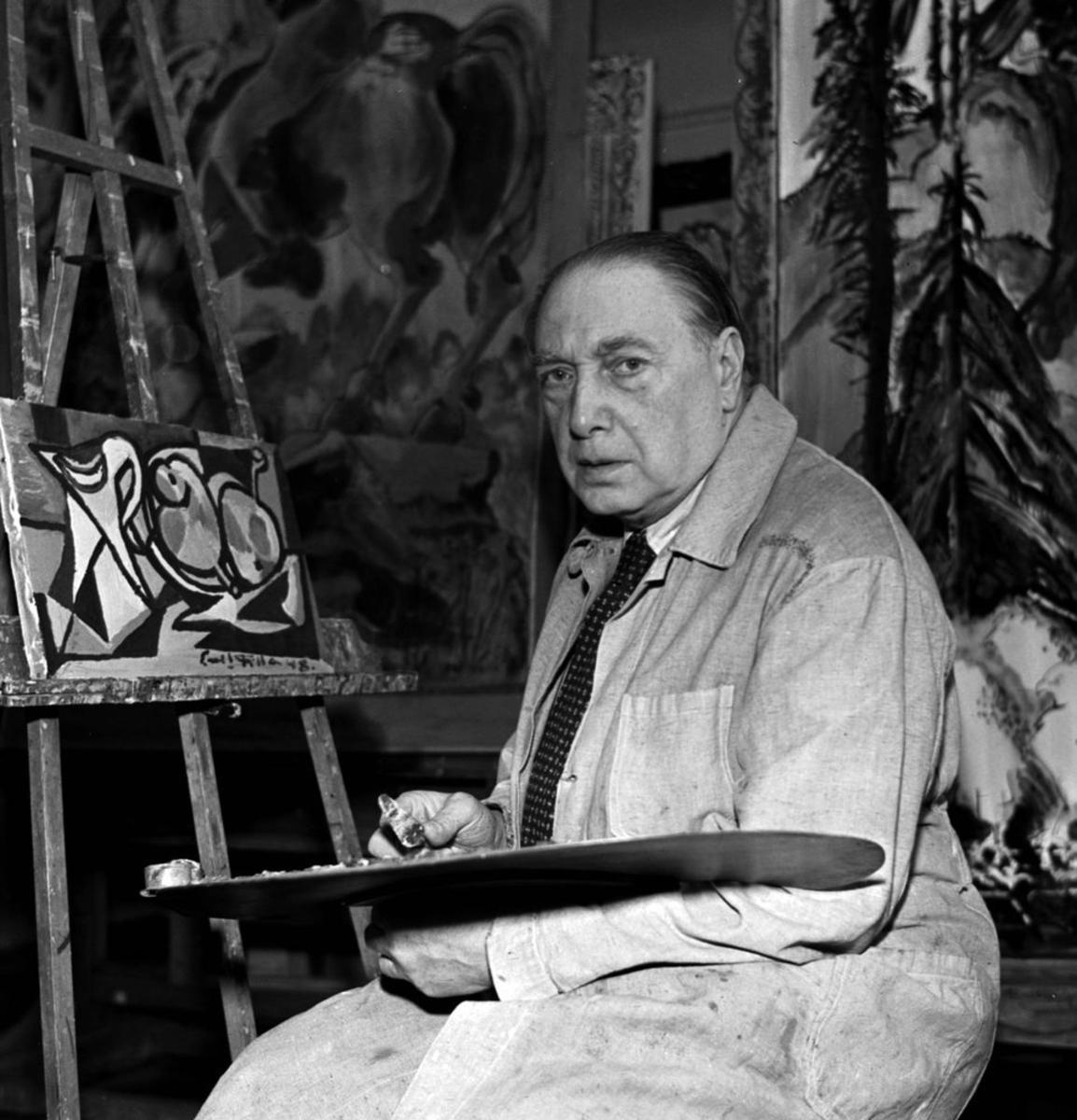
Eastern Europe — Auction price
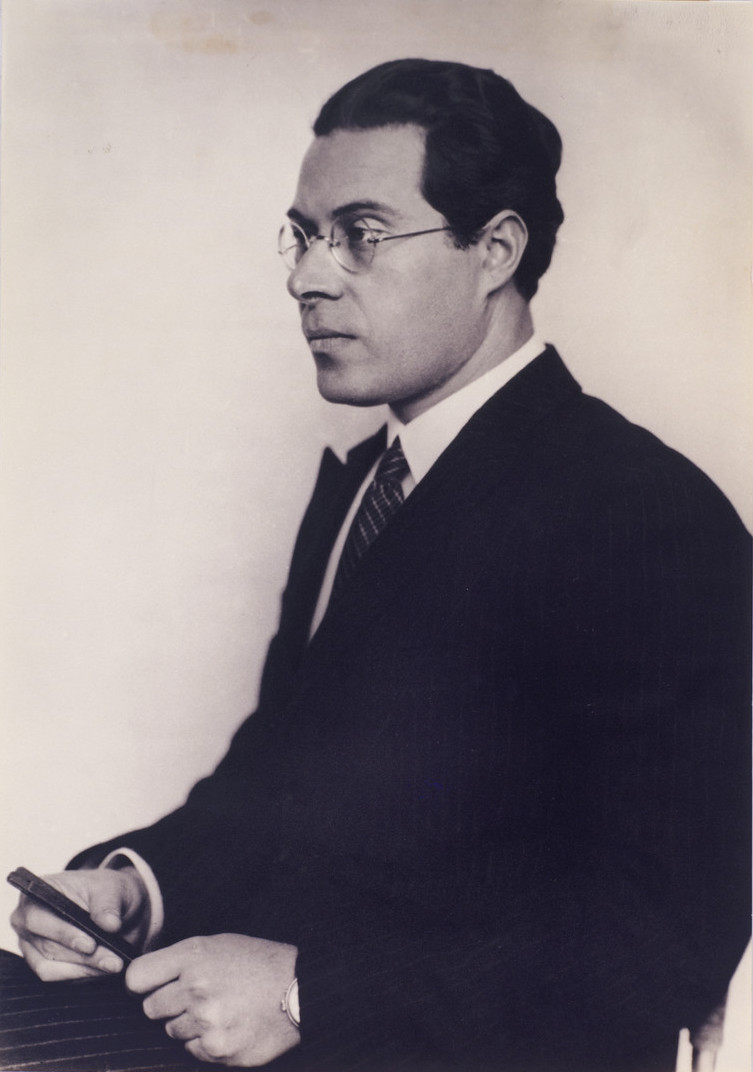



Laszlo Moholy-Nagy, a Hungarian-American artist, was a visionary in the integration of technology and art, profoundly influencing modern art education in the United States. His journey began in post-World War I Europe, where he immersed himself in the avant-garde art scene, eventually joining the Bauhaus school in Germany. There, Moholy-Nagy embraced various mediums, from photography and film to painting and sculpture, pioneering the movement known as the New Vision, which emphasized the unique perspectives that photography and film could offer compared to the human eye.
Laszlo Moholy-Nagy's innovative approach extended to photograms, a camera-less photographic technique that captures the shadows and silhouettes of objects placed on photosensitive paper. His exploration of light and shadow in this medium underscored his belief in the transformative power of art and technology. Beyond his technical achievements, Moholy-Nagy was a dedicated educator, shaping future generations of artists at the Bauhaus and later in Chicago, where he founded the New Bauhaus, which evolved into the Illinois Institute of Technology's Institute of Design.
His work is celebrated in various prestigious collections, including MoMA and the Smithsonian American Art Museum, where his contributions to modernism and design are acknowledged and revered. Moholy-Nagy's legacy is not only in his artistic output but also in his profound impact on art education and the philosophical discourse around art and technology.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Laszlo Moholy-Nagy's work offers a deep dive into the intersection of art, technology, and education. To stay informed about exhibitions and auctions related to Moholy-Nagy's works, consider subscribing to updates from art galleries and auction houses, ensuring you remain connected to the evolving appreciation and understanding of this pivotal figure's contributions.
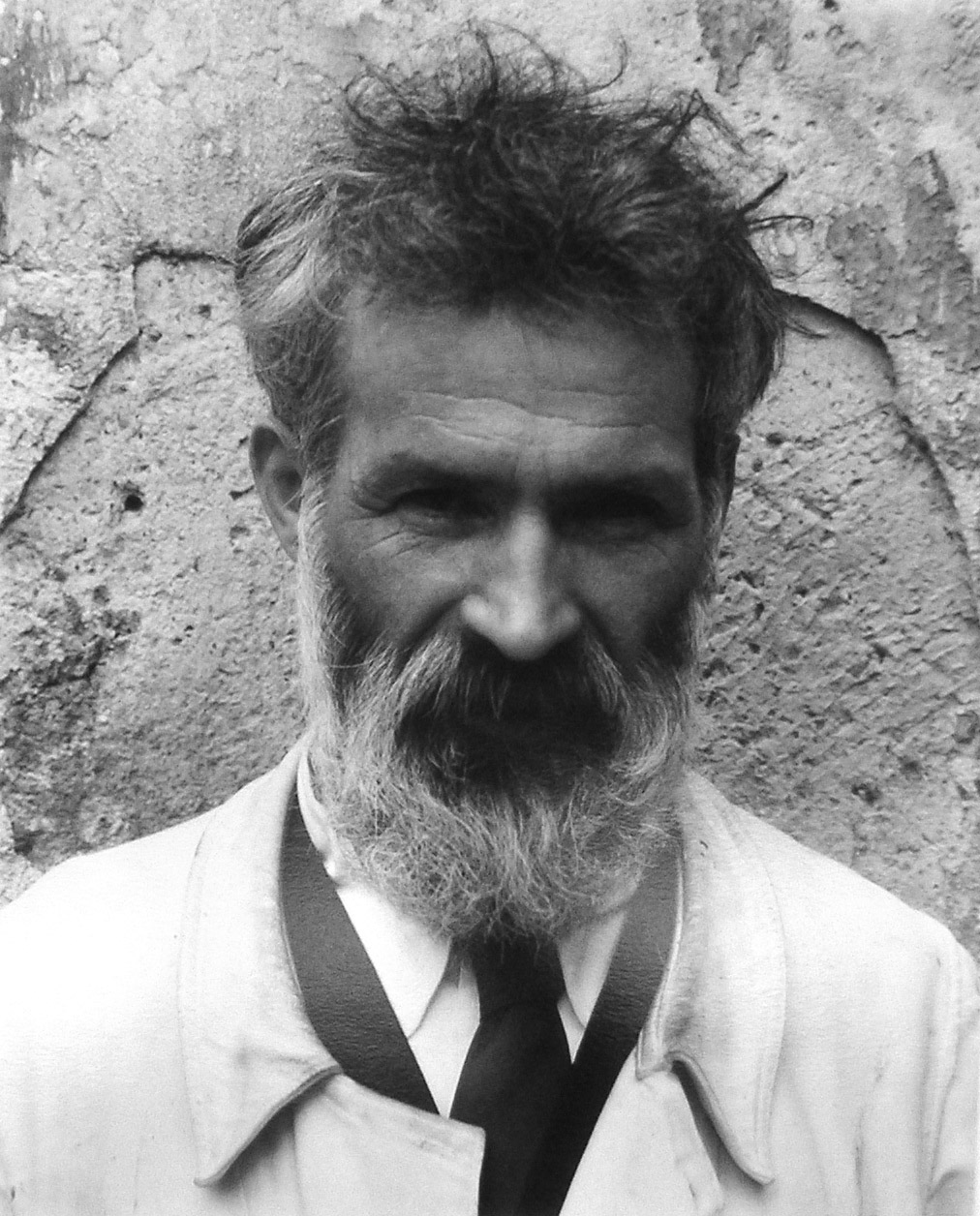


Constantin Brâncuși was a Romanian sculptor, painter, and photographer who made his career mainly in France, becoming one of the pivotal figures of modern sculpture and a pioneer of modernism. Born in 1876 in Hobița, Romania, Brâncuși displayed a talent for carving from a young age, a skill honed during his early life as a shepherd in the Carpathian Mountains. His work evolved from traditional forms to groundbreaking abstract sculptures that sought to capture the essence rather than the literal representation of his subjects.
After moving to Paris in 1904, Brâncuși's unique style began to take shape. He worked briefly in the studio of Auguste Rodin, but soon left to pursue his own vision, stating that "Nothing can grow under big trees." This decision marked the beginning of his pursuit to distill forms to their simplest essence, a philosophy that would define his career. Brâncuși's sculptures, such as "The Kiss" and "Bird in Space," are celebrated for their smooth, simplified forms that evoke the core of the subject matter with minimal detail. His work in wood, bronze, and marble often carried a serene, timeless quality, blending modernist aesthetics with a touch of his Romanian heritage.
Brâncuși's contributions to art were not limited to sculpture. He was also an accomplished photographer, using his camera to capture the spatial relationships and compositions of his studio and sculptures, an extension of his artistic vision. His works are held in high regard worldwide and are featured in prominent collections, such as the Museum of Modern Art in New York and the Tate in the United Kingdom.
The legal battle over "Bird in Space" in 1927 highlighted the challenges Brâncuși faced in having his work recognized as art by traditional standards. This case, which eventually ruled in his favor, established a precedent for modern art's recognition beyond traditional forms and representations.
For art collectors and experts, Brâncuși's oeuvre represents a bridge between the tactile craftsmanship of earlier periods and the conceptual, form-driven concerns of modern art. His legacy is a testament to the power of innovation, vision, and the enduring appeal of simplicity in form.
For those interested in the evolution of sculpture and the role of art in transcending cultural and temporal boundaries, Constantin Brâncuși's work offers profound insights. We invite you to sign up for updates on new product sales and auction events related to Brâncuși's work, ensuring you stay informed about opportunities to engage with the legacy of this pioneering artist.
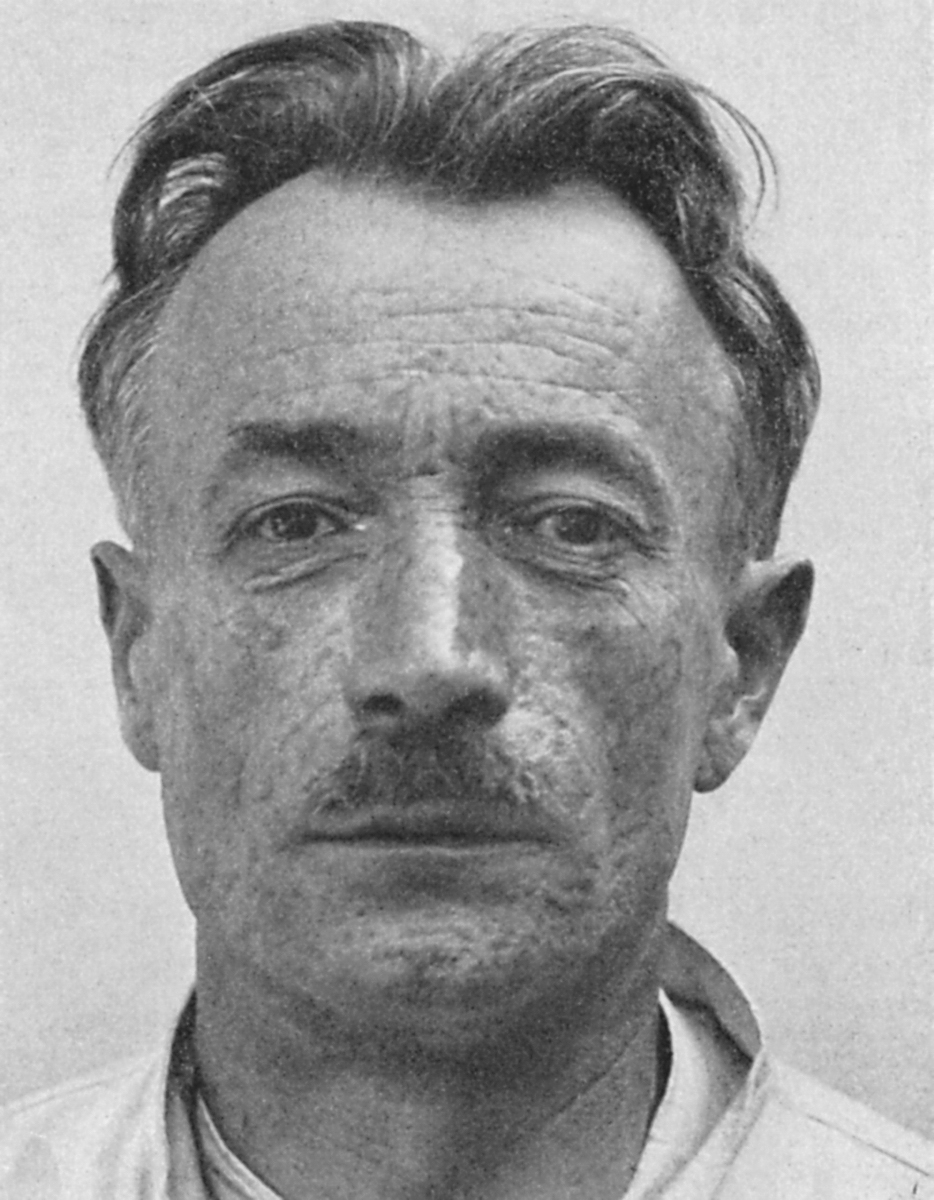


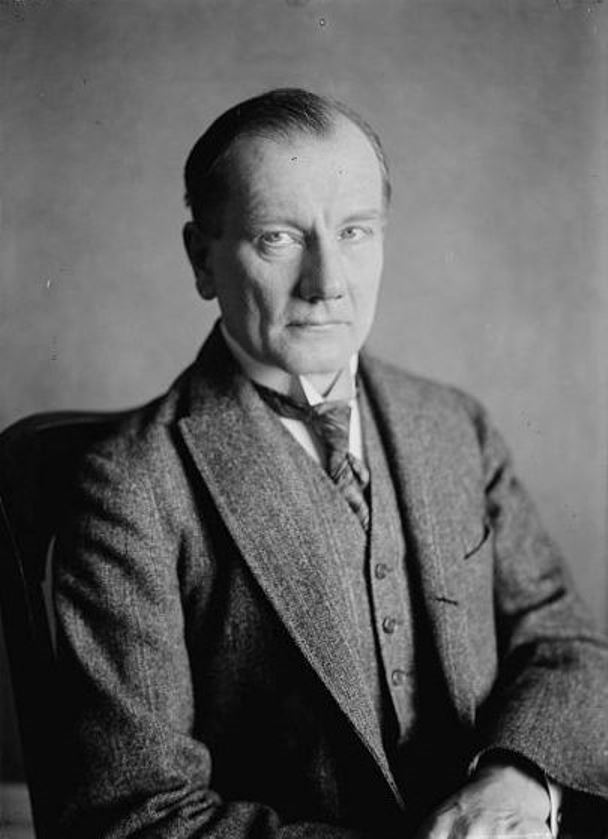
František Kupka was a Czech painter and graphic artist. He was a pioneer and co-founder of the early phases of the abstract art movement and Orphic Cubism (Orphism). Kupka's abstract works arose from a base of realism, but later evolved into pure abstract art.
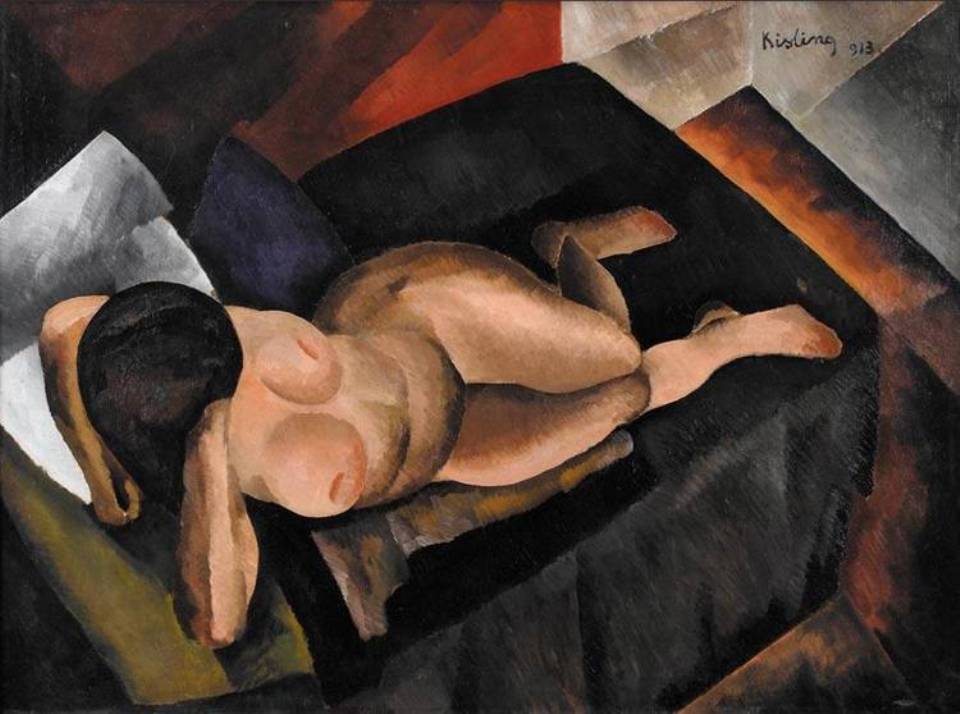


Moïse Kisling was a Polish-born French painter renowned for his contributions to modern art, particularly his highly stylized and evocative portraits. Born in Kraków in 1891, Kisling moved to Paris at the age of 19, quickly immersing himself in the vibrant artistic community of Montmartre and Montparnasse. His work, characterized by bold colors and dynamic compositions, spans a variety of themes, including landscapes, still lifes, and nudes, reflecting influences from Cubism and Post-Impressionism.
Kisling's artistry is celebrated for its unique blend of realism and abstraction, marked by a fluid, colorful style that evolved from his early influences, including Cezanne and Cubism. He was a central figure in the School of Paris, engaging with contemporaries such as Pablo Picasso, Georges Braque, and Amedeo Modigliani, the latter of whom he shared a close friendship and mutual artistic admiration. Modigliani's portraits of Kisling underscore their deep personal and professional bond. Notable works by Kisling include "La Sieste à Saint-Tropez," "Portrait du peintre (Autoportrait)," and "Le pêcheur," showcasing his versatility and skill in capturing the essence of his subjects.
During World War II, Kisling's Jewish heritage forced him to flee to the United States, where he continued to exhibit his work in New York City and California before returning to France after the war. His legacy is preserved in numerous public collections, including the Metropolitan Museum of Art, the National Gallery of Art, and the Brooklyn Museum, among others. This wide recognition attests to his significant impact on the development of modern art.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Kisling's work represents a pivotal intersection of cultural and artistic movements of the early 20th century. His paintings are not only visually stunning but also historically significant, embodying the spirit of an era marked by innovation and experimentation. The Musée du Petit Palais in Geneva holds a large collection of his works, offering a comprehensive overview of his artistic journey.
We invite enthusiasts and collectors to stay updated on new discoveries, sales, and auction events related to Moïse Kisling's work. Subscribing to updates ensures you won't miss the opportunity to engage with the rich legacy of this remarkable artist. This subscription is a gateway to exploring the vibrant world of Kisling's art, from his captivating portraits to his lush landscapes and still lifes, all of which continue to enchant and inspire.
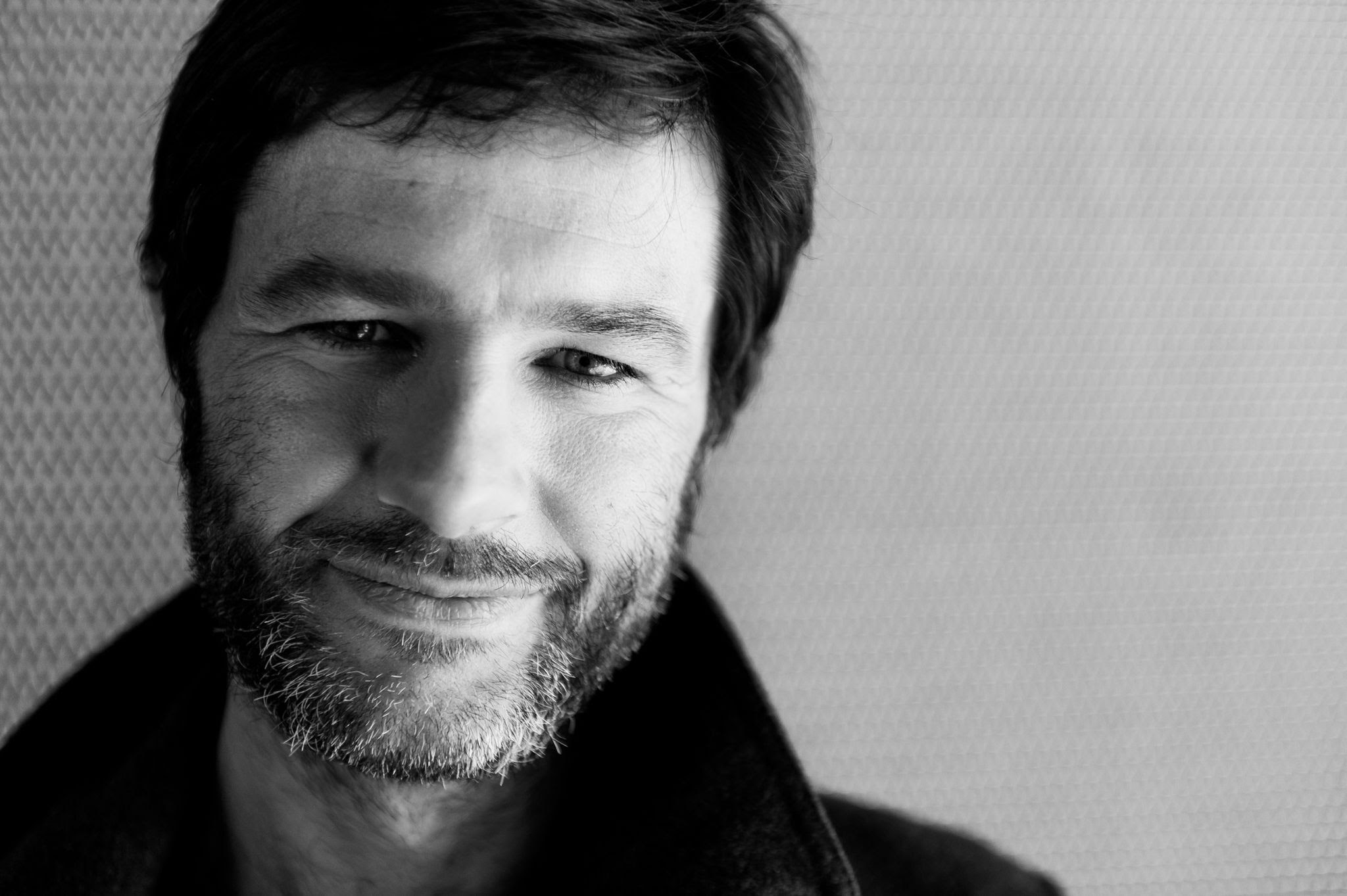


Wilhelm Sasnal is a Polish painter, photographer, poster artist, illustrator and filmmaker.
Sasnal graduated from the Academy of Fine Arts in Krakow, specializing in painting. Besides painting, he creates drawings in pencil and ink. The artist takes his subjects from everyday life, using images from media, propaganda and pop culture. Sasnal often paints from photographs and moves freely from figurative painting to abstraction.
Wilhelm Sasnal is considered one of the most prominent and internationally successful Polish contemporary artists.
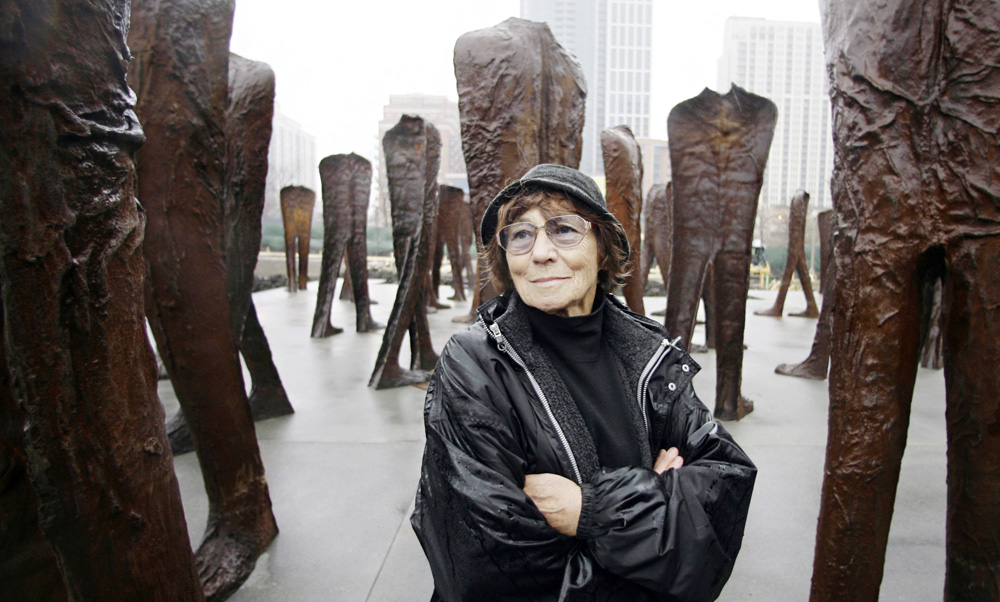


Magdalena Abakanowicz was a distinguished Polish artist, celebrated for her innovative use of textiles as a sculptural medium. Born on June 20, 1930, in Falenty, Poland, and passing away on April 20, 2017, in Warsaw, she carved out a significant place in the art world with her unique artistic expressions that often explored themes of crowd behavior, the trauma of war, and the individuality of the human condition.
Abakanowicz's education at the Academy of Fine Arts in Warsaw was a period of both artistic and personal growth, shaping her future works. During the 1960s, she began creating the "Abakans," large-scale textile sculptures that challenged conventional forms and expressed dynamic movement and vivid emotion. Her works often featured organic, tactile materials like burlap, resin, and wood, which added a profound depth and rawness to her sculptures.
Her sculptures are well-represented in major public installations and collections worldwide, including the National Museum in Wrocław, Poland, Grant Park in Chicago, and the National Gallery of Art Sculpture Garden in Washington, D.C. These pieces are not just art forms but are experiences, inviting viewers to explore deeper psychological and existential themes.
For those captivated by the profound impact and the stirring beauty of Magdalena Abakanowicz's work, subscribing for updates can provide regular insights and information on exhibitions and sales of her works at auctions. This is an excellent way to stay connected with the legacy of an artist who continuously redefined the boundaries of sculpture and installation art.