Writers 16th century


Cornelius Gerardi Aurelius, also called Goudanus, was a Dutch humanist scholar, writer, and historian.
Aurelius was a permanent canon (monk) of the Augustinian monastic order and is one of the first humanists of the Netherlands in the 16th century. He wrote poetry, historiography, hagiography, political and theological works. Aurelius also corresponded with many of the famous men of his day, especially Erasmus.
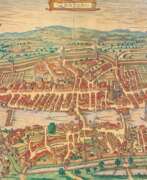

Georg Braun was a German topographical geographer, cartographer and publisher.
Braun was the editor-in-chief of the Civitates orbis terrarum, a groundbreaking atlas of cities, one of the major cartographic achievements of the 16th century. It was the first comprehensive and detailed atlas, with plans of the world's famous cities and bird's-eye views, and became one of the best-selling works of the time.
The book was prepared by Georg Braun in collaboration with the Flemish engraver and cartographer Frans Hoogenberg. Braun, as editor-in-chief, acquired tables, hired artists, and wrote the texts. They drew on existing maps as well as maps based on drawings by the Antwerp artist Joris Hofnagel and his son Jacob. Other authors include Pieter Bruegel the Elder (c. 1525-1569), Jacob van Deventer (c. 1505-1575), and more than a hundred other artists and engravers.


Otto Brunfels (also Brunsfels, Braunfels) was a German theologian, botanist and physician.
After studying theology and philosophy at the University of Mainz, Brunfels went to a Cartesian monastery near Strasbourg and later became interested in botany there. 1524 he opened a school in Strasbourg. In 1530, Brunfels began studying medicine at the University of Basel and two years later became city physician in Bern, where he remained for the rest of his life.
In addition to theological works, Brunfels published works on education, Arabic, pharmacy, and botany. His Herbarium Vivae Icones (1530 and 1536) and Contrafayt Kreüterbuch (1532-1537) contain woodcuts of German plants with their German common names. The 135 original woodcuts are detailed, accurate, and realistic depictions of living plants by the German artist and engraver Hans Weiditz. Brunfels' work contributed to the shift away from medieval outdated herbalism to the establishment of botany as a modern science. Carl Linnaeus considered Brunfels one of the founders of modern botany.


Pedro de Oña, full name Pedro de Oña y Villegas de Acurcio, was the first known poet born in Chile.
Pedro was the son of a military captain, Gregorio de Oña, who died during the Spanish conquest of Chile. After studying at the University of San Marcos in Lima, he joined the army and participated in several battles against rebellious Indians. De Oña is known to have spent many years in Peru.
Pedro de Oña's best-known literary work is Primera parte de Arauco domado (The First Part of the Conquest of Araucana, 1596), a verse epic in rhymed couplets depicting the deeds of the Marquis Hurtado de Mendoza, viceroy of Peru from 1556 to 1560. The realistic descriptions of violence and sensationalized accounts of Mapuche customs offended many, including the Bishop of Lima, and the book was banned. Today, however, it is valued as an eyewitness account of historical events.


Antonio de San Román de Ribadeneyra, also San Román de Rivadeneira/Ribadeneira, was a Spanish Benedictine monk and historical writer.
He served at the monastery of San Zoil near Carrión de los Condes and wrote several historical books. In particular, an account of King Sebastião I's disastrous invasion of Morocco in 1578 and his death in battle entitled Jornada y muerte del Rey Don Sebastião de Portugal (1603). Antonio de San Román de Ribadeneyra also wrote A General History of Eastern India (1603). This historical work focuses on the Portuguese expeditions to Asia and the Americas, including a description of Christopher Columbus.


Jacopo Filippo di Bergamo, or Giacomo Filippo Forèsti (Latin: Iacobus Philippus Bergomensis) was an Italian Augustinian monk, theologian and chronicler.
Jacopo di Bergamo was born into a noble family, received his ecclesiastical education at the local monastery, and early showed a penchant for literary work. After traveling in Europe, he took the tonsure and was abbot of monasteries, engaged in their improvement.
He is known as the author of a number of significant early printed works, a chronicler and biblical scholar. His Supplementum chronicarum (1483) is a universal chronicle that survived many subsequent editions. And De claris mulieribus, published in 1497, contains the first account of the voyage of the discoverer Columbus.


John Donne was a British preacher and poet, a major exponent of English Baroque literature.
His father was a wealthy merchant, and he was educated at Oxford, Cambridge, and Lincoln's Inn. Then began to write satires, which were willingly passed from hand to hand. The first three of Donne's famous satires date from 1593, and the others were written at various times before 1601. In 1594 he began his travels in Europe, accompanied the Earl of Essex on the capture of Cadiz in 1596 and on the expedition of 1597, and was in Italy and Spain.
In 1601. John Donne wrote his remarkable poem "The Progress of the Soul", in 1610 published his prose work against Catholics "Pseudo-Martyr", and in 1611. - an even harsher polemical treatise, Ignatius in Conclave. John Donne was also the author of many sonnets, love poems, elegies, epigrams, and religious sermons.
In 1621 John Donne was appointed rector of St. Paul's Cathedral in London, and near the end of his life he became a popular eloquent preacher whose sermons were eagerly printed and published. 160 of his sermons have survived, including the most famous, Death's Duel, which he delivered in Whitehall before King Charles I on February 25, 1631, a few weeks before his own death.


Armand-Jean du Plessis, duc de Richelieu, also known as Cardinal Richelieu or the Red Cardinal (French: l'Éminence rouge) was a Roman Catholic cardinal, aristocrat and statesman of France.
Armand Jean's father, François du Plessis, Signor de Richelieu, was the grand proclaimer (chief magistrate) of Henry III, but left his family devastated at his death. At the age of 22, Armand was ordained a priest and began to build a career. Thanks to his intellectual talents, he was soon appointed chaplain to the new Queen Anne of Austria, and in 1616 he was appointed Secretary of State for War and Foreign Affairs. Further events and a palace coup led to his exile, but he returned to Paris five years later.
The Duc de Richelieu became a cardinal in 1622, and from 1624 until his death in 1642 he was chief minister to King Louis XIII of France. His main goals were to establish royal absolutism in France and to end the Spanish-Habsburg hegemony in Europe. He made significant strides in reforming France, especially in terms of the administrative structure of the government.
The intrigues of his opponents accompanied the Duc de Richelieu throughout his political life. In the last years of his life he found himself involved in religious conflicts, in opposition to the pope in a struggle with the French church over the distribution of revenues intended to finance the war.
Richelieu possessed outstanding intellectual ability, willpower, and industriousness. He directed his own wealth to patronizing the arts and the University of Paris; he established the French Academy. Richelieu was also a talented playwright and musician.


Wilhelm Fabry von Hilden or Fabricius von Hilden (Latin: Fabricius Hildanus) was a German and Swiss Renaissance physician and surgeon, the founder of scientific surgery.
In 1576 he began a four-year apprenticeship as a surgeon with a barber in Neuss. Surgery at that time was considered the craft of bath and barbers; surgeons or wound doctors treated wounds, broken bones, inflammations, and many other ailments. After completing his apprenticeship, Fabry worked for five years as an assistant wound surgeon to Cosmas Slot (died 1585) at the court of Duke Wilhelm V in Düsseldorf. To expand his anatomical knowledge, Fabry constantly dissected and prepared cadavers. In later years, he also encouraged his students to do so and conducted public autopsies to draw attention to the importance of anatomical knowledge. He also made it a habit to do practice procedures on a cadaver before surgery.
In 1615 Fabry was appointed city physician of Bern. Here he wrote several books on gunshot wounds. In 1623 the versatile physician published a small book, "Christian and Good-Hearted Caution against Drunkenness," which he republished in more detail the following year under the title Christlicher Schlafftrunck. Fabry's most important surgical treatise was Observationem et curationem chirurgicam centuriae sex ("Six hundred surgical observations and cures"), first published in 1606. This compilation remained the most important book of German surgery until Lorenz Heister. It describes new surgical methods and surgical instruments for the treatment of amputations, nasal polyps, bladder stones, dropsy, hernias, ascites, etc., etc., etc.
For centuries, Fabricius remained one of the most respected surgeons not only in Germany and Switzerland, but throughout Europe. Among his many accomplishments in the field of surgery may be enumerated his innovation in the amputation of the thigh, for which he invented a special tourniquet; the excision of involved axillary glands in breast cancer; the first classification of burns into three degrees with the appropriate treatment for each variety; and the first description of a medical field chest for military purposes.
Although in his later years Fabritius had already given up practicing medicine, he continued to write medical papers and maintain an active scientific correspondence until his death. He authored some 20 medical books. It was his surgical works, translated into German, French, Latin, English and Dutch, that ensured his recognition centuries later.


Gabriele Falloppio was an Italian physician and anatomist of the Renaissance.
Originally a priest, Falloppio soon left for Ferrara to study medicine and was later appointed anatomy professor there, and in 1548 he became head of the anatomy department at Pisa. Three years later he accepted the offer of the Venetian Senate to become professor of anatomy, surgery, and botany at Padua, where he remained for the rest of his life. It was in this city that he made his most famous discoveries, was director of the famous botanical garden, and wrote two medical textbooks.
He also gained a reputation as an excellent teacher and lecturer, attracting many Italian and foreign students to the medical faculty of the University of Padua. As a physician, he made a thorough study of the clinical aspects and treatment of syphilis, and proposed the condom as a defense against venereal disease.
Falloppio was a versatile scientist and an able physician and surgeon, describing, among other things, the semicircular canals, the cuneiform sinuses, the trigeminal, auditory and lingual pharyngeal nerves, the canal of the facial nerve, and the fallopian tubes, named Fallopian tubes in his honor. Falloppio described his discoveries in his three-volume work Opera genuina omnia, published in Frankfurt in 1600 and in Venice in 1606.


Leonhart Fuchs was a German humanist scientist, botanist, and physician.
Fuchs received a humanistic education under Catholic guidance, but later became a Protestant. He studied medicine and became a professor in Tübingen. He was most interested in the medicinal properties of plants. Well acquainted with the Greek and Latin classics and an excellent observer, he gave precise descriptions, and his beautiful engravings of plants established the tradition of depicting plants with precise illustrations and in alphabetical order.
In 1542 Fuchs published his most important work, De Historia Stirpium Commentarii Insignes (Famous Commentaries on the History of Plants). The book was a great success, especially because of the magnificent woodcuts and the 487 plants, which were described for the first time in such a systematic form. De Historia Stirpium survived several editions and was translated into Dutch and German.


Philips Galle was a Dutch publisher, best known for publishing old master prints, which he also produced as designer and engraver. He is especially known for his reproductive engravings of paintings.
As a resident of Antwerp, Galle witnessed numerous events of the Eighty Years War, notably the siege and looting of the town in 1576 by the Spaniards, called "The Spanish Fury". This rather personal book, which was translated in several languages soon after its first publication, shows Galle as a peace-loving person who intended to stay far away from the political and military turmoil of his era.


Ben Jonson or Benjamin Jonson was an English poet, playwright, actor and dramatic theorist.
Jonson came from a simple family, served in the army, seriously engaged in self-education, and in 1586 began a career in the theater. In the 1590s he had the good fortune to meet William Shakespeare. In 1598 Shakespeare was able to put in the theater "Globe" Jonson's play "Every man for his own good," where he played one of the roles. The two playwrights became friends and collaborated on productions of the plays. Jonson was one of the most erudite playwrights of his time and was sure to apply his deep knowledge of Greek and Roman classics in his work.
Jonson's daring character failed him more than once: he often got into fights and duels, and later began to prefer direct violence mockery of his opponents in his plays. But even in this case, he not once got into serious trouble and even sat in prison.
In 1605 Jonson with great success put in the "Globe" play "Volpone". A great admirer of Johnson's work was King James, and the next ten years were the most colorful in his career. His plays written between 1605 and 1615 - Epicoen, The Alchemist, Catalina, Bartholomew Fair and The Devil is an Ass - were a great success, rivaling Shakespeare himself.
Ben Jonson is a vivid representative of English literature of its Renaissance period. His best works ridicule human weaknesses with the help of comic realism, verbal brilliance and a remarkable gift for caricature and parody.


Francis Junius the Elder, born François du Jon, was a French linguist, exegete and professor of Reformed theology, and diplomat.
Junius first studied law and then theology and became a student of Jean Calvin and Theodore Beza in Geneva. For his success and knowledge of languages he was appointed minister at Antwerp, but was forced to flee to Heidelberg in 1567.
In collaboration with Immanuel Tremellius he wrote one of the significant translations of the Bible into Latin, and his theological work De Vera Theologia is the most important work on Reformed dogmatics. Some of du Jon's works were published in 1882 by Abraham Kuyper in his Reformed Library. His son François du Jon the Younger (1591 - 1677) became a noted art historian and founder of Germanic philology.


Levinus Lemnius (Dutch: Lieven Lemse, Lenneus, Lennius, Lemmens, Lemnii of Lemnes) was a Dutch physician, philosopher, botanist and writer.
He studied under the famous Swiss botanist and bibliographer Conrad Gesner at the University of Louvain and under the famous Flemish anatomist Andreas Vesalius at the University of Padua. Lemnius's book On the Habit and Constitution of the Body was translated by Thomas Newton, an Anglican clergyman who translated some of Lemnius's treatises into English, as well as other modern continental and classical works.
Lemnius is considered the first author to describe the plants mentioned in the Bible, in T. Newton's translation, Herbal for the Bible (1587). Levin Lemnius's most famous book is Occulta naturae miracula (1559), a book of mysteries that was reprinted many times over a period of four hundred years.


Fortunio Liceti (Latin: Fortunius Licetus) was an Italian physician, natural philosopher, writer and educator.
Liceti studied philosophy and medicine at the University of Bologna and earned doctorates in these disciplines. He taught logic and philosophy at the University of Pisa, and became professor of philosophy at the University of Padua and the University of Bologna. At the University of Padua, Liceti became friends with Galileo Galilei.
Liceti's inquisitive mind was interested in a wide range of subjects: from genetics and reproduction to gems and animals. In general, Fortunio Liceti was a very industrious and prolific scientist: he published a book each year, writing more than seventy works on a wide range of subjects, including the human soul, reproduction, and birth defects.
In 1616, Liceti wrote and published the first edition of De monstruorum causis, natura et differentiis (On the Causes, Nature, and Differences of Monsters), a chronologically ordered catalog of monsters from antiquity to the seventeenth century. Among these monsters were infants with congenital malformations. Liceti was one of the first scholars to attempt to systematically categorize birth defects according to their causes, including numerous causes not related to the supernatural. This topic interested the scientist greatly and he returned to it several times during his life, supplementing it with illustrations, among other things. From 1640 to 1650. Liceti also wrote and published seven different volumes in which he answered questions from famous people on a wide variety of medical topics.


Niccolò di Bernardo Machiavelli was an Italian philosopher, politician and diplomat, historian and Renaissance writer.
As a young man, Niccolò Machiavelli faced financial difficulties due to his father's debts, but had access to a rich library. Machiavelli's early life and career began during a period of political upheaval in Italy. After the expulsion of the Medici family in 1494, for 14 years Niccolo Machiavelli served as a diplomat to the Florentine Republic. During this service, he gained a reputation as a cunning and unconventional thinker. However, when the Medici returned to power in 1512, Machiavelli was dismissed, imprisoned, and temporarily removed from political life.
During this period Machiavelli wrote his famous work The Sovereign, which has become one of the key works in the history of political philosophy. This book epitomizes the Machiavellian approach to politics, where the means justify the end, and where a leader should use any method to consolidate his power. The treatise drew criticism from the Pope, who condemned it for supporting rule through deceit and fear. Nevertheless, The Sovereign is still an important work of political literature, and Machiavelli has come to be called "the father of modern political theory."
Machiavelli lived the rest of his life in a small village near Florence, where he continued his creative endeavors, writing On the Art of War, as well as poems and plays. His literary legacy has become an integral part of the history of political philosophy.


Thomas Moffet was a British naturalist-naturalist and physician.
After receiving his MD degree in 1580, Thomas Moffet studied the anatomy of the mulberry silkworm in Italy, then returned to England to study arthropods in general, especially spiders. He edited and expanded the work Insectorum sive Minimorum Animalium Theatrum ("Insect Theater"), an illustrated guide to the classification and life of insects.
Moffet was also an ardent supporter of the Paracelsian system of medicine.


Thomas More was a British lawyer, humanist philosopher, writer and statesman.
As the son of a London judge of the Royal High Court, Thomas studied at Oxford and then in London with the best lawyers. More also studied the works of the ancient classics, improved in Greek and Latin languages, composed his works. In 1497 More met and became friends with Erasmus of Rotterdam, became a member of his humanist circle.
In 1510-1518 Thomas More was deputy sheriff of London, and in 1517 entered the service of the king, becoming one of the most effective and trusted civil servants of Henry VIII. He acted as his secretary, interpreter, speech writer, chief diplomat, counselor, and confidant. He was knighted in 1521, became Speaker of the House of Commons in 1523, and in 1525. - Chancellor of the Duchy of Lancaster. Around 1515. More wrote The History of Richard III, and in 1516 he published his most significant work, Utopia, in which he described an imaginary ideal state.
Thomas More opposed the divorce of King Henry VIII from Catherine of Aragon and refused to recognize the king as the head of the Church of England, as required by the Act of Supremacy in 1534. For his refusal, he was beheaded in the Tower of London in 1535. 400 years later, in 1935 Thomas More was canonized by the Catholic Church, and in 1980 the Church of England recognized him as a "saint and hero of the Christian Church."


Sebastian Münster was a German Renaissance scholar, cartographer and cosmographer, historian and linguist-translator.
Münster studied at the University of Tübingen and later taught at the Universities of Basel and Heidelberg. He published several editions of Hebrew grammars and translations from that language, and was the first German to produce an edition of the Hebrew Bible.
In 1544 Münster published his Cosmographia, which was the earliest description of the history, geography, and organization of the world in German. This book was a great success, translated into many European languages and reprinted more than twenty times. "Cosmographia" contained many illustrations and geographical maps of the continents of the world, created by the best engravers of the time.
Among his other works were the "Trilingual Dictionary" (1530) in Latin, Greek, and Hebrew and the "Map of Europe" (1536).


Giovanni Nardi was an Italian physician and natural philosopher.
After studying at the University of Pisa, Nardi worked as a physician in Florence. He corresponded with many of the leading natural philosophers and antiquarians of his time, including members of the Accademia dei Lincei. In 1620 Nardi became court physician to Duke Ferdinando II Medici of Tuscany and accompanied him on his travels. In his Florentine home, Nardi amassed a collection of antiques and curiosities.
Nardi wrote several volumes on natural philosophy, as well as a commentary on Lucretius entitled Titi Lucretii Cari De rerum naturae libri sex (1647). Nardi's commentaries on Lucretius's natural history, medicine, physics, and theory of atomism far exceed the poem itself.


Nostradamus (French: Michel de Nostredame) was a French physician-pharmacist, writer, poet, astrologer and alchemist.
Nostradamus was born into a family of baptized Jews and studied various sciences in Avignon. At that time the plague was rampant in Europe, and Nostradamus decided to become a healer, in 1526 he even invented an anti-plague medicine, and later received a degree of Doctor of Medicine. He began his medical practice around the 1530s in Agen. During the plague outbreaks in Aix and Lyon in 1546-1547, he gained fame for his innovative treatments. Nostradamus described his methods of dealing with epidemics in several medical works. In addition to medicine, he also practiced astrology.
Nostradamus gained worldwide fame thanks to his gift as a seer. He began making prophecies around 1547 and first published them in 1555 in a book called Centuries. The book was written in rhymed quatrains - catrines - with predictions of future events in European history. Some of his prophecies were close to the truth, and the fame of the visionary Nostradamus reached the court of Catherine de Medici, who ordered him to compile horoscopes of her children. In 1564 he was appointed physician to Charles IX, to whom he also made several predictions that came true.
Nostradamus's book of prophecies was a huge success, and it still arouses interest, but he wrote allegorically and many of the katrines cannot be interpreted unambiguously.


Bernard Palissy was a French natural scientist, painter, ceramicist and sculptor, geologist and writer of the French Renaissance.
Born into a family of artisans, Palissy apprenticed with his father as a glass artist and traveled throughout southwestern France comprehending pottery and studying geology. Today he is best known for his amazing lead-glazed pottery with images of various animals and people. After seeing a white glazed cup, probably of Chinese porcelain, in the 1540s, he set out to learn the secrets of its manufacture. His early research is described in De l'art de la terre. Although Palissy never succeeded in reproducing what he saw, his experiments gave him a thorough knowledge of the chemical compositions of minerals.
From 1575 in Paris, Palissy gave public lectures on natural history, which were published as Discours admirables (1580). In this treatise, Bernard Palissy touches on an incredibly wide range of subjects, from the techniques of ceramics, metallurgy and chemistry to hydrology, geology and fossils. He correctly identified fossils as the remains of ancient life. This work reveals him as a writer and scientist, a creator of modern agronomy and a pioneer of the experimental method, with scientific views generally more advanced than those of his contemporaries.


Paolo Ricci (Italian: Paolo Ricci, Latin: Paulus Ricius, German: Paul Ritz), also known as Ritz, Riccio, or Paulus Israelita, was a humanist convert from Judaism, a writer-theologian, Kabbalist, and physician.
After his baptism in 1505 he published his first work, Sol Federis, in which he affirmed his new faith and sought through Kabbalah to refute modern Judaism. In 1506 he moved to Pavia, Italy, where he became a lecturer in philosophy and medicine at the university and met Erasmus of Rotterdam. Ricci was also a learned astrologer, a professor of Hebrew, philosophy, theology, and Kabbalah, a profound connoisseur and translator of sacred texts into Latin and Hebrew, and the author of philosophical and theological works.
Paolo Ricci was a very prolific writer. His Latin translations, especially the translation of the Kabalistic work Shaare Orach, formed the basis of the Christian Kabbalah of the early 16th century.


Celio Rodigino (Latin: Caelius Rhodiginus), real name Ludovico Ricchieri, was an Italian writer, educator and Renaissance humanist.
Rodigino studied in Ferrara and Padua, and then was professor of Greek and Latin at Rovigo. In 1515 he became chair of Greek at the University of Milan.
His principal work was Antiquarum Lectionum in sixteen books, published in Venice in 1516. In this work Rodigino collected a considerable number of short essays and notes on Latin and Greek antiquity, from literature, philology, and science to philosophy, history, anthropology, and morality, as well as reflections on ancient music. He also wrote commentaries on Virgil, Ovid, and Horace.


Werner Rolewinck (Latin: Wernerus Rolewinkius) was a German chronicler, historian, and theologian.
Werner Rolewinck was a Cartesian monk. His best known and most important work is Fasciculus temporum, a history from the creation of the world to Pope Sixtus IV. Already during his lifetime this work was republished many times in Latin, French, Dutch, and German. Drawing on major Christian historiographical sources such as Orosius and Eusebius, Fasciculus presents the history of the world in the form of a genealogy, a traditional historiographical structure dating back to late antiquity.
Another famous work by Rolewink is a description of the manners and customs of his homeland entitled De laude veteris Saxsoniæ nunc Westphaliæ dictæ.


Marco Aurelio Severino was an Italian surgeon, anatomist and zoologist, one of the founders of comparative anatomy.
From childhood Severino studied Latin, Greek, rhetoric, poetry and law in various schools in Calabria, then continued his studies in Naples, soon moving from law to medicine. In Naples he met Tommaso Campanella, who had a great influence on the formation of his worldview. After receiving a medical degree in Salerno in 1606, he studied surgery in Naples with Giulio Jasolino. In 1615 Severino was appointed the first surgeon at Ospedale degli Incurabili. Severino made significant contributions to the transformation of naturophilosophy, medical and surgical practice, to which much of his printed work is devoted.
Severino's main contribution, however, lies in his anatomical works, especially the Zootomia Democritea. This work may be called the earliest comprehensive treatise on comparative anatomy. Severino is considered one of the pioneers of comparative anatomy.
Severino's cultural interests extended far beyond medicine. He corresponded with many prominent physicians and scientists of his time, including William Harvey and John Houghton in England, Thomas Bartolin and Ole Worm in Denmark, J.G. Volkamer and Johannes Wesling in Germany, and Campanella, Jasolino, and Tommaso Cornelio in Italy. Severino was tried by the Inquisition for allegedly unorthodox religious and philosophical views, but was eventually acquitted. He died of the plague in Naples.


William Shakespeare was a British poet and playwright and writer.
William's father, John Shakespeare, was a merchant and official in Stratford. There are reports that he was a sailor for a time before joining a theater company in London. Beginning in the 1590s, Shakespeare began writing plays, and in 1593 he published a poem, Venus and Adonis, which became popular. He dedicated it to the Duke of Southampton, who was a philanthropist and patron of talent, and soon his business was booming.
From 1592 to 1600 Shakespeare wrote his dramas and romantic comedies "Richard III", "The Taming of the Shrew", "Romeo and Juliet", "A Midsummer Night's Dream" and "The Merchant of Venice", as well as the comedies "Much Ado About Nothing", "Twelfth Night" and the tragedy "Julius Caesar". The playwright's business was so successful that he even bought a large house in Stratford. In 1599, Shakespeare became one of the owners, playwright and actor of the new theater "Globe". In 1603 King James took Shakespeare's troupe under his direct patronage. In the mature period, the great playwright turned to tragedies, there were "Hamlet", "Othello", "King Lear", "Macbeth" and others.
Although in the 19th century researchers had some doubts about the authorship of many of these works, William Shakespeare is considered the greatest English playwright, one of the best playwrights in the world. His plays have been translated into all major languages and to this day form the basis of the world theatrical repertoire, most of them have been screened many times. According to the Guinness Book of Records, Shakespeare remains the world's best-selling playwright, and his plays and poems have sold more than 4 billion copies in the nearly 400 years since his death.


John Skelton was an English poet and writer of the Tudor period.
He was educated at the University of Cambridge, followed by degrees in rhetoric at Oxford, in the Netherlands, and at Cambridge. He was also a translator of ancient Greek and Roman authors. In 1488 Skelton was appointed court poet to Henry VII and then tutor to the Duke of York (later Henry VIII). In 1498 he took holy orders.
Skelton was known as a poet and satirist on both political and religious subjects. His best-known works include the moralizing play Magnyficence (1516), the humorous poem The Tunning of Elinor Rumming (1520), and numerous satirical poems in which he ridiculed both secular and ecclesiastical authorities. His reputation was confirmed by Erasmus of Rotterdam himself, who spoke highly flatteringly of Skelton.


Johannes Stumpf was an early writer on the history and topography of Switzerland as well as a theologian and cartographer.
When he converted to Protestantism, Stumpf had carried over with him most of his parishioners, whom he continued to care for, as the Protestant pastor at Bubikon, till 1543.
Stumpf also published a monograph (very remarkable for the date) about Henry III, Holy Roman Emperor (1556) and a set of laudatory verses about each of the thirteen Swiss cantons.


Immanuel Tremellius or Giovanni Emmanuele Tremellio was an Italian reformer, Hebraist, translator, and professor of Hebrew.
Born in Ferrara to a Jewish family, Tremellius was educated in Padua and converted to Catholicism in 1540, but converted to Protestantism a year later and had to move from place to place. He taught Hebrew at Srasburg, at Cambridge, and later became professor of Old Testament at Heidelberg, Germany (1561). He eventually found refuge at Sedan College, where he died.
Immanuel Tremellius' main literary work was a Latin translation of the Bible from Hebrew and Syriac. He also translated Calvin's Catechism into Hebrew and Greek (1551) and published Bucer's Commentary on Ephesians, based on lectures he had heard at Cambridge (1562), as well as an Aramaic and Syriac Grammar (1569).


André Valladier was a French Jesuit, theologian and writer.
Valladier served as abbot of the Benedictine abbey of Saint-Arnoux and worked as professor of rhetoric at Avignon. He published about ten works on various subjects. The first of these was The Royal Labyrinth, a book describing the visit of King Henry IV and his new wife, Maria de' Medici, to the city of Avignon. This illustrated book was a great success and went through many editions.


Giorgio Vasari, polymath of the Italian Renaissance, left an indelible mark on painting, architecture, and art history. Born on July 30, 1511, in Arezzo, Italy, Vasari was deeply influenced by the patronage of the Medici family during his artistic education in Florence. Exposure to the works of Andrea del Sarto and the profound influence of Michelangelo's work shaped his development as an artist and architect. Vasari's artistic career was characterized by his contributions throughout Italy, including significant works in Florence and Rome, and his role in founding the Florentine Academy and the Society of the Fine Arts in 1563 underscores his commitment to art and education.
Vasari's architectural skill is evident in the design of the Uffizi Loggia in Florence, testifying to his ability to combine functionality with aesthetic grandeur, creating a space that harmonizes with the urban landscape while blending into the riverside environment. His contribution extends to the Vasari Corridor, an architectural marvel that connects the Uffizi to Palazzo Pitti across the Arno River, demonstrating his innovative approach to public and private space.
Perhaps Vasari's most enduring legacy stems from his seminal work, Lives of the Most Excellent Painters, Sculptors, and Architects, in which he outlined biographies of Renaissance artists, laying the foundation for the discipline of art history. This work not only elevated the status of artists in society, but also created a history of the development of art that emphasizes the Renaissance as a period of rebirth and innovation. Vasari's narratives, although their accuracy is sometimes criticized, remain a cornerstone in the study of Renaissance art, offering invaluable insights into the lives and works of the era's most prominent figures.
Vasari's work is represented in prominent museums and galleries, including the Minneapolis Institute of Arts and the National Gallery of Art, which houses important works such as the Six Tuscan Poets and works commissioned by the Pope. His architectural and artistic contributions, combined with his innovative historiographical approach, have cemented his reputation as a key figure of the Renaissance and the annals of art history.
Giorgio Vasari's multifaceted contributions to painting, architecture, and art history not only underscore his genius, but also play a key role in shaping our understanding of the Renaissance. His works and writings continue to inspire collectors, experts, and enthusiasts. For those seeking to delve deeper into the world of Renaissance art and Vasari's profound influence, subscribing to updates on new sales and auction events related to Vasari can offer a wealth of information and the opportunity to explore his enduring legacy.
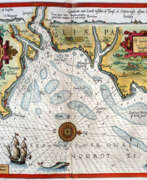
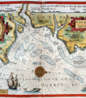
Lucas Waghenaer, full name Lucas Janszoon Waghenaer, was a famous Dutch cartographer, navigator, navigator and writer of the Golden Age.
Between 1550 and 1579, Waghenaer sailed the seas as a senior assistant captain and probably socialized with Portuguese, Spanish, and Italian navigators. The knowledge of nautical charts and the instructions Waghenaer received as a result of these contacts had a great influence on his later work as a cartographer. It is evident that the charts he made had to be based on his observations, and in all his work he had to draw on his own extensive experience of practical navigation. His book Spieghel der Zeevaerdt ("The Navigator's Mirror") or Speculum nauticum super navigatione, first published in 1584, occupies a unique place among the nautical printed works of the sixteenth century, for it is the first printed work with maps.
Moreover, in terms of the magnificent design of the maps and text, it surpasses all other editions of this period and served as a model for pilotage guides and folios with maps even a century later. It is an atlas of nautical charts with instructions for navigation in the western and northwestern coastal waters of Europe. Thanks to the unrivaled skill of engravers Baptiste and Johannes van Deitekom, Waghenaer's original maps were transformed into the most beautiful maps of the time. This book was a huge success, reprinted several times and translated into English, German, Latin and French.
In 1592, Waghenaer's second pilot book Thresoor der zeevaert ("Treasure of Navigation") was published, and in 1598, the third and last publication Enchuyser zeecaertboeck ("Enkhuizen Book of Nautical Charts").


Huldrych or Ulrich Zwingli was a leader of the Reformation in Switzerland, born during a time of emerging Swiss patriotism and increasing criticism of the Swiss mercenary system. He attended the University of Vienna and the University of Basel, a scholarly center of Renaissance humanism. He continued his studies while he served as a pastor in Glarus and later in Einsiedeln, where he was influenced by the writings of Erasmus.





















































































