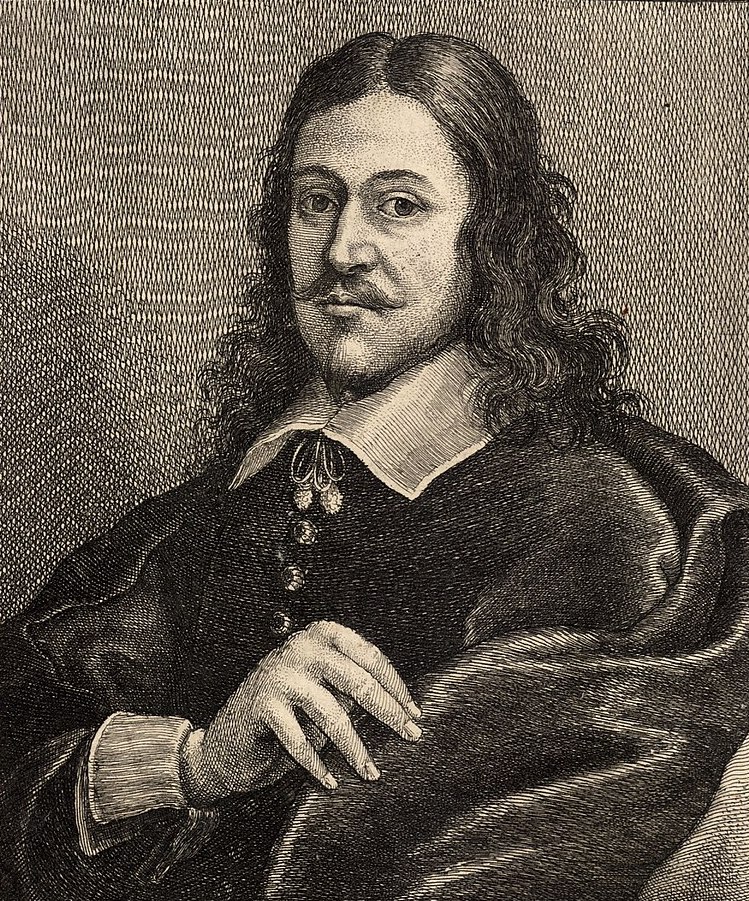

Bonaventura Peeters the Elder was a prominent Flemish painter, draughtsman, and etcher specializing in marine art during the 17th century. His extensive body of work encompassed marine battles, storms at sea, shipwrecks, and views of ships in rivers and harbours.
Peeters displayed a keen understanding of ships, capturing their intricate details. His earlier works exhibited tonal landscapes influenced by Dutch painting, while later pieces reflected vibrant colors inspired by Italian classicism. He skillfully depicted dramatic shipwrecks, serene ports, and intricate portrayals of ships. Many of his paintings depicted actual locations along the North Sea and the river Scheldt, while others showcased imagined scenes of far-away Mediterranean and Middle Eastern ports. Peeters also collaborated with family members and fellow artists, and his drawings and engravings were included in notable publications like Blaeu's Atlas Maior.
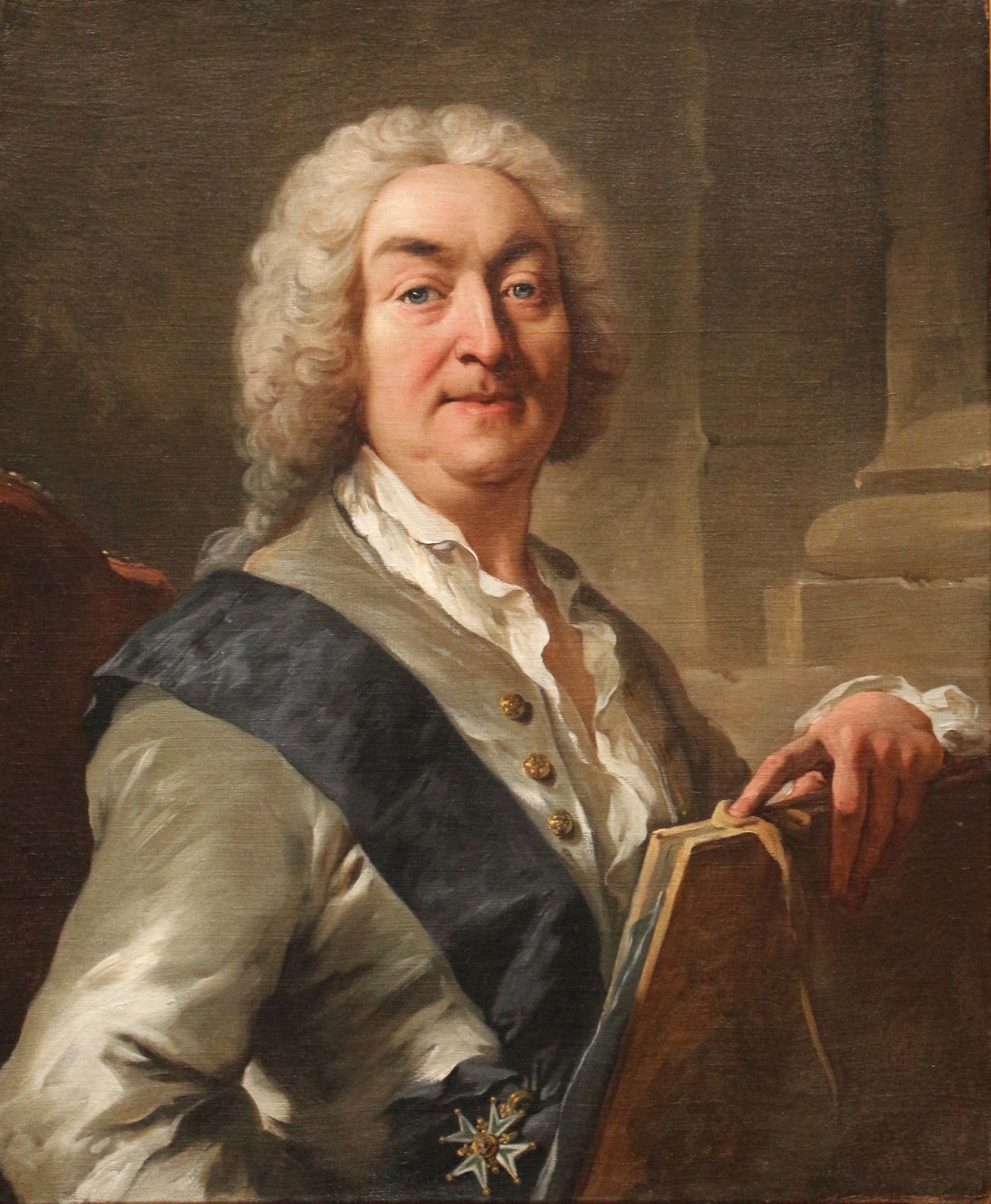

Jean-François de Troy was a French Rococo easel and fresco painter, draughtsman and tapestry designer. One of France's leading history painters in his time, he was equally successful with his decorative paintings, genre scenes and portraits. He was the inventor of the tableaux de modes ('paintings of fashions'), which attempted to provide a spirited portrayal of contemporary fashions, pastimes and manners.
He was the Director of the French Academy in Rome from 1738.
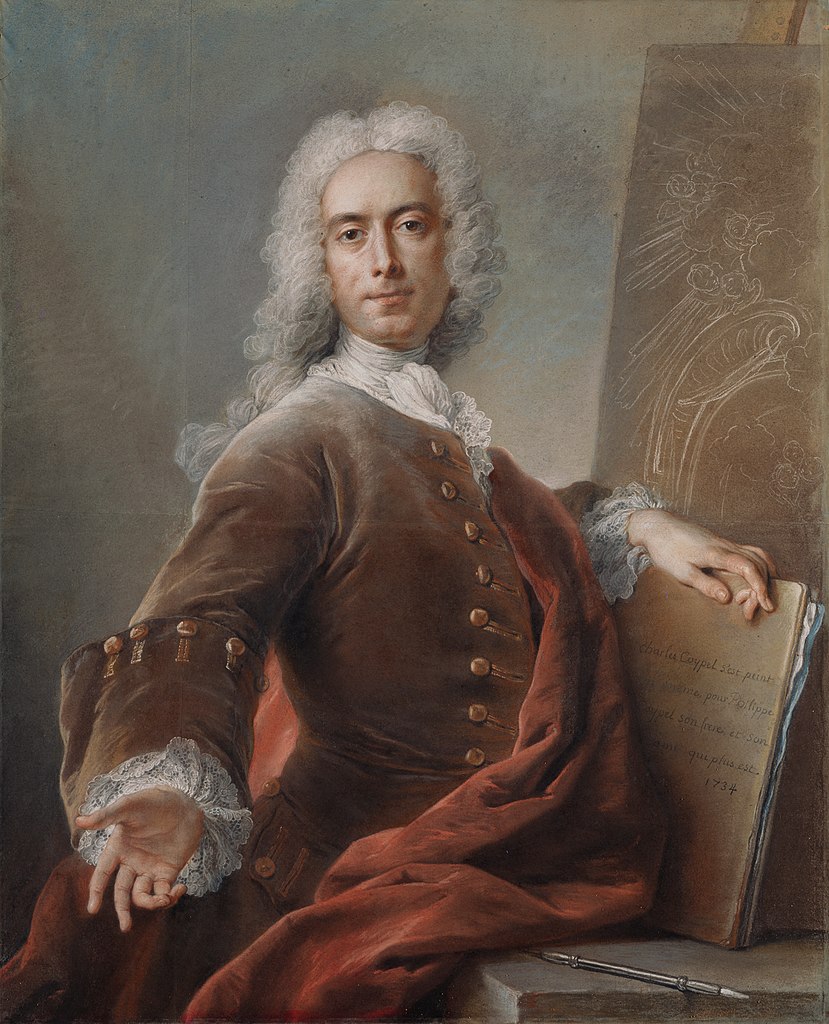

Charles-Antoine Coypel was a multifaceted French Rococo artist, known for his contributions as a painter, designer, playwright, and art critic. Born into a family with a significant artistic legacy, Coypel rose to prominence in the French court, eventually serving as the court painter and the director of the Académie Royale. His work, which often blended dramatic narrative with intricate detail, played a pivotal role in the development of Rococo art in France, reflecting the opulent and expressive tendencies of the period.
Coypel's artistic output includes a range of subjects, from religious themes, as seen in his etching "The Virgin and Child," to theatrical history paintings that convey operatic passions and high drama. His ability to infuse his compositions with emotional depth and narrative complexity, alongside his mastery of the Rococo style's playful and ornamental characteristics, distinguishes his work within the era. Notably, Coypel was also involved in the design of tapestries for the Gobelins Manufactory, illustrating scenes from Miguel de Cervantes's "Don Quixote," which remained influential through the end of the 18th century.
His artworks, such as "The Virgin and Child," showcase not only his technical skill but also his sensitivity to composition and form, contributing to his reputation as one of the leading painters in the French court during the 18th century. Coypel's legacy is preserved in his paintings, etchings, and tapestry designs, which continue to be celebrated for their artistic and historical significance.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Charles-Antoine Coypel's work represents an essential connection to the Rococo period's rich cultural and aesthetic traditions. His contributions to French art history, particularly through his role at the Académie Royale and his influence on the development of Rococo style, make his work a valuable study for those interested in the dynamics of French art and culture during the 18th century.
To stay informed about updates related to Charles-Antoine Coypel, including new discoveries, sales, and auction events of his works, consider signing up for updates. This service will provide tailored notifications to enthusiasts and collectors eager to explore and acquire pieces by Coypel, ensuring they remain at the forefront of developments in the field of Rococo art.

Charles-Antoine Coypel was a multifaceted French Rococo artist, known for his contributions as a painter, designer, playwright, and art critic. Born into a family with a significant artistic legacy, Coypel rose to prominence in the French court, eventually serving as the court painter and the director of the Académie Royale. His work, which often blended dramatic narrative with intricate detail, played a pivotal role in the development of Rococo art in France, reflecting the opulent and expressive tendencies of the period.
Coypel's artistic output includes a range of subjects, from religious themes, as seen in his etching "The Virgin and Child," to theatrical history paintings that convey operatic passions and high drama. His ability to infuse his compositions with emotional depth and narrative complexity, alongside his mastery of the Rococo style's playful and ornamental characteristics, distinguishes his work within the era. Notably, Coypel was also involved in the design of tapestries for the Gobelins Manufactory, illustrating scenes from Miguel de Cervantes's "Don Quixote," which remained influential through the end of the 18th century.
His artworks, such as "The Virgin and Child," showcase not only his technical skill but also his sensitivity to composition and form, contributing to his reputation as one of the leading painters in the French court during the 18th century. Coypel's legacy is preserved in his paintings, etchings, and tapestry designs, which continue to be celebrated for their artistic and historical significance.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Charles-Antoine Coypel's work represents an essential connection to the Rococo period's rich cultural and aesthetic traditions. His contributions to French art history, particularly through his role at the Académie Royale and his influence on the development of Rococo style, make his work a valuable study for those interested in the dynamics of French art and culture during the 18th century.
To stay informed about updates related to Charles-Antoine Coypel, including new discoveries, sales, and auction events of his works, consider signing up for updates. This service will provide tailored notifications to enthusiasts and collectors eager to explore and acquire pieces by Coypel, ensuring they remain at the forefront of developments in the field of Rococo art.