poison book
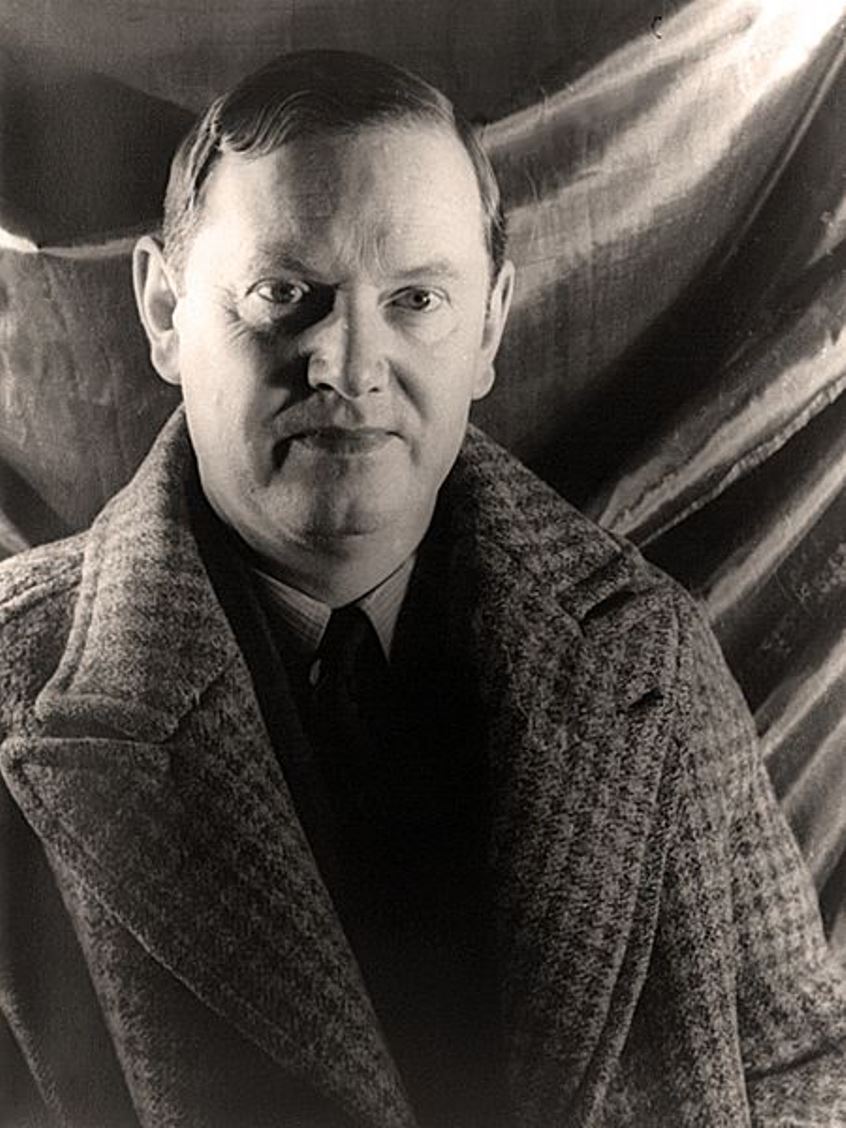





Evelyn Waugh, full name Arthur Evelyn St. John Waugh, was a British satirical writer, travel writer and historian.
Evelyn Waugh studied at Lancing College in Sussex and at Hertford College in Oxford. He then began traveling and writing, soon earning a reputation as a witty satirist. He visited Ethiopia and the Belgian Congo, and traveled to South America. His works are almost always based on personal experience; notable among the early ones are Decline and Fall (1928), Nasty Bodies (1930), Black Mischief (1932), and others.
During World War II, Evelyn Waugh served in the Royal Marines and the Royal Horse Guards. Written at this time, the novel "Return to Brideshead" (1945) is about an aristocratic English Roman Catholic family. In the trilogy "Men in Arms" (1952), "Officers and Gentlemen" (1955) and "Unconditional Surrender" (1961), the author conducted a serious analysis of the events of World War II, as an eternal struggle between good and evil, civilization and barbarism. Later on these works were filmed television series.
Evelyn Waugh also left a significant trace in journalism and literary criticism, he is considered one of the finest stylists in English prose of the XX century.
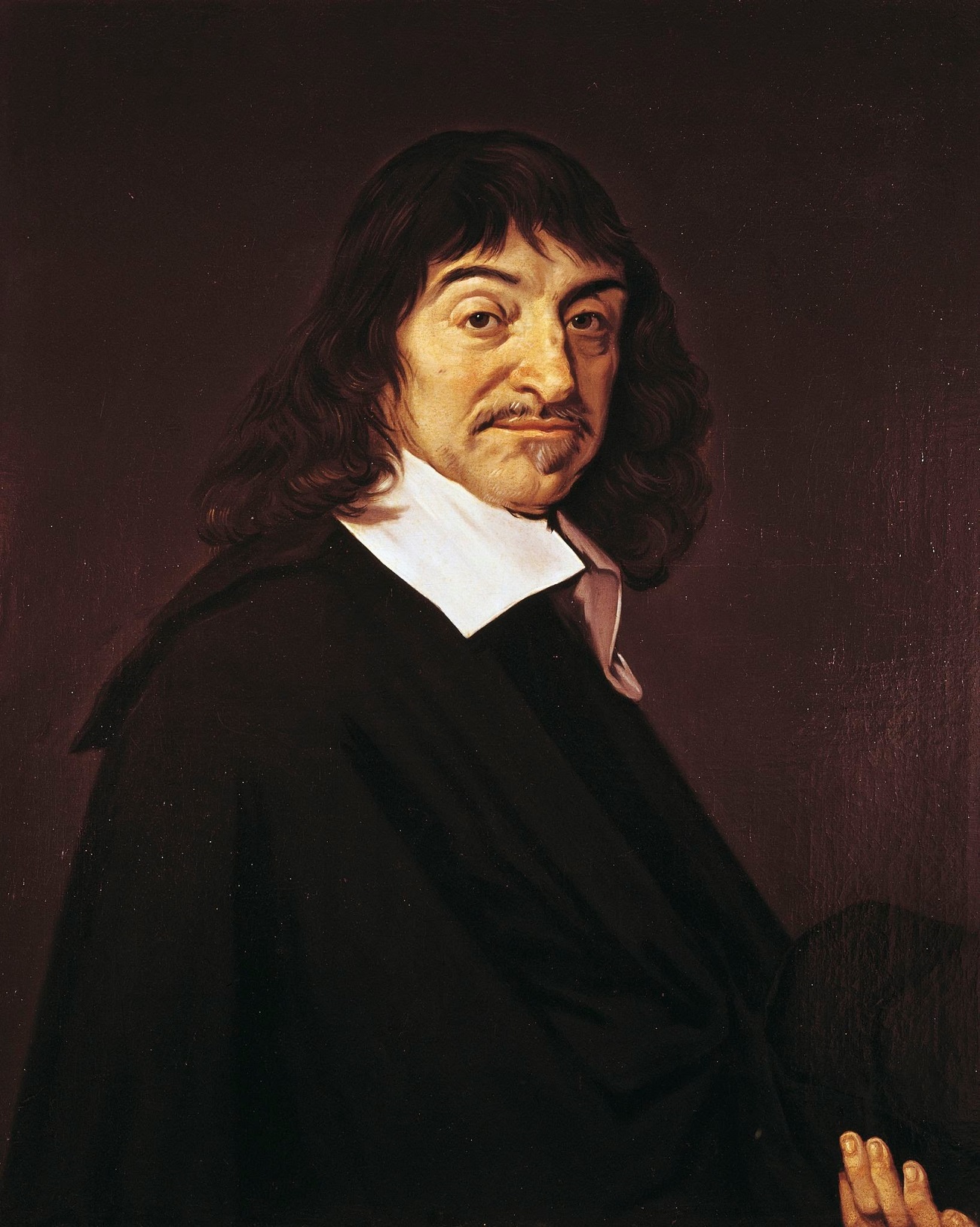


René Descartes was a French philosopher, mathematician, and natural scientist who is considered the founder of modern philosophy.
Descartes was a very versatile scientist: besides numerous philosophical reflections, he wrote works on optics, meteorology and geometry. Contemporaries noted his extensive knowledge in many sciences. Descartes owns the famous saying "I think, therefore I exist" (best known in the Latin formulation "Cogito, ergo sum", although it was originally written in French: "Je pense, donc je suis").
He developed a metaphysical dualism that radically distinguished between mind, whose essence is thought, and matter, whose essence is extension in three dimensions. Descartes' metaphysics is rationalistic, based on the postulation of innate ideas of mind, matter, and God, but his physics and physiology, based on sense experience, are mechanistic and empirical.
Unlike his scientific predecessors, who felt a holy awe at the incomprehensibility of the divine essence of the universe, Descartes admired the ability of the human mind to understand the cosmos and to generate happiness itself, and rejected the view that human beings were inherently unhappy and sinful. He believed that it was inappropriate to pray to God to change the state of things and the world; it was much more productive to change oneself.






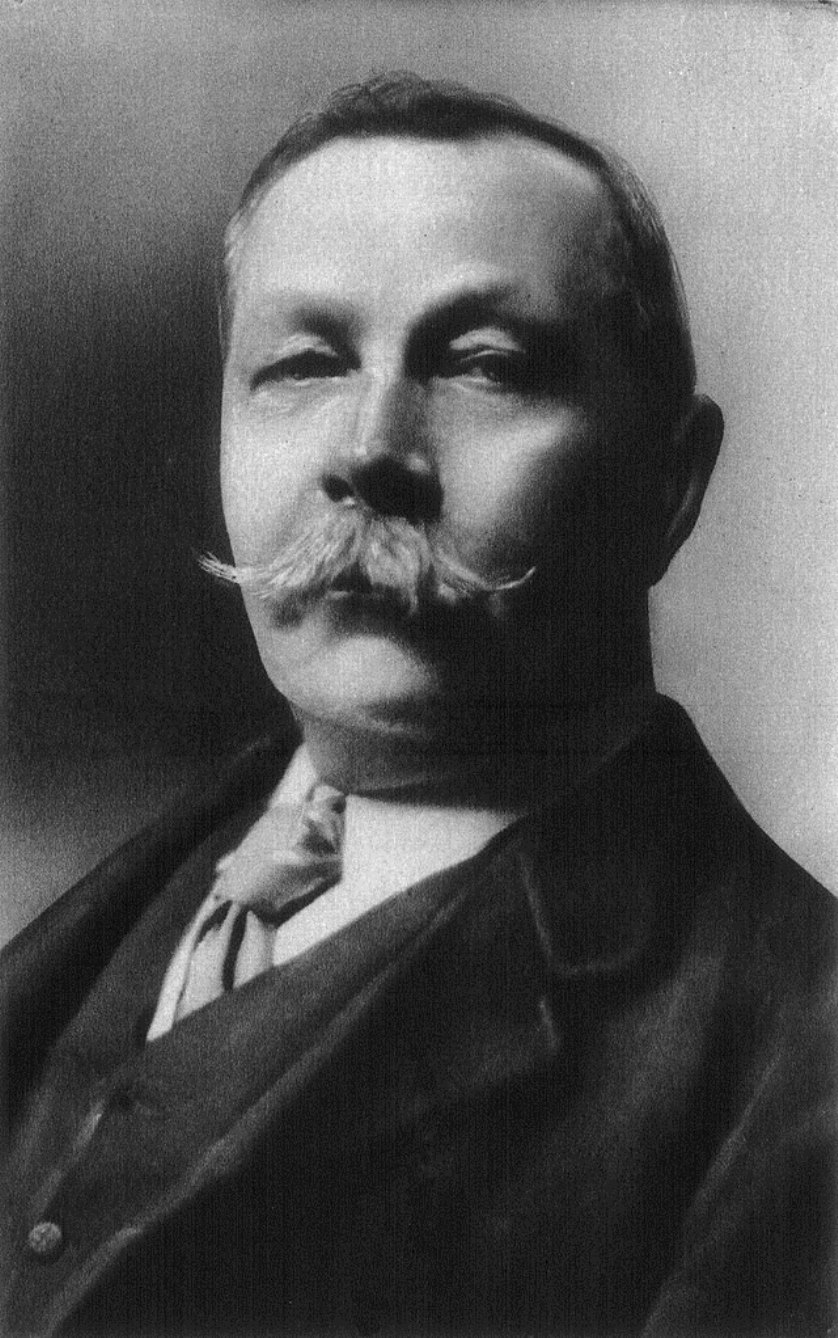




























![[AUDOT, Louis-Eustache (1783-1870)].](/assets/image/picture_2734934/e5375/fa73b47efe2f2b9b381423fcba0b52581679526000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[AUDOT, Louis-Eustache (1783-1870)].](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_2734934/e5375/fa73b47efe2f2b9b381423fcba0b52581679526000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
















![[DESCARTES, René (1596-1650)]](/assets/image/picture_2500811/a67fb/9ee6c1d6009ac0da55c5104d2c2f17ad1667984400jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[DESCARTES, René (1596-1650)]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_2500811/a67fb/9ee6c1d6009ac0da55c5104d2c2f17ad1667984400jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)




















