Educators Romanticism


Hendrikus van de Sande Bakhuyzen was a Dutch landscape painter and teacher.
Bakhuyzen studied at The Hague Academy of Art. He is known for his romantic pastoral scenes, especially paintings of livestock, with detailed landscapes.
In 1822 he became a member of the Royal Academy of Arts in Amsterdam and a member of the board of the Academy of Arts in The Hague. He was later elected director of the Hague Academy. Hendrikus Bakhuyzen made a significant contribution to the Romantic period in Dutch art through his work and activities, raising many talented students and followers who founded the artistic movement known as the Hague School.
His children were also very talented: son Julius van de Sande Bakhuyzen (1835-1925) became a renowned landscape painter; daughter Gerardine Jacob van de Sande Bakhuyzen (1826-1895) became a still life painter; son Henrik Gerard van de Sande Bakhuyzen (1838-1923) became a prominent astronomer, member of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences and director of the Leiden Observatory; son Ernest-Fredrich van de Sande Bakhuyzen was also an astronomer at the Leiden Observatory.


Sabine Baring-Gould was a Victorian British clergyman, poet, writer and folklorist.
He traveled extensively in Europe, studied at Clare College, Cambridge, was ordained in the Church of England in 1864, and was appointed vicar at Horbury. Baring-Gould was a polyglot and knew six languages. Despite his ministry, he had a serious interest in supernatural phenomena and in 1865 published a book called The Book of Werewolves.
In addition to this, Baring-Gould was interested in a wide range of subjects. His work is diverse and covered theology, history, poetry, hymns, fiction, biography, travel, social commentary, and folklore. Baring-Gould collected the folk songs of old English singers, personally visiting them and recording the words and music. In 1889 he published a collection of Songs of the West in four parts, of which he was proud, and also wrote several patriotic hymns.
Baring-Gould was a very prolific writer: during his life he wrote many novels, published short stories in periodicals, the popular "Curious Myths of the Middle Ages," and others, his bibliography numbering some 1,250 works.


Harriet Beecher Stowe, full name Harriet Elisabeth Beecher Stowe, was an American writer and poet, an activist for the eradication of slavery in the country.
Beecher Stowe is the author of the world-famous novel Uncle Tom's Cabin. Published first in a newspaper and first published as a book in 1852, it aroused widespread anger in the country and galvanized the fight against slavery in the southern United States. This novel was later reprinted many times in all languages of the world and has been screened more than once.
In her youth, Beecher Stowe received an academic education, wrote poetry, notes and essays on social topics. In addition to "The Shack", she wrote several other novels and was engaged in teaching.


Bernardo Blanco y Pérez was a Spanish lithographer, painter and illustrator.
He studied at the Royal Academy of San Fernando, mainly drawing and lithography, and taught. Bernardo Blanco was one of the artists whose work was included in a series of lithographs on the Spanish-Moroccan War (1859-1860).


Johann Christian Brand was an Austrian landscape painter and graphic artist, copperplate etcher.
He received his first lessons in painting from his father, the landscape painter Christian Hilfgott Brand (1695-1750), then studied at the Vienna Academy of Painting. In 1758 Brand was commissioned by the imperial family for a series of hunting scenes. In addition to many landscapes, he also created 16 oil paintings for Vienna's Museum of Military History, depicting various types of cavalry of the Austrian army during the reign of Empress Maria Theresa.
From 1772 Brand was professor of painting at the Vienna Academy.


Max Bruch, full name Max Christian Friedrich Bruch, was a German composer and conductor, violinist and teacher of the late Romantic period.
Bruch studied with the composer and pianist Ferdinand Hiller (1853-1857), wrote a symphony at age 14, and won a scholarship that allowed him to study in Cologne. His first opera, Joke, Deceit and Revenge, was performed in 1858. He conducted orchestral and choral societies in Germany, England and Poland, and from 1890 to 1911 he was a professor at the Berlin Academy of Arts.
Bruch was an ambitious and prolific composer. His greatest success during his lifetime was his huge works for chorus and orchestra, Beautiful Ellen (1867) and Odysseus (1872). He was also the author of string concertos and pieces for violin and orchestra. His Violin Concerto No. 1 in G minor (1866) is one of the most popular Romantic violin concertos.


Anton Bruckner, full name Joseph Anton Bruckner, was an Austrian composer, organist and music educator.
Bruckner was born into a poor family, which prevented him from receiving an education suited to his musical talent. His father taught him to play the violin and organ, and he worked as a teacher and organist for many years. Already after the age of 30, he began composing organ and choral works, including the Solemn Mass (1854). In 1855 he became organist at Linz Cathedral and took a five-year course in harmony and counterpoint with the Viennese teacher Simon Sechter. A little later Bruckner studied orchestration with Otto Kitzler, who in 1863 introduced him to the music of Wagner - a powerful impetus for him to begin composing significant compositions.
After moving to Vienna in 1686, Bruckner taught at the Conservatory and the University of Vienna and composed at the same time. Over the next 28 years he wrote most of his famous works: symphonies Nos. 2-9, a string quintet and the Te Deum. But it was not until the premiere of his Seventh Symphony in Leipzig in 1884 that he received the recognition he deserved. Until his death, he continued to compose new works and rework his earlier works.
Anton Bruckner was an outstanding virtuoso organist and a superb teacher. His symphonies are often considered symbolic of the final phase of Austro-German Romanticism, and he also composed much sacred secular choral music and chamber works.


Petr Ilich Chaikovskii (Russian: Петр Ильич Чайковский) was a great Russian composer, teacher, conductor and music critic.
Petr was born into the family of a mining engineer; later his father became manager of the Alapaev and Nizhnekamsk factories and director of the Technological Institute in St. Petersburg. Already at the age of five Peter began to learn to play the piano and compose. Educated as a lawyer, he was appointed to the Ministry of Justice and retired in 1867.
In 1865, Chaikovskii graduated with honors from the St. Petersburg Conservatory, composing several significant works during his years of study. From 1866-1878, Chaikovskii was a professor at the Moscow Conservatory, translated several musical-theoretical works, and wrote A Guide to the Practical Study of Harmony. In 1868 he made his first appearance in the press as a music critic, and later worked as a music reviewer for the Moscow newspapers Sovremennaya Annals and Russkiye Vedomosti.
Petr Ilich destroyed his first operas - "Voevoda" and "Undina" - apparently dissatisfied with the result, but his next concertos and symphonies, the operas "Oprichnik" (1874) and "Vakula the Blacksmith" (1876) were already quite successful. In 1877 patron of the arts and admirer Nadezhda von Meck arranged for Chaikovskii to receive an annual subsidy of six thousand roubles, thanks to which he devoted his later life to composing, and from 1888 the composer also received an annual pension of three thousand roubles from the Russian Emperor Alexander III.
From the 1880s Chaikovskii became known not only in Russia but also abroad: he gave numerous concerts in European cities, and his music was recognized and loved in the USA.
A man of extraordinary sensitivity, Petr Chaikovskii revealed in music the inner world of man from lyrical intimacy to the deepest tragedy, creating the highest examples of operas, ballets, symphonies and chamber works. During this period he wrote the operas "Eugene Onegin" (1878), "The Maid of Orleans" (1879), "Mazepa" (1883), "Cherevichki" (1885), "Queen of Spades" (1890), "Iolanta" (1891) and others. And also ballets "Swan Lake" (1876), "Sleeping Beauty" (1889), "The Nutcracker" (1892). All of these works are still going with enduring success in all the world's theaters.
His cycle The Seasons and his Sixth Symphony ("Pathetique") are also widely known. Chaikovskii 's six symphonies, the symphony "Manfred" (1885), "Italian Capriccio" (1880), three concerti for piano and orchestra (1875-93), a concerto for violin and orchestra, "Variations on a Rococo Theme for Cello and Orchestra" (1876), a piano trio "In Memory of the Great Artist" (1882), and romances belong to the world's masterpieces.
Chaikovskii died unexpectedly, having contracted cholera during an epidemic in St. Petersburg. In honor of the composer in 1958, one of the most prestigious performing competitions was organized - the International Chaikovskii Competition, which is held in Moscow every four years. The city of Chaikovskii in the Perm Region, streets in many cities in the former Soviet Union, and a crater on Mercury are named in the composer's honor. The Moscow State Conservatory bears Tchaikovsky's name. Petr Chaikovskii is one of the most performed composers all over the world.


Adolf Iosifovich Charlemagne (Russian: Адольф Иосифович Шарлемань) was a renowned Russian painter, born in 1826 in Saint Petersburg. He excelled in historical, genre, and battle scenes, deeply influenced by his artistic lineage—his father was an architect and his grandfather a sculptor. Educated at the Imperial Academy of Arts under Fyodor Bruni and Bogdan Willewalde, Charlemagne's works are celebrated for their historical accuracy and intricate details.
Charlemagne's notable works include "The Capture of Kazan by Ivan the Terrible" and "The Battle of Kulikovo," which vividly capture significant moments in Russian history. His paintings are known for their meticulous attention to detail, dramatic compositions, and ability to convey the emotional intensity of historical events. These masterpieces are housed in prestigious Russian museums, showcasing his contributions to Russian cultural heritage.
Throughout his career, Charlemagne received numerous accolades, including the titles of Academician and Professor at the Imperial Academy of Arts. His dedication to historical accuracy and artistic excellence made him a prominent figure in Russian art.
For collectors and enthusiasts, owning a piece by Adolf Iosifovich Charlemagne means acquiring a significant part of Russian history. To stay updated on new product sales and auction events related to Charlemagne's works, sign up for our updates today.


Lewis Carroll, real name Charles Lutwidge Dodgson, was a British writer and photographer, philosopher and logician, and professor of mathematics.
In 1851 Lewis entered one of the best colleges in Oxford - Christ Church. Showing an extraordinary aptitude for mathematics, soon he was able to give lectures himself, and for the next quarter of a century he was a professor of mathematics at Oxford. In parallel with his studies, the young man began to compose short stories and poems, publishing them under a pseudonym.
And then he wrote the famous "Alice's Adventures in Wonderland" (Alice's Adventures in Wonderland, 1865) and "Alice in Looking-Glass" (Through the Looking-Glass, and What Alice Found There, 1871). These books quickly became popular, they were translated into numerous languages, and then repeatedly screened. The prototype of the main character was four-year-old Alice Liddell, the daughter of the new dean of the college where Carroll taught. Lewis Carroll also wrote "The Knotty Story", a humorous poem "Hunting the Snark", "Mathematical Curiosities", "Sylvia and Bruno" and other books. Carroll himself considered his main work a slightly absurd novel-tale "Sylvia and Bruno" (1889-1893).
Under his real name, the writer-mathematician published scientific works on mathematics and logic, he also owns a number of popular books on entertaining mathematics. Lewis Carroll left Oxford only once - in 1867, visiting Russia as part of a delegation of the Anglican Church on the route St. Petersburg-Moscow-Nizhny Novgorod. This was Carroll's only overseas trip, and he described it in his Diary of a Trip to Russia 1867. Lewis Carroll was also a talented chess player and amateur inventor. Photography was also a big part of the writer's life.


Nikolay Nikanorovich Dubovskoy (Russian: Николай Никанорович Дубовской) was a distinguished Russian landscape painter, renowned for his significant contributions to the "Landscape of Mood" movement alongside Isaac Levitan. Born into a Don Cossack family in Novocherkassk in 1859, Dubovskoy demonstrated artistic talent from an early age, initially encouraged by his uncle A.V. Pyshkin. Despite his father's initial insistence on a military career, Dubovskoy pursued his passion for art, studying under Mikhail Clodt at the Imperial Academy of Arts and later refusing a conventional academic path to instead exhibit with the Imperial Society for the Encouragement of the Arts. His work, "Winter," gained him early recognition when acquired by the Tretyakov Gallery in 1884.
Dubovskoy's legacy includes several masterpieces, such as "After the Rain," a beautiful example of his mature period that demonstrates the influence of French Impressionism, with its open composition and luminous treatment of light. This piece and others underline his mastery in capturing the nuanced interplay of light and atmosphere, resonating with both the Impressionist and Itinerant movements. Unfortunately, the distribution of his works across various museums after his death and the Soviet Union's collapse has made accessing his complete oeuvre challenging, requiring a journey across multiple countries.
Dubovskoy's contributions to Russian landscape painting and his unique ability to evoke mood and atmosphere in his works have cemented his place among the greats of the art world. His paintings, such as "The Calm Evening," praised as a "poem in gold" by critics, demonstrate his exceptional skill in rendering the delicate interplay of light and color. For those interested in exploring the depths of Russian landscape painting, Nikolay Nikanorovich Dubovskoy's works offer a rich and emotive experience, embodying the spirit of an era and the beauty of the Russian landscape.
To stay updated on sales and auction events featuring works by Nikolay Nikanorovich Dubovskoy, sign up for our updates. This subscription will ensure you're informed about new opportunities to appreciate and acquire pieces by this illustrious artist, focusing solely on relevant product sales and auction events.


Edward William Elgar (Sir Edward William Elgar, 1st Baronet) was a British composer of the Romantic period.
The son of an organist, Elgar was a fine violinist, played the bassoon, and worked as a Kapellmeister and church organist. Then in Malvern, Worcestershire, he began composing music himself. He composed several major choral works, notably the oratorio The Light of Life (Lux Christi (1896,), and in 1898-99 he wrote the popular Enigma Variations for orchestra. Another major work followed in 1900, the oratorio The Dream of Gerontius, which is considered his masterpiece.
From 1905 to 1908 Elgar was the first Professor of Music at the University of Birmingham. During World War I, he periodically wrote patriotic works. His marches, introductions, symphonies, and concertos for strings are well known. Elgar's vibrant works contributed to the revival of English music in the 20th century during the transition from late Romanticism.


Yermolai Ivanovich Esakov (Russian: Ермолай Иванович Есаков) was a Russian painter, renowned for his landscape and battle scenes. Born in 1790, Esakov studied at the Imperial Academy of Arts under M. M. Ivanov and graduated in 1809. He gained recognition for his painting "Waterfall in a Mountainous Area," which earned him a gold medal and a position as a pensioner at the Academy.
Esakov worked as a domestic artist for the Stroganov family from 1810 to 1824. During this period, he accompanied Count P. A. Stroganov to Moldova during the Russo-Turkish War, where he painted "Russian Camp near Silistra." This work earned him the title of Academician at the Imperial Academy of Arts.
Esakov's paintings are characterized by their detailed representation of nature and historical events, showcasing his skill in capturing both the serene and the dramatic. His works are housed in various Russian museums, continuing to attract art lovers and collectors.
Stay informed about new product sales and auction events related to Yermolai Ivanovich Esakov by signing up for our updates.


Eleanor Fortescue-Brickdale was a British Pre-Raphaelite painter, illustrator and stained glass artist.
At the age of 17, she enrolled at Crystal Palace School of Art and was later admitted to the Royal Academy of London and she initially worked with illustration. In 1897, Eleanor won a prize for her painting "Spring", which allowed her to begin work on her first large-scale oil painting, "The Pale Color of True Love". The painting was exhibited at the Royal Academy in 1899.
In 1902 Eleanor Fortescue-Brickdale was elected the first female member of the Institute of Oil Painters. She illustrated many books, including Tennyson's Royal Idylls in 1911. She taught at the Byam Shaw School of Art in Kensington. During the First World War, the artist designed posters for government departments and later several commemorative stained glass windows and a memorial in York Cathedral. In 1919 she became a member of the Royal Society of Watercolor Painters.


Jean-Baptiste Fresez was a German painter of French origin.
He began his studies at the Luxembourg School of Drawing and then continued at the Royal Academy in Brussels and obtained Luxembourg citizenship. Fresez worked as an engraver and painter at the Villeroy and Boch porcelain factory in Mettlach on the Saar River, and from 1824 he successfully taught at the Luxembourg Drawing School.
Fresez produced beautiful landscapes and very lively portraits. These are mainly of members of the Grand Ducal family and other well-known local personalities. A collection of 30 lithographs was published based on his landscape drawings, which today are considered very valuable in documentary terms, and each of them has a detailed description. Fresez's landscapes are characterized by their almost photographic depictions of the city of Luxembourg. After the publication of this work, he was elected a member of the Archaeological Society of the Grand Duchy.


Aleksandr Konstantinovich Glazunov (russian: Александр Константинович Глазунов) was a Russian late Romantic composer, conductor and teacher.
Glazunov belonged to a well-known dynasty of book publishers in St. Petersburg and showed musical ability early on. He studied music with Balakirev and Rimsky-Korsakov, wrote his first symphony at the age of sixteen, and was noticed by the patron of the arts Mitrofan Belyaev, who became his admirer and benefactor. Thanks to him, the young Glazunov traveled all over Europe and was introduced in Weimar to Franz Liszt, who promoted the performance of his First Symphony at the congress of the General German Musical Union.
After the death of composer Borodin, Glazunov helped Rimsky-Korsakov finish his opera Prince Igor, and in the late 1890s he was already collaborating with the Imperial Theaters and writing three ballets. In 1899 Glazunov was appointed professor at the St. Petersburg Conservatory, and from the end of 1905 he became its director, retaining this post even after the October Revolution of 1917. Glazunov's personality is characterized by the fact that he spent his director's salary on helping poor students. And in general, during the hungry years of post-revolutionary devastation, he supported students, even if he did not share their musical beliefs - among them the greats Sergei Prokofiev and Dmitri Shostakovich.
In 1922, Aleksandr Glazunov was named People's Artist of the young Soviet republic. In 1928 he traveled to Vienna to take part in the jury of the Schubert Centenary Composition Competition and never returned to the USSR. However, even while living in Europe, he retained his Soviet citizenship. Officially, Glazunov's stay in Paris was explained by his serious state of health and the need for medical treatment. Already in 1972 Glazunov's ashes were transported to the USSR and reburied in the Alexander Nevsky Lavra.
In addition to ballets, Aleksandr Glazunov wrote eight symphonies (the ninth remained unfinished), seven string quartets and a great deal of orchestral music. He wrote mainly for piano and organ, and at the end of his life he composed works for saxophone - a solo concerto and a quartet for saxophones. Glazunov's most popular works today are his ballets The Seasons (1898) and Raymonda (1897), his Fourth, Fifth and Sixth Symphonies, the Polonaise from Les Sylphides, and his two concert waltzes.


Maximilian Joseph Haushofer was a German painter of the mid-nineteenth century. He is known as a landscape painter and teacher, professor of painting at the Prague Academy of Fine Arts.
Born into the family of a teacher at the court of the Bavarian king, Haushofer began to study law, but soon indulged himself in art. His favorite subjects for a long time were the Alpine foothills and lakes illuminated by the midday sun. His students continued the tradition of his school, making Haushofer a prominent figure in the art world.
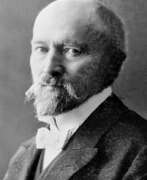

Johann Caspar Herterich was a German painter of the last third of the nineteenth century. He is known as a historical and genre painter, as well as a teacher at the Royal Academy of Fine Arts in Munich.
Herterich created a number of portraits in addition to canvases on historical, religious and genre themes. His works included dramatic scenes, sentimental genre scenes from family life. The artist actively participated in the Arts and Crafts movement and was involved in designing chandeliers and other decorative elements. Among the master's pupils was his younger brother Ludwig von Herterich, who also became a famous artist.


Enos Hitchcock was an American clergyman, author, educator, and education advocate.
He graduated from Harvard College and soon began preaching. When hostilities between the colonies and Great Britain broke out in 1775, Hitchcock joined the army, serving as a chaplain in the Continental Army from 1779-1780. After the war ended, Rev. Hitchcock preached in various localities until he settled in Providence, NC, in 1783 as pastor of the First Congregational Church, becoming an active member of its benevolent society.
In 1788 Hitchcock received his doctorate from Brown University and maintained close ties with it thereafter. With the president of that university, James Manning (1738-1791), and other prominent citizens of Providence, he was active in educational matters, and by the time of his death had succeeded in establishing a public school system in Providence. In addition to these activities, Rev. Hitchcock was a member of the Pennsylvania Society for Promoting the Abolition of Slavery.
Enos Hitchcock also wrote several epistolary works in which, among other things, he objected to the use of suicide as a plot point. His bullied rural heroes and heroines are ultimately rewarded for their virtue and courage.


Gustav Holst, birth name Gustavus Theodore Von Holst, is an English composer and educator. Holst studied at the Royal College of Music in London, including playing the trombone, and for several years after graduation he earned a living as a trombonist in various orchestras. In 1905 he became a music teacher at St. Paul's Girls' School and later music director of Morley College, positions he retained throughout his life. A brilliant educator, Holst pioneered music education for women.
Holst's music is often built on English national folklore and has much in common with the work of composer and contemporary Vaughan Williams. However, he combines it with an international flavor based on the styles of Maurice Ravel, Igor Stravinsky, and other innovators, with a continuation of English Romanticism. This influence is reflected in Holst's most famous work, the orchestral suite The Planets. Also in the Hindu opera Savitri and other cosmopolitan works.
Holst's works also include the opera Sita, Hymn to Jesus for chorus and orchestra (1917); Ode to Death for chorus and orchestra (1919), the opera The Perfect Fool (1923), the Choral Symphony (1923-24), the Double Concerto for Two Violins and Orchestra (1929), and Hammersmith for Orchestra (1930).


Leoš Janáček, birth name Leo Eugen Janáček, was a Czech composer and musicologist, folklorist, publicist and teacher.
Janáček was a singer in Brno, and studied at the Prague, Leipzig and Vienna Conservatories. In 1881 he founded the Collegium of Organists in Brno, which he directed until 1920. From 1881 to 1888 he directed the Czech Philharmonic Orchestra, and in 1919 he became professor of composition at the Prague Conservatory.
Janáček was deeply in love with national music, collecting folklore and publishing the journal Musical Pages. He was inspired by Moravian and other Slavic music, including Eastern European folk music, to create an original modern musical style.
In his early period of creativity, Janáček was strongly influenced by the musical style and aesthetics of his friend Dvořák. His first opera, Šarka (1887-88), was a romantic work in the spirit of Wagner and Smetana. In his later operas he developed his own distinctly Czech style, built on the intonations of his native speech and folk melodies. Janáček's most important operas are Jenůfa (1904) and Her Foster Daughter, which established the composer's international reputation; The Case of Macro Pulos (1926), From the Dead House (1930), and others. Most of Janáček's operas have been staged in Czech.
Janáček visited Russia three times, and his interest in Russian language and literature resulted in the opera Katya Kabanova (1921) and the orchestral rhapsody Taras Bulba (1918). Janáček also wrote a number of instrumental chamber works. The world-famous composer spent most of his life in Brno, where the vast majority of his works were performed for the first time. Today, Janáček is the most frequently performed Czech opera composer in the world.


Ferdinand Keller was a German painter of the last third of the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. He is known as a genre and historical painter as well as a teacher.
Keller earned his first major success in 1867 with his painting The Death of King Philip II of Spain. In his monumental works, he celebrated historical, dynastic, and cultural episodes in the history of Germany and Baden. One of his famous works is the painting "Apotheosis of Kaiser Wilhelm I", which was purchased by Kaiser Wilhelm II. Keller's works now grace the halls of theaters including the Baden State Theater and the Semper Opera in Dresden.


Anton Mikhailovich Legashov (Russian: Антон Михайлович Легашов) was a Russian artist of the first half of the 19th century. He is known as a painter, graphic artist and teacher.
Anton Legashov painted landscapes, portraits, genre paintings and still lifes. Many of them - using Chinese motifs and subjects. The painter lived more than 10 years in Beijing, where he was very popular with the local population for his work. He also created a series of religious paintings and icons for the Russian Spiritual Mission in Beijing.


Charles Robert Leslie was a prominent British painter-painter and writer.
Leslie was born in London to American parents who returned to the United States when he was 5 years old, but at the age of 19 he came to England to study. While studying at the Royal Academy of Arts, he traveled throughout Europe and painted extensively. The subjects of his paintings were often based on the great plays of Shakespeare, the works of Irving and Scott. Leslie was talented and unusual in transforming scenes from famous plays into works of art: Sancho Panza and Don Quixote, Juliet, Petruccio, Florizel and other characters come to life on his canvases. Leslie also painted historical works for Queen Victoria, including The Princess's Christening, Queen Victoria in Coronation Dress.
In addition to painting, Leslie made a name for himself as an art writer not only in Europe but also in the United States. He lectured and wrote various English language textbooks and created the popular "Handbook for Young Artists."
In 1821 Leslie was elected a Fellow of the Royal Academy and five years later a full Royal Academician. Charles Robert's son, George Dunlop Leslie (1835-1921), was similarly an artist, producing elegant genre works.


Rafail Sergeevich Levitsky (Russian: Рафаи́л Сергее́вич Леви́цкий) was a Russian artist of the last third of the 19th century to the first third of the 20th century. He is known as a painter-painter, photographer and teacher, professor of porcelain painting.
Rafail Levitsky painted genre paintings, portraits, landscapes, interiors, battle scenes from life. He is also considered the first artist in history to become a photographer. His many famous photographic portraits replaced models for painters, lithographers, illustrators, and engravers, as in the case of the portrait of Emperor Alexander III, which was reproduced on Russian banknotes.


Mathias Gabriel Lori the Younger was a Swiss landscape painter, draughtsman, watercolorist and master of etching.
He mastered the art of painting under the guidance of his father, the painter Gabriel Ludwig Lori the Elder (1763 - 1840). In collaboration with his father, Matthias created the album "A Pictorial Journey from Geneva to Milan". He also co-authored a famous book on Swiss costume with 55 fine engravings.


Friedrich Carl Mayer was a German painter.
For his architectural paintings he took the motifs mostly from Nuremberg and Augsburg. He preferred to depict interiors and placed particular emphasis on strict drawing and correct representation of details with fine illumination by incident sunlight.


Felix Mendelssohn (full name Jakob Ludwig Felix Mendelssohn Bartholdy) was a German composer, pianist, conductor, teacher, and one of the greatest representatives of Romanticism in music.
Felix was born into a Jewish musical family that later converted to Christianity. He received a versatile education and already as a child wrote many musical compositions, including 5 operas, 11 symphonies for string orchestra, concertos, sonatas and fugues. Mendelssohn's first public performance took place in Berlin in 1818, when he was nine years old. In 1821 Mendelssohn was introduced to J.W. von Goethe, for whom he performed works by J.S. Bach and Mozart and to whom he dedicated his Piano Quartet No. 3 in B minor. A friendship developed between the famous wise poet and the 12-year-old musician.
A few years later, the talented musician began conducting in various orchestras in Europe, and became acquainted with Carl Weber. In England, where Mendelssohn visited very often, by the middle of the 19th century his music had become very popular, even with Queen Victoria he was the most favorite composer. He dedicated his Symphony No. 3 in A minor major (Scottish Symphony) to the Queen.
Among Mendelssohn's most famous works are A Midsummer Night's Dream (1826), the Italian Symphony (1833), a violin concerto (1844), two piano concertos (1831, 1837), the oratorio Elijah (1846) and several chamber pieces. The tradition of playing the "Wedding March" from A Midsummer Night's Dream in wedding processions dates back to its performance at the wedding of a royal princess in 1858, already after Mendelssohn's death.
In 1843, Mendelssohn founded a conservatory in Leipzig, where he taught composition with Schumann. Mendelssohn was one of the first great Romantic composers of the nineteenth century.


Apollon Nikolaevich Mokritsky (Russian: Аполлон Николаевич Мокрицкий) was a Ukrainian-Russian painter and art educator, known for his contributions to the 19th-century art scene. Born in 1810 in Pyryatyn, Ukraine, Mokritsky became an influential figure in Russian academic art, specializing in portrait and historical painting.
Mokritsky's work is celebrated for its detailed realism and emotional depth. His portraits often capture the essence of his subjects, showcasing his skill in rendering lifelike expressions and intricate details. One of his most notable works is the portrait of the renowned Russian poet, Taras Shevchenko, which exemplifies his ability to combine technical precision with profound sensitivity.
In addition to his painting, Mokritsky played a significant role as an educator. He taught at the Moscow School of Painting, Sculpture and Architecture, where he mentored many young artists who would go on to shape Russian art. His influence extended beyond his own works, helping to cultivate a new generation of artists.
Today, Mokritsky's paintings can be found in various museums and galleries, including the Tretyakov Gallery in Moscow. His contributions to art and education continue to be recognized and celebrated by art collectors and historians alike.
Sign up for updates to learn more about new product sales and auction events related to Apollon Nikolaevich Mokritsky.


Alfons Maria Mucha, a Czech Art Nouveau painter and decorative artist, was celebrated for his innovative contributions to art, particularly his distinctive style that became synonymous with the Art Nouveau movement. Born in 1860 in the Moravian town of Ivancice, Mucha exhibited artistic talent from a young age, initially showing a proclivity for drawing and music, which were closely intertwined in his perception of creative expression. Despite early financial and educational hurdles, Mucha's passion for art led him to Vienna and subsequently Munich, where he honed his skills and absorbed influences that would shape his future work.
Mucha's career took a pivotal turn in Paris, where his poster for the actress Sarah Bernhardt's play "Gismonda" gained him immediate fame. This partnership with Bernhardt catalyzed a prolific period during which Mucha produced a flurry of artworks, including paintings, posters, and illustrations, as well as designs for jewelry, wallpaper, and theatre sets. His works are characterized by their depiction of beautiful young women in flowing robes, surrounded by lush, natural elements and often featuring pastel colors—a stark contrast to the bold hues preferred by his contemporaries.
Despite his commercial success, Mucha aspired for his art to convey a deeper spiritual message rather than merely adhering to the trendy Art Nouveau style. This led him to undertake projects that were more personal and culturally significant, such as "The Slav Epic"—a series of paintings celebrating Slavic history. Mucha's legacy is not only preserved in his diverse body of work but also in his influence on the aesthetic values of craftsmanship and design.
Collectors and experts in art and antiques continue to venerate Mucha for his unique ability to blend artistic beauty with cultural expression. His works, which are housed in museums and galleries worldwide, remain a testament to his vision and creativity.
For those keen on exploring the world of Alfons Maria Mucha further and staying updated on new sales and auction events related to his work, signing up for updates is an excellent way to ensure you never miss an opportunity to appreciate or acquire pieces related to this iconic artist. This subscription is tailored for collectors and art enthusiasts, focusing solely on new product sales and auction events concerning Mucha's legacy.


Carlos Múgica y Pérez was a Spanish painter, draftsman and illustrator.
He illustrated many historical works, depicting the kings and high nobility of Spain, as well as battle scenes. His drawings are in the Album of the African War, with a series of lithographs on the Spanish-Moroccan War (1859-1860).


Balthasar Paul Ommeganck was a distinguished Flemish painter, born in Antwerp, Belgium, in 1755. He garnered acclaim for his unique approach to landscape painting, blending realism with an idealized portrayal of nature. Ommeganck's work is characterized by detailed observation of nature, a sure line, and subtle use of color. His favorite subjects were undulating landscapes, often featuring grazing animals like cows, sheep, and goats.
Balthasar Paul Ommeganck's talent was not confined to painting alone; he was also a skilled draughtsman and dabbled in sculpture, producing some clay models of sheep and cows. His main contribution to art was combining the light found in Dutch Italianate painters' work from the 17th century with meticulous observation of nature, finding a synthesis between realism and an idealized representation of nature.
In 1799, Balthasar Paul Ommeganck's landscape painting won the first prize in Paris, a competition he had not intended to enter but was submitted to by a friend. His success extended beyond the borders of Belgium, as he became a member of several academies, including those in Amsterdam, Brussels, Ghent, Munich, and Vienna. In 1809, he was recognized as a corresponding member of the Institut de France.
Despite his death in 1826, Balthasar Paul Ommeganck's style continued to influence landscape painting in the 18th and early 19th centuries. However, later art critics have sometimes viewed his adherence to classic tradition and preference for the picturesque and conventional as a form of 'hopeless traditionalism'.
For collectors and enthusiasts of art and antiques, Balthasar Paul Ommeganck's works represent a significant period in the history of landscape painting. His paintings, with their fusion of realistic detail and atmospheric beauty, are a testament to his skill and vision.
To keep abreast of the latest news, sales, and auction events related to Balthasar Paul Ommeganck's art, consider subscribing to our updates. This service ensures you stay informed about opportunities to delve deeper into the works of this notable landscape artist.


Charles Henry Owen was a British military artillery officer, professor and artist, and a Fellow of the Royal Academy.
Owen served with the Royal Artillery throughout the Crimean War of 1854-1855, including the Battle of Inkerman (November 5, 1854) and the siege and fall of Sevastopol. Charles Owen rose to the rank of Major General, serving as Professor of Artillery at the Royal Military Academy at Woolwich from 1858-1873. He was also a member of the Special Committee on Artillery Weapons and in 1873 wrote a manual, Principles and Practice of Modern Artillery.
Concurrently with his service, Owen was an artist and painted landscapes of the Crimea.


Kapiton Stepanovich Pavlov (Russian: Капитон Степанович Павлов) was a Russian and Ukrainian artist of the first half of the 19th century. He is known as a painter, landscape painter, portraitist, author of genre compositions and teacher.
Kapiton Pavlov was one of the first painters in Ukraine, who depicted in his paintings real scenes from the lives of ordinary people. His portraits are characterized by poetization of the human environment. A special place in his work were children's portraits, which, according to critics, reflected the sentimental and poetic temperament of the Ukrainian soul.


Vasily Dmitrievich Polenov (Russian: Васи́лий Дми́триевич Поле́нов) was a distinguished Russian painter, celebrated for his contribution to landscape and historical painting. Born into an enlightened family in St. Petersburg in 1844, Polenov's artistic journey was nurtured by both his heritage and formal education at the Imperial Academy of Arts. His mastery in capturing the serene beauty of the Russian countryside and his innovative approach to biblical themes have cemented his place in the annals of art history.
Polenov's artistry was marked by his pioneering use of plein air painting, a technique that brought a fresh vibrancy and realism to his landscapes. Works such as "Moscow Courtyard" (1878) and "Overgrown Pond" (1879) not only showcase his technical prowess but also reflect his profound connection to Russian rural life and nature. His depiction of biblical scenes, notably in "Christ and the Sinner" (1886–87), broke new ground by intertwining these sacred stories with his love for landscapes, imbuing them with a unique sense of place and time.
A notable period in Polenov's career was his travels in Europe, where encounters with artists and cultures deeply influenced his work. Despite these influences, it was his Russian vistas that garnered the most acclaim, demonstrating his ability to infuse landscapes with a deeply personal and nationalistic sentiment. His commitment to art was intertwined with his belief in its power to evoke happiness and joy, a philosophy that guided his teaching career at the Moscow School of Painting, Sculpture and Architecture, where he mentored future luminaries of Russian art.
Polenov's legacy extends beyond his paintings. His estate, Polenovo, near Tarusa, has been transformed into a national art museum, ensuring that his contributions to Russian art and culture continue to inspire future generations. This dedication to the arts was recognized by his appointment as a People's Artist of the USSR in 1926, a testament to his enduring impact on the cultural landscape.
For art collectors and experts, Polenov's work represents not just aesthetic beauty but a rich narrative of Russia's cultural and natural heritage. His paintings, held in prestigious galleries like the State Tretyakov Gallery and the State Russian Museum, offer a window into the soul of Russian art, marked by a quest for harmony and a deep reverence for the natural world.
For those interested in exploring the works and legacy of Vasily Dmitrievich Polenov further, signing up for updates on new product sales and auction events related to his art can provide valuable insights into his enduring influence. This subscription is an opportunity to stay connected with the world of one of Russia's most beloved artists, ensuring access to the latest offerings and scholarly research surrounding his oeuvre.


Nikolai Andreevich Rimskii-Korsakov (russian: Николай Андреевич Римский-Корсаков) was a Russian composer, teacher and conductor, music critic, and member of the Mighty Handful.
Originally from an old noble family, Rimskii-Korsakov studied piano from the age of six and by the age of nine was already trying to compose music. After graduating from the St. Petersburg Naval School, in 1862-1865 he was on a round-the-world voyage, during which he was made an officer. He participated in an expedition to the shores of North America, visited Great Britain, Spain, Norway. In 1873-1884 he worked as an inspector of military bands of the fleet.
During his studies at the school and during the expedition Nikolai Rimskii-Korsakov continued to study music. His acquaintance in 1861 with the composer Miliy Balakirev and his circle "The Mighty Handful", which included composers Caesar Cui, Modest Mussorgsky and Alexander Borodin, became the impetus for his work. Rimskii-Korsakov 's aesthetic views and worldview were formed under the influence of the "Mighty Handful" and its ideologist V. Stasov.
Nikolai Rimskii-Korsakov was very prolific, and almost all of his works are based on folk and classical Russian literature and melodies. He composed 15 operas, including The Pskovite Girl (1872), May Night (1879), The Snow Maiden (1881), Sadko (1896), The Tsar's Bride (1898), The Tale of Tsar Saltan (1900), Kashchey the Immortal (1902), The Tale of the Invisible City of Kitezh..." (1904), The Golden Cockerel (1907). Fragments from some operas have become the most performed in the world, among them "The Song of the Indian Guest" from "Sadko" and "The Flight of the Bumblebee" from "Saltan".
The composer's works also include three symphonies (the first of which he completed while sailing around the world), symphonic works, instrumental concertos, cantatas, chamber instrumental, vocal and sacred music. In 1886-1890 Rimskii-Korsakov conducted the "Russian Symphonic Concertos" in St. Petersburg, and in 1898 - in Moscow, at the same time he was also engaged in teaching. In 1871 he became a professor at the St. Petersburg Conservatory, where he taught classes in practical composition, instrumentation and orchestration.
As a teacher, Rimskii-Korsakov trained over 200 composers and musicians, including Alexander Glazunov, Mikhail Gnesin, Alexander Grechaninov, Anatoly Lyadov, Sergei Prokofiev, and Igor Stravinsky. He also published several textbooks on harmony and orchestration. Rimskii-Korsakov's work had a great influence on the development of Russian classical and foreign music.


Susanna Rowson, née Haswell, was an American writer and poet, playwright, actress, and educator.
Susanna Haswell was the daughter of an officer in the Royal Navy. She published her first novel, Victoria, in 1786 and soon married businessman William Rowson. Susanna's greatest success was her first American bestseller, the novel Charlotte, A Tale of Truth (1791, in later editions under the title Charlotte Temple). This novel, a conventional sentimental story of seduction and remorse, was immensely popular and went through more than 200 editions.
In 1792 she became an actress and performed with her bankrupt husband in Scotland, as well as in Philadelphia, Baltimore, and Boston. In 1797, after retiring from the stage, Susanna opened the first "female academy" in Boston. Susanna Rowson also wrote many plays and musicals, and in doing so, helped to develop the performing arts in the United States. Later, she also edited the Boston Weekly Magazine, wrote geography and spelling textbooks, and moralizing manuals.


Michael Emil Sachs was a German painter of the second half of the nineteenth century. He is known as a landscape painter and teacher.
Sachs resided in Wiesbaden from 1860 to 1865 and then ran a woodcarving school near Partenkirchen. His landscapes, created in various regions of Germany, from the Lahn and Rhine to the Eifel, Taunus and the Bavarian Alps, are imbued with poetry. They are characterized by precise details and convey the living force of nature.
Sachs has gone down in the history of German art as the master who captured the beauty of German nature in his works.


Alexander Ivanovich Sauerweid (Russian: Александр Иванович Зауервейд) was a Baltic German painter born on February 19, 1783, in the Duchy of Courland and Semigallia. He is best known for his detailed battle scenes and military portraits, which earned him significant acclaim in the 19th century. His early education in the arts took place at the Dresden Academy of Fine Arts, where he developed a strong foundation in painting.
Sauerweid's talent for depicting military subjects brought him to the attention of prominent figures of his time, including Napoleon and Tsar Alexander I of Russia. Invited to Saint Petersburg in 1814, Sauerweid became the official painter of the Russian General Staff and later a professor at the St. Petersburg Imperial Academy of Arts. His role involved teaching battle painting and producing works that depicted various military uniforms and scenes, a specialty that set him apart from his contemporaries.
Among his notable works are "The Battle of Leipzig" and "The Siege of Varna," which showcase his ability to capture the dynamism and drama of military engagements. Many of Sauerweid's paintings are housed in Russian Imperial Palaces, reflecting their historical and artistic value.
For collectors and enthusiasts, keeping abreast of Alexander Ivanovich Sauerweid's works is essential. Subscribe to our updates to be the first to know about new product sales and auction events related to this distinguished artist. Sign up now!


Franz Peter Schubert was an Austrian composer who combined classical and romantic music.
Franz was born into a musical family, where a quartet played at home and his father founded a music school. The future composer played the violin, piano and organ. At the age of 10, the young Schubert won a place in the Vienna Imperial Court Chapel Choir and quickly gained a reputation as an aspiring composer, writing several light string quartets. In 1814 Schubert began teaching, but at the same time he continuously composed a wide variety of works. These included 145 songs, the Second and Third Symphonies, two sonatas and a number of miniatures for solo piano, two masses and other short choral works, four stage works, a string quartet, and much more.
Soon the popularity of Schubert's dance music and songs grew so much that musical evenings known as "Schubertiades", where Schubert performed his own compositions while accompanying himself on the piano, became fashionable in Vienna. The talented composer effortlessly composed many masterpieces, including the song cycles Lonely Müllerin and Winterreise, as well as the Eighth ("Unfinished") and Ninth ("Great") Symphonies, the Octet for winds, three string quartets, two piano trios, the String Quintet, the Wanderer Fantasia and six sonatas for solo piano.
Despite his boundless talent, Franz Schubert was always insecure, indecisive and reserved, causing him to be tormented by lack of money throughout his life. The composer was able to buy his own piano almost at the end of his short life - with the royalties from his first and only public concert in March 1828. Eight months later, the brilliant musician died of illness at the age of 31.


Johann Karl Schultz was a German painter, graphic artist, and teacher.
Schultz was educated at the Berlin Academy of Fine Arts and specialized in depicting architectural structures. He painted the interior and exterior views of cathedrals and other architectural monuments with great technical skill and care.


Bedřich Smetana, baptized Friedrich, was a prominent Czech composer, pianist and conductor, and the founder of the Czech national school of composition.
Smetana studied music under his father, who was an amateur violinist, and also began piano lessons early and performed as early as the age of six. He later became a music teacher and opened a piano school in Prague in 1848. Smetana was a recognized piano virtuoso.
In 1856 Smetana wrote his first symphonies and in the same year was appointed conductor of the philharmonic of Gothenburg (Sweden), where he remained until 1861, and then, returning to his homeland, he became one of the founders of the national opera theater. Smetana's first opera, The Brandenburgers in Bohemia, was staged in Prague in 1866, and in the same year the public saw his second opera, The Sold Bride, and he gained a reputation as the national Czech composer.
By the end of 1874 Smetana had gone completely deaf, but for several years he continued to create: he wrote a cycle of six symphonic works, concertos, many piano pieces and other works. Smetana's works, in particular The Sold Bride, My Country and the Piano Trio, are still performed all over the world.
Bedřich Smetana is rightly considered the founder of the national school of composition: he was the first composer to use Czech folk themes and motifs in his works, and the opera Brandenburgers in Bohemia was written entirely in Czech for the first time. Smetana's work had an enormous influence on Czech composers of subsequent generations - Antonín Dvořák and Zdeněk Fibich - and the symphonic poem Vltava from the cycle My Homeland became the unofficial Czech national anthem.


Georg Wilhelm Timm (Russian: Василий Фёдорович Тимм, Вильгельм Фридрихович) was a Russian painter and lithographer originally from the Baltic Germans.
The son of a Riga burgomaster, Timm first studied art in Riga, then moved to St. Petersburg and entered the Imperial Academy of Arts. After graduating, he moved to Paris, where he worked under Horace Vernet. He traveled extensively in Russia, visited the Caucasus, where there was still a struggle with the mountaineers, and during the Crimean campaign accompanied Russian commanders. In 1852 he accompanied Tsar Nicholas I on his visit to Finland.
Timm was the author of battle, historical and genre paintings, he was an academician of the Academy of Arts and a professor at the Prussian Academy of Arts, and published the Russian Art Bulletin.
In 1867 Timm moved to Berlin, where he painted panels and ceramics. In 1876 he was appointed professor at the Prussian Academy of Arts and since then worked at the Royal Porcelain Manufactory in Berlin.


Fyodor Petrovich Tolstoy (Russian: Фёдор Петрович Толстой) was a Russian sculptor, painter, and medallist, renowned for his contributions to Russian classicism and romanticism. Born in Saint Petersburg in 1783, he became a prominent figure in the Russian art world. As a vice-president of the Imperial Academy of Arts, Tolstoy produced significant works, including medallions commemorating the Patriotic War of 1812.
Tolstoy's artistic style is characterized by its meticulous detail and classical influence. His works, such as the intricate medallions and bas-reliefs, often depict historical and allegorical scenes. These pieces are celebrated for their technical precision and emotional depth, embodying the spirit of the era.
Many of Tolstoy's creations are housed in prestigious collections, including the State Hermitage Museum and the State Tretyakov Gallery. His legacy continues to inspire and influence Russian art and culture, making him a significant figure in the history of Russian fine arts.
Subscribe for updates on new product sales and auction events related to Fyodor Petrovich Tolstoy. Stay informed about the latest opportunities to acquire pieces of his artistic legacy.


Thomas Uwins was a British painter and illustrator, and a Royal Academician.
Uwins was a versatile artist, painting portraits, genre scenes, landscapes in watercolor and oil, and book illustrations. Uwins taught, was a member of the Society of Old Watercolorists, and held a number of high-ranking artistic positions, including librarian of the Royal Academy, inspector of Queen Victoria's paintings, and curator of the National Gallery.


Alexey Alexandrovich Vasilyev (Russian: Алексей Александрович Васильев) was a Russian artist of the mid-19th century. He is known as a portrait painter and teacher.
Alexey Vasilyev painted portraits, which were distinguished by psychologicalism and elegance of execution. He created a gallery of portraits of his family, as well as his self-portrait and portraits of famous figures, mostly related to the naval service.
The artist's works are kept in all key Russian state art museums.


Peter Joseph von Cornelius was a German painter of the first half of the 19th century. He is known as a painter, draftsman, teacher, and representative of Romanticism.
Von Cornelius was one of the founders of the Nazarene society in Rome and sought to revitalize and modernize German fresco painting. He led the fresco decoration work in Munich and the Ludwigskirche, and was also involved in the design of murals for the Berlin cemetery. The art school founded by Cornelius revitalized mural painting in Germany and influenced other European countries. In addition to monumental works, the artist also created illustrations for literary works including Faust and The Song of the Nibelungs.


Philipp von Foltz was a German painter of the mid-nineteenth century. He is known as a historical painter and teacher, and court painter to the kings of Bavaria.
Von Foltz created a series of paintings in the Romanticism style, including the famous painting "King Otto I of Greece's Farewell to Munich". This work stands out for its painterly and romantic approach, different from academic classicism. The master's recent works include historical canvases for King Maximilian II and paintings of hunting scenes.
Foltz was also rector of the Munich Academy of Fine Arts.


Otto Friedrich Theodor Möller (Russian: Фёдор Антонович Моллер), a Russian academic painter of Baltic-German descent, was renowned for his detailed and expressive portraits, figure paintings, and genre scenes. Born in 1812 in Kronstadt, Saint Petersburg, Möller was deeply influenced by his mentor, Karl Briullov, at the Imperial Academy of Fine Arts. His journey as an artist was marked by a successful tenure in Italy, where he embraced the vibrant local culture and further honed his skills, particularly in portraying everyday Italian life and historical narratives .
Möller's artworks are celebrated for their clarity of composition and expressive color palette, traits he mastered under Briullov's guidance. His notable works, like the portrait of Nikolai Gogol, are admired for their lifelike representation and emotional depth. These paintings not only showcase his technical skill but also his ability to capture the subtle nuances of his subjects' personalities.
Möller's contributions to Russian art extend beyond his paintings. He was a professor and a significant figure at the Imperial Society for the Encouragement of the Arts, dedicating much of his later years to teaching and supporting fellow artists. His works are held in high esteem and continue to be featured in major Russian museums, including the Tretyakov Gallery and the Russian Museum.
For collectors and enthusiasts wishing to stay updated on exhibitions and auction events featuring Otto Friedrich Theodor Möller's works, signing up for newsletters and alerts from relevant art institutions can be highly beneficial. This ensures that you remain informed about opportunities to view or purchase his esteemed works.


Ferdinand Johann von Olivier was a German painter, draughtsman, engraver-xylographer and lithographer of the Romantic era. Member of the Olivier family of painters. Worked mainly in the genre of landscape. Artistically, he was close to the Nazarenes.
In 1830, Ferdinand Johann Olivier moved to Munich. There, at the request of Peter von Cornelius, he succeeded Ludwig von Schorn as secretary general of the Munich Academy of Arts. In 1833, Olivier was appointed professor of art history.





































































































