Cartographers 18th century


William Baillie was a British artist who lived and worked in India in the late 18th century.
He went to India in 1777 as a cadet in the Bengal Infantry and remained there for the rest of his life. After retiring, he published a newspaper in Calcutta, painted landscapes with views of the city and surrounding countryside, made engravings, and made topographical maps. In 1794, William Baillie published a set of hand-colored aquatints entitled Twelve Views of Calcutta.


Joachim Bouvet was a French Jesuit monk and missionary who worked in China.
Joachim Bouvet was one of six Jesuit mathematicians chosen by Louis XIV to travel to China as his envoys and work as missionaries and scholars. In 1687 in Beijing, Bouvet began this work, especially in mathematics and astronomy, and in 1697 the Chinese emperor Kangxi (1654-1722) sent him as ambassador to the French king. Kangxi expressed his wish that Bouvet should bring more missionary scientists with him. Thus, in addition to his scholarly work, Bouvet was also an accomplished diplomat and served as a liaison between the Chinese Emperor Kangxi and King Louis XIV of France.
Bouvet brought to France a manuscript describing Kangxi's life with an eye for diplomatic subtleties, as well as a collection of drawings depicting graceful Chinese figures in traditional and ceremonial dress. The first French edition of The Historical Portrait of the Emperor of China was published in Paris in 1697, and was subsequently translated and published in other languages. And Bouvet returned to China in 1699 with ten new missionaries and a collection of King Louis XIV's engravings for Emperor Kangxi. He remained in China for the rest of his life.
Juan de la Cruz Cano y Olmedilla was a Spanish artist, engraver, and cartographer of the Enlightenment.
Using the most accurate cartographic calculations and methods in the 18th century, he created many geographic maps of Africa and South America, the Strait of Magellan, and others. While in the service of King Carlos III of Spain for many years, Olmedilla mapped Spain and Spanish possessions in Latin America.
Olmedilla also created a multi-volume work devoted to Spanish costume. This collection recorded the various outfits worn by Spaniards, both common and noble, covering all regions of the country and all of its colonies. The topographical and architectural details included in the plates provide additional insight into the mores and geographical features of the various cities and towns depicted. The work was first published in Madrid between 1777 and 1788. These engravings proved incredibly popular and were reprinted in both France and Germany.



Justus Danckerts I was a Dutch engraver and print publisher who along with other members of the Danckerts family created one of the leading Dutch geographical map and atlas publishing houses. Justus Danckerts was the son of Cornelis Danckerts I (1603-1656), who established the Danckerts cartographic family business in Amsterdam. After producing in the early 1680s over 20 folio-sized atlas maps, he published in 1686-1887 the first Danckerts atlas. In 1690, another 26-sheet geographical atlas was published; between 1698 and 1700, a 60-sheet atlas was completed. Its map sheets and plates were used by various publishers until the middle of the 18th century.
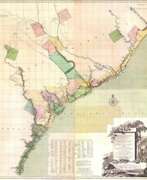

Johann Wilhelm Gerhard von Brahm, also known as John William Gerard de Brahm, was a German cartographer, military engineer, and surveyor who worked for Great Britain to develop the lands of the New World.
His father was court musician to the Elector of Trier and gave his son an excellent early education. After a successful career as a military engineer in the Bavarian army, de Brahm traveled to Georgia in 1751 at the head of a group of German emigrants. There he displayed his talents as a surveyor and engineer, worked as a cartographer, and was commissioned by South Carolina Governor James Glen to design and build a system of fortifications for Charleston.
In 1755 de Brahm was appointed inspector general of lands for South Carolina and soon for the entire New World. He settled in St. Augustine, where he spent the next six years researching and preparing maps. His major works, "Map of South Carolina" and "Map of South Carolina and Part of Georgia," provide detailed topography and even describe underwater features. And his "Report of a General Survey of the Southern District of North America" records every detail from tide times to tips on tilling the soil. De Brahm's book The Atlantic Pilot, an instruction manual for sailing in Florida, was published in London and included the first published map of the Gulf Stream.
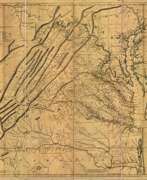
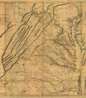
Joshua Fry was a British and American politician and planter, surveyor and cartographer.
Educated at Oxford University, Fry emigrated to the colony of Virginia around 1726. He soon founded a grammar school for the sons of the local gentry, then headed the mathematics department of the college, and worked as a professor of philosophy. Through a successful marriage, he became a large landowner and gained prominence, serving as a member of the House of Burgesses and justice of the peace in Essex County and later in Albemarle.
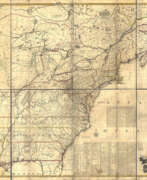
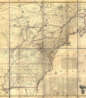
When Albemarle County was established in Virginia in 1745, Joshua Fry was appointed here as chief surveyor in charge of land surveying. Beginning in 1746, Fry was assisted throughout his work by his close friend Peter Jefferson, father of future U.S. President Thomas Jefferson. Together they not only explored new lands, but also created maps that documented the new territories with great accuracy. Their main project was the so-called Frye-Jefferson map, published in 1751, depicting Virginia and Maryland.
This map was unique for its time because it was based on actual geodetic data. The map showed the "Great Road from the Yadkin River through Virginia to Philadelphia 455 miles."
At the outbreak of the Seven Years' War, Joshua Fry was appointed head of the Virginia Regiment and died of his injuries in the campaign on May 31, 1754.


John Gantz was an Austrian-born architect, painter, surveyor and lithographer.
Gantz worked for the East India Company from about 1800 to 1803 as a draftsman and architect. A manuscript list of Madras residents dated March 1819 lists him as "Architect, originally from India". By 1827, Gantz had installed the first lithographic printing press in Madras, one of the first such printing presses in India. Gantz's drawings depict the bridges and architectural structures of the city, the inhabitants in their daily activities, modes of transportation, crafts and professions of Indians, he also painted picturesque landscapes of India.
Gantz had two sons, architect Justinian and Julius.


Samuel Johannes Holland was a Dutch-born British military engineer, surveyor and cartographer, and the first Inspector General of British North America.
He began his military career in 1745 in the Dutch artillery, moving to England in 1754 and becoming a lieutenant in the Royal American Army. In early 1756 Holland traveled with the British army to North America, where he created the first maps of New York State, worked as a military engineer, surveyed Louisbourg, Halifax, and Fort Fredericton, and participated in the siege of Quebec in 1759.
In 1764 Holland was appointed inspector general of the Northern District of North America and was appointed to the Quebec Council. From 1764 to 1767, he surveyed Prince Edward Island, the Madeleine Islands, and Cape Breton. He then mapped the northeast coast for the British army and helped negotiate provincial and state boundaries in the northeast. In 1779, Samuel Holland was appointed a member of the Legislative Council of Quebec and continued to serve as Inspector General for the rest of his life.


Johann Baptist Homann was a German geographer and cartographer, who also made maps of the Americas. In 1702 he founded his own publishing house. Homann acquired renown as a leading German cartographer, and in 1715 was appointed Imperial Geographer by Emperor Charles VI. In the same year he was also named a member of the Prussian Academy of Sciences in Berlin. In 1716 Homann published his masterpiece Grosser Atlas ueber die ganze Welt (Grand Atlas of all the World). Numerous maps were drawn up in cooperation with the engraver Christoph Weigel the Elder, who also published Siebmachers Wappenbuch.
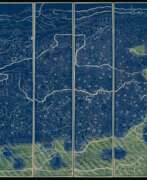

Qianren Huang was a Chinese cartographer and clerk who worked in the 18th century during the reign of the Qianlong Emperor.
His grandfather, Huang Zongxi (1610-1695), was a famous Qing Chinese polymath, Confucian scholar, cartographer, and father of the Chinese Enlightenment.
Qianren Huang is known for his 1767 revision of the map created by his grandfather Huang Zongxi, the so-called famous "Blue Map" of the world. Continuing the family tradition of outstanding scientific achievements, his grandson pointed out the addition of new territories such as Tibet and Xinjiang on the updated map, emphasizing the continuous strengthening of the Chinese state.


Peter Jefferson was an American cartographer and surveyor, father of the third President of the United States, Thomas Jefferson.
Peter Jefferson was the son of a large landowner in Virginia, and served as sheriff, surveyor, and justice of the peace. He was also a cartographer and surveyor. Along with Colonel and County Surveyor Joshua Fry, he spent several years exploring new lands. In 1750, Lewis Burwell, acting governor of Virginia, commissioned Frye and Jefferson to map the colony, which was done.
This map of early America was based on Frye and Jefferson's meticulous research and accurately delineated the boundaries, roads, settlements, and trails of the original inhabitants. It also included significant new geographic information reported by early wilderness travelers, including George Washington, Christopher Gist, and John Dalrymple. The map was completed in 1751 and engraved and published a few years later. Afterward, Jefferson worked on numerous surveying projects throughout Virginia.
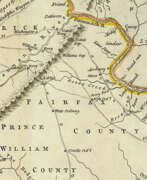
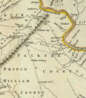
Thomas Jefferys was an 18th-century British cartographer and geographer, engraver and publisher.
As the best in the business of map-making, Jefferys held the honorary title of "King George III's geographer". He is known for his detailed and large-scale maps of the districts and counties of Great Britain as well as North America, particularly Virginia (1776). He was the leading map supplier of his day, engraving and printing maps for government and other official bodies.



John Montresor was a British military engineer and cartographer who worked in North America.
His father was a military engineer and his youth was spent in British Gibraltar. Montresor studied in London, and in 1754 accompanied his father to North America when he was appointed chief engineer to Major General Edward Braddock's troops. John participated in various expeditions, delivered dispatches, and witnessed the sieges of Louisbourg and Quebec. During his service, he also did the necessary research and prepared maps of Acadia, the St. Lawrence River, and his route along the Kennebec River.
One of John Montresor's major accomplishments is the strategic map of the Hudson River, one of the most detailed maps of the New York City area during the American Revolution, first published in 1775. The map extends from Lake Champlain down the Hudson to Long Island, with insets of Lake Champlain and the White Hills in the upper Connecticut Valley.
John Montresor was promoted to captain in 1776, returned to England in 1779, and retired from the army. He died in prison 20 years later, accused of excessive spending while in the service.
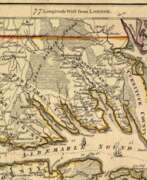
William Henry Mouzon, Jr. was an American cartographer and civil engineer.
Henry Mouzon, Jr. was the grandson of a Huguenot immigrant and was sent to France at the age of eight, where he was trained as a civil engineer and surveyor. In 1771 he and Ephraim Mitchell were sent to survey the boundaries of South Carolina. As a result, a map was created and published in 1775 that included both North and South Carolina with corrections to previous maps.
This map was entitled "An Accurate Map of North and South Carolina with their Indian Boundaries," and clearly showed all the mountains, rivers, swamps, marshes, bogs, bays, creeks, harbors, sandbanks and shoals on the coasts, and gave the names of the land owners. American, British, and French troops used this map during the American Revolution. A copy of this map, owned by George Washington, is now in the library of the American Geographical Society.


Reinier & Joshua Ottens was a Dutch printing publishing partnership of two brothers.
The publishing house was founded in 1726 in Amsterdam by brothers Reinier Ottens (1698-1750) and Joshua Ottens (1704-1765). After the death of Reinier I, his son Reinier II continued the business until 1765. Much of the activity of this business consisted of reissuing old plates.
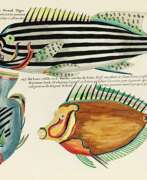

Louis Renard was a Dutch painter, printmaker and book publisher born in France.
Renard published map atlases and illustrated works of natural history popular in 18th-century Europe. In Amsterdam he acquired many cartographic plates by Frederick de Wit, which he combined with minor updates and corrections into an Atlas of Navigation and Commerce and published in 1715. He later sold the plates to R. & J. Ottens, who republished it in 1745.
In 1718 -1719 Renard published the first edition of his most famous multi-volume work, Poissons, écrevisses et crabes... que l'on trouve autour des Isles Moluques, et sur les cotes des Terres Australes ("Fish, crayfish and crabs, of varied colors and unusual forms, which are found around the Moluccas Islands and on the coasts of the southern lands."). This book was the world's first encyclopedia of fish illustrated in color. While working on it, Renard copied drawings by other artists, notably the talented Dutch artist Samuel Fallors. The result was 460 hand-colored copperplate prints.
The creatures in Renard's book are so fanciful that they may seem fictional, but only about 10 percent are, including the depiction of a mermaid. Most likely, these fantasies were included for the sake of attracting buyers. The work is now believed to be an important part of eighteenth-century scientific literature.

John Ross was an American military cartographer and surveyor.
Lieutenant John Ross served as a surveyor in the 34th Regiment of the British Army. After the Treaty of Paris in 1763, a British expedition was sent into Illinois Territory to demand the surrender of Fort de Chartres, the last outpost under French control in the area. John Ross traveled with this expedition, surveyed the lower river to the mouth of the Mississippi River, and created a unique map. It was titled "The Course of the Mississippi River from Balise to Fort Chartres; taken on an Expedition to Illinois" and published in London in 1775.
Lieutenant Ross's large-scale map of the Mississippi River is one of the few large format maps of the Mississippi published in the 18th century. Ross's map was the first official English survey of the Lower Mississippi and one of the most historically significant American maps. It delineated British territorial acquisitions after the French and Indian War and then established the future western boundary of the new United States. The map opened the territory to settlement from the east and defined the western boundaries of the American colonies.


Paul Sandby was a British watercolorist, draughtsman and printmaker, and a founder member of the Royal Academy.
Sandby first worked as a draughtsman and cartographer before painting his first paintings, watercolors of bridges, fortifications and Scottish landscapes, as well as views of Windsor. These works eventually made him a sought-after artist. Sandby also painted many caricatures and skillfully documented eighteenth-century British social life.
In 1768, Sandby, his brother Thomas Sandby and 27 other artists became founding members of the Royal Academy in London. He is now considered one of the founders of English watercolor.


Johann Carl Schleich the Elder was a German engraver. On the basis of paintings he created engraving portraits of famous contemporaries, made topographical works. His son, Johann Carl Schleich the Younger, was also an engraver.


William Scull was an American cartographer and officer during the War of Independence.
William Scull was an officer during the Revolutionary War and then lived in Philadelphia and worked as a cartographer. He was the grandson of the famous Nicholas Scull, who served as Surveyor General of Pennsylvania during the colonial era. William Scull, fulfilling a commission from Penn Brothers landowners, created the famous map of Pennsylvania with southern boundaries showing Philadelphia, Bucks, Northampton, Berks, Chester, Lancaster, Cumberland, and York counties. William based his work on a map created by his grandfather and supplemented and expanded it with his own 1769 surveys.
As a result, Scull's 1770 map is among the largest and finest maps produced in America in the eighteenth century. It was published and reprinted many times in England and France; it was often included in composite atlases containing related maps. William Scull served in the Geographical Department of the Continental Army and was also a member of the American Philosophical Society.


Jan Christiaan Sepp was a Dutch book publisher, printmaker and illustrator.
Jan Christiaan Sepp belonged to a dynasty of collectors, publishers and traders in printed books founded by his father, Christian Sepp (c. 1700-1775) in Goslar, Germany. Jan Christian Sepp is known for being the chief illustrator, creating the magnificent engravings for Cornelius Nozeman's highly prized work entitled Nederlandsche Vogelen (Birds of the Netherlands, 1770-1829). These copperplate engravings, superbly composed, meticulously engraved and hand-colored are of great value.
After Christian Sepp's death, the work of illustrating the five volumes was completed by his son, Jan Sepp. Each volume of this five-volume work of science and art contains 50 images of bird species, and each species is described on several pages.

Antonio Zatta was an Italian cartographer and publisher who was based in Venice. He may have lived from 1722 to 1804. One of his major contributions include the Atlante Novissimo, a four volume atlas of the world. He also published an edition of the plays of Goldoni with engravings in 1789.