armorial &
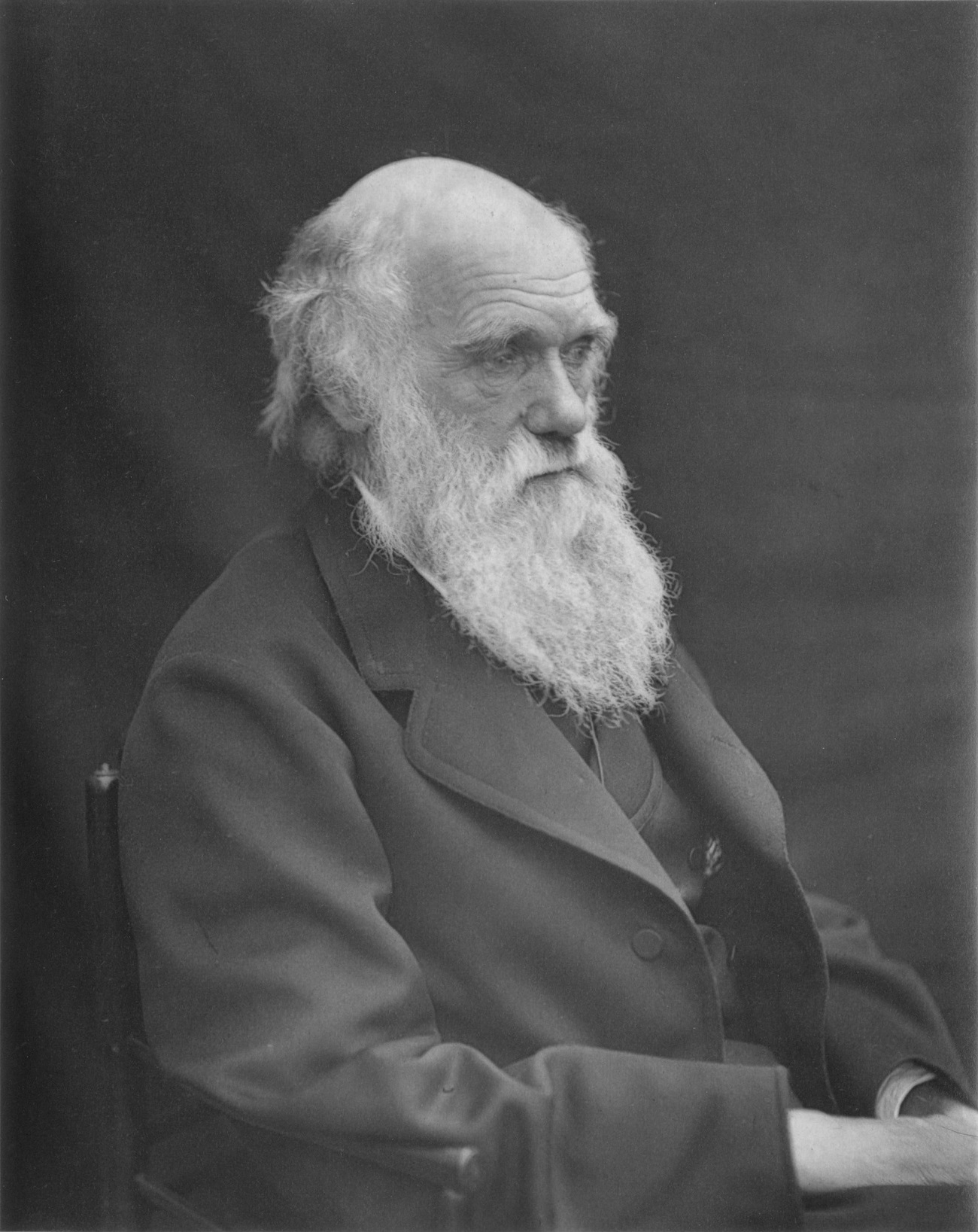

Charles Robert Darwin was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for contributing to the understanding of evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended from a common ancestor is now generally accepted and considered a fundamental concept in science. In a joint publication with Alfred Russel Wallace, he introduced his scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process that he called natural selection, in which the struggle for existence has a similar effect to the artificial selection involved in selective breeding. Darwin has been described as one of the most influential figures in human history, and he was honoured by burial in Westminster Abbey.
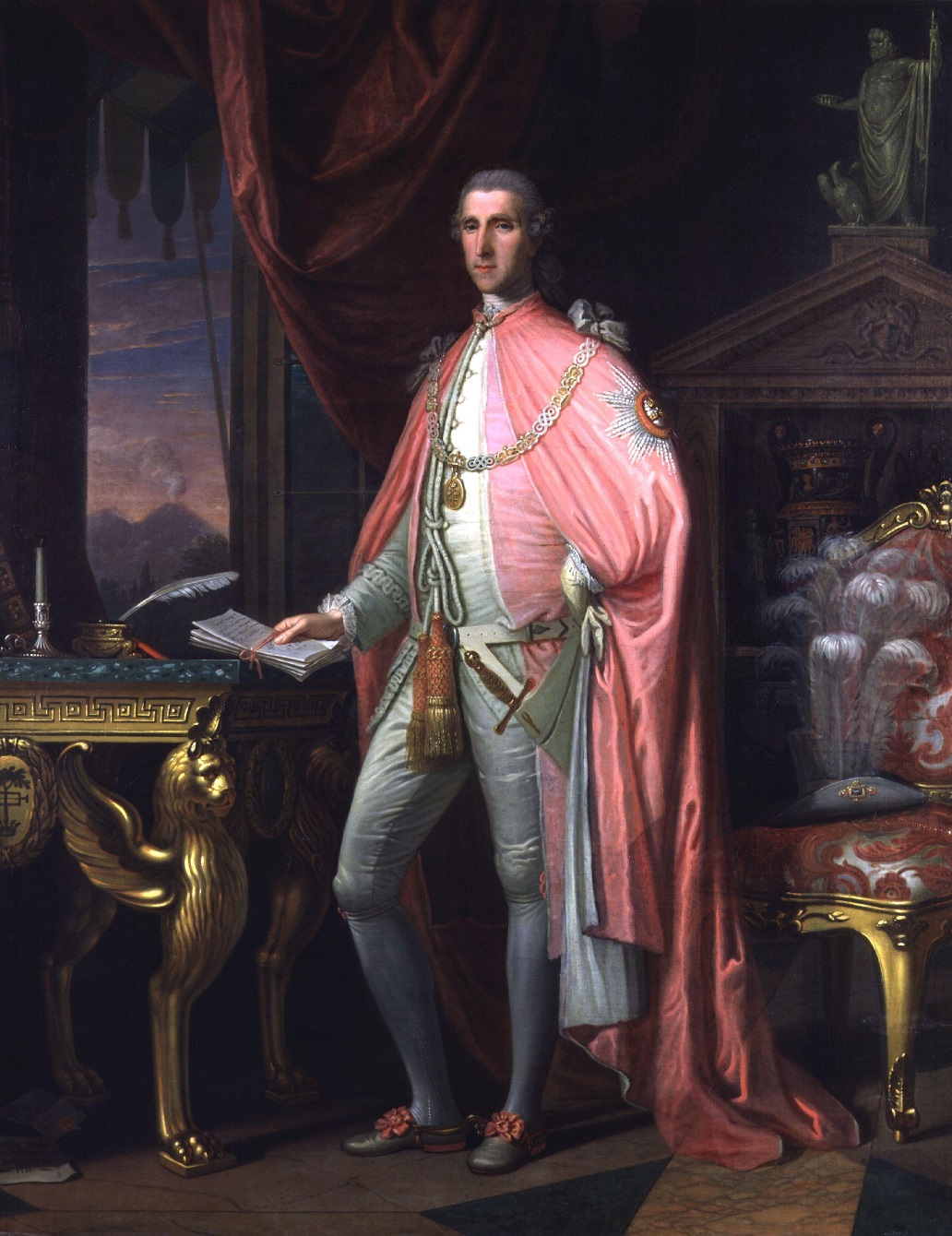


Sir William Douglas Hamilton was a British diplomat, archaeologist and volcanologist, a famous collector, and a Fellow of the Royal Society of London.
He served as British Ambassador to the Kingdom of Naples from 1764 to 1800, but most importantly, he was a passionate researcher of history, art and natural sciences and was a member of the Society of Dilettantes, established for the purpose of studying ancient art.
In Naples, Hamilton amassed a unique collection of antique vases and published an illustrated book about them. In parallel, Sir Hamilton studied the volcanoes Vesuvius and Etna, local volcanic and seismic activity, and the causes of earthquakes in the Neapolitan territory. As a corresponding member of the Royal Society, he sent the results of his research to London. His publications were very valuable for the time.
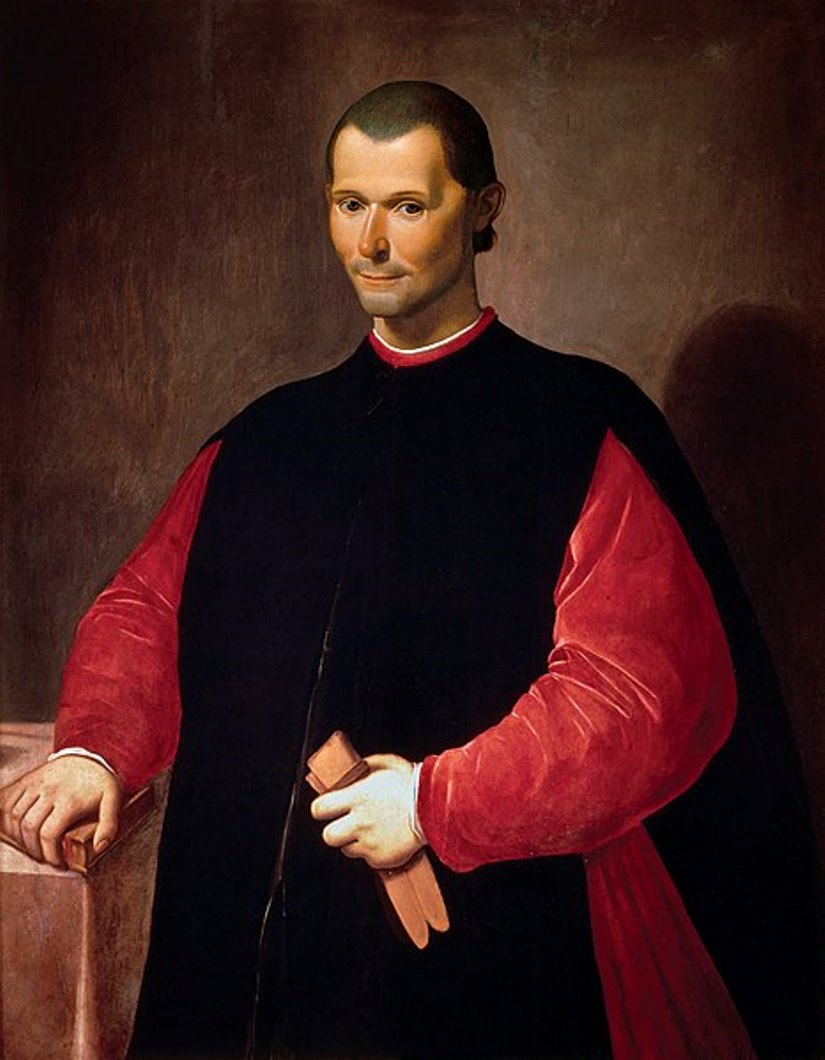


Niccolò di Bernardo Machiavelli was an Italian philosopher, politician and diplomat, historian and Renaissance writer.
As a young man, Niccolò Machiavelli faced financial difficulties due to his father's debts, but had access to a rich library. Machiavelli's early life and career began during a period of political upheaval in Italy. After the expulsion of the Medici family in 1494, for 14 years Niccolo Machiavelli served as a diplomat to the Florentine Republic. During this service, he gained a reputation as a cunning and unconventional thinker. However, when the Medici returned to power in 1512, Machiavelli was dismissed, imprisoned, and temporarily removed from political life.
During this period Machiavelli wrote his famous work The Sovereign, which has become one of the key works in the history of political philosophy. This book epitomizes the Machiavellian approach to politics, where the means justify the end, and where a leader should use any method to consolidate his power. The treatise drew criticism from the Pope, who condemned it for supporting rule through deceit and fear. Nevertheless, The Sovereign is still an important work of political literature, and Machiavelli has come to be called "the father of modern political theory."
Machiavelli lived the rest of his life in a small village near Florence, where he continued his creative endeavors, writing On the Art of War, as well as poems and plays. His literary legacy has become an integral part of the history of political philosophy.
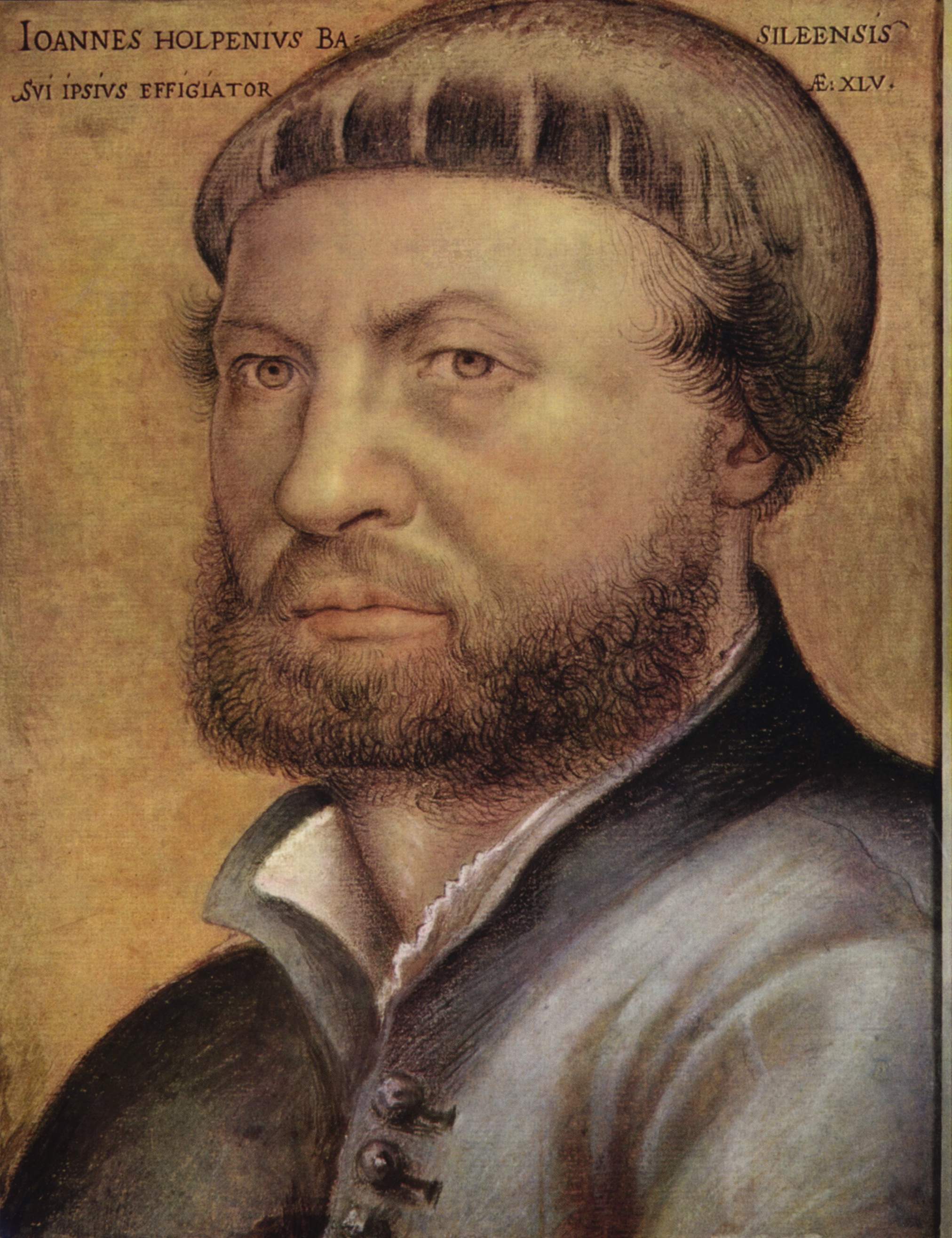






Hans Holbein the Younger was a German-Swiss painter and printmaker who worked in a Northern Renaissance style, and is considered one of the greatest portraitists of the 16th century. He also produced religious art, satire, and Reformation propaganda, and he made a significant contribution to the history of book design. He is called "the Younger" to distinguish him from his father Hans Holbein the Elder, an accomplished painter of the Late Gothic school.
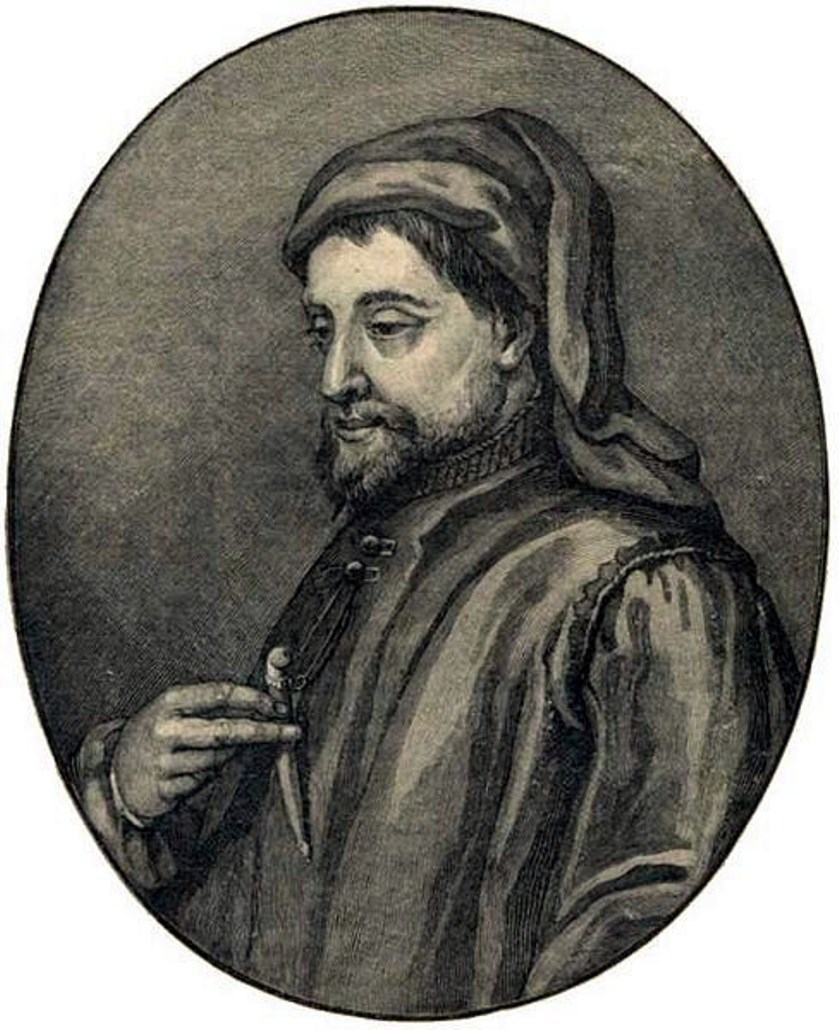


Geoffrey Chaucer was a medieval English poet and novelist, one of the founders of the literary English language.
Geoffrey Chaucer came from a wealthy family, in 1357 became a civil servant of Countess Elizabeth of Ulster and remained at the British court all his life. Later in his royal service, he traveled on diplomatic missions to France, Spain, and Italy. He made important contributions to the management of public affairs as a courtier, diplomat and civil servant. And very importantly, in these travels Chaucer was exposed to the works of Dante, Petrarch and Boccaccio, which later had a profound influence on his writing.
"The Canterbury Tales" became Geoffrey Chaucer's most famous and recognized work, although this voluminous work remained unfinished. He also wrote the popular science treatise "A Treatise on the Astrolabe", the historical poems "Troilus and Criseyde" and "Legends of Glorious Women", and many poems.
Geoffrey Chaucer is called the forerunner of the literature of the English Renaissance. He was the first to write works in his native language instead of Latin, for which he earned the title of "father of English poetry." Chaucer was buried in Westminster Abbey, and his grave became the first in the so-called "Poet's Corner", where Charles Dickens, Rudyard Kipling and Alfred Tennyson were later buried.


Geoffrey Chaucer was a medieval English poet and novelist, one of the founders of the literary English language.
Geoffrey Chaucer came from a wealthy family, in 1357 became a civil servant of Countess Elizabeth of Ulster and remained at the British court all his life. Later in his royal service, he traveled on diplomatic missions to France, Spain, and Italy. He made important contributions to the management of public affairs as a courtier, diplomat and civil servant. And very importantly, in these travels Chaucer was exposed to the works of Dante, Petrarch and Boccaccio, which later had a profound influence on his writing.
"The Canterbury Tales" became Geoffrey Chaucer's most famous and recognized work, although this voluminous work remained unfinished. He also wrote the popular science treatise "A Treatise on the Astrolabe", the historical poems "Troilus and Criseyde" and "Legends of Glorious Women", and many poems.
Geoffrey Chaucer is called the forerunner of the literature of the English Renaissance. He was the first to write works in his native language instead of Latin, for which he earned the title of "father of English poetry." Chaucer was buried in Westminster Abbey, and his grave became the first in the so-called "Poet's Corner", where Charles Dickens, Rudyard Kipling and Alfred Tennyson were later buried.
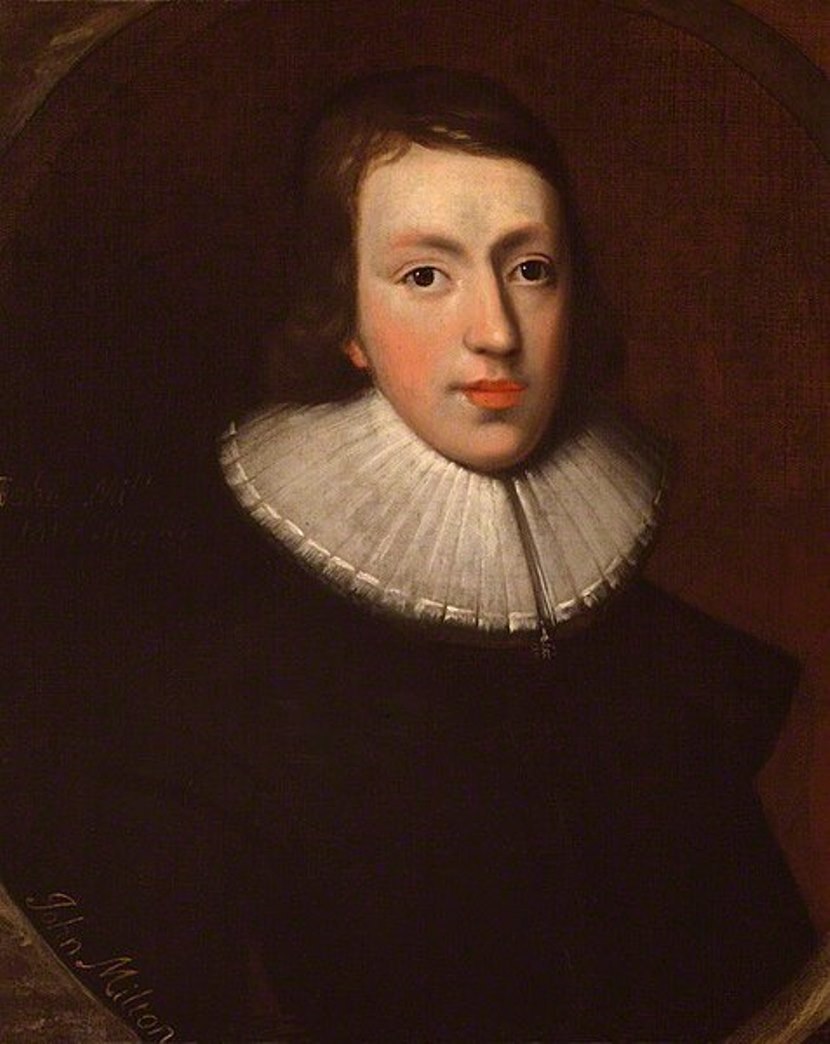


John Milton was a British poet and writer-publicist, intellectual and politician of the English Revolutionary period.
Milton first planned to become a priest, studied at Cambridge University, and then abandoned this activity. Several years he spent reading and self-education, learning many languages. In 1638 Milton traveled around the continent for about a year and a half, spending much time in Italy, primarily in Rome and Florence. He befriended young Italian literati, and his encounter with Galileo further influenced his writing.
Milton became best known for his poem Paradise Lost in Ten Books, which declares its purpose to justify the ways of God to man, but also touches on both universal and personal themes. Milton was the first author to use the word "cosmos" in our modern sense of "outer space," and his space epic takes place in a confidently Copernican universe.
In his prose works, Milton advocated the abolition of the Church of England and the execution of Charles I. From the outbreak of the English Civil Wars in 1642 and long after the restoration of Charles II as king in 1660, he spoke out against tyranny and state-sanctioned religion in all his works. As a Protestant, Milton was often in conflict with the Roman Catholic Church. As a civil servant, Milton became the voice of the English Commonwealth after 1649 and then under Oliver Cromwell, conducting international correspondence and defending the government against polemical attacks from abroad.
John Milton is considered the most important English writer after William Shakespeare. Author of political pamphlets and religious treatises, he is one of the most famous writers of the 1650s, the vibrant era of the English Revolution (Civil War).


Niccolò di Bernardo Machiavelli was an Italian philosopher, politician and diplomat, historian and Renaissance writer.
As a young man, Niccolò Machiavelli faced financial difficulties due to his father's debts, but had access to a rich library. Machiavelli's early life and career began during a period of political upheaval in Italy. After the expulsion of the Medici family in 1494, for 14 years Niccolo Machiavelli served as a diplomat to the Florentine Republic. During this service, he gained a reputation as a cunning and unconventional thinker. However, when the Medici returned to power in 1512, Machiavelli was dismissed, imprisoned, and temporarily removed from political life.
During this period Machiavelli wrote his famous work The Sovereign, which has become one of the key works in the history of political philosophy. This book epitomizes the Machiavellian approach to politics, where the means justify the end, and where a leader should use any method to consolidate his power. The treatise drew criticism from the Pope, who condemned it for supporting rule through deceit and fear. Nevertheless, The Sovereign is still an important work of political literature, and Machiavelli has come to be called "the father of modern political theory."
Machiavelli lived the rest of his life in a small village near Florence, where he continued his creative endeavors, writing On the Art of War, as well as poems and plays. His literary legacy has become an integral part of the history of political philosophy.
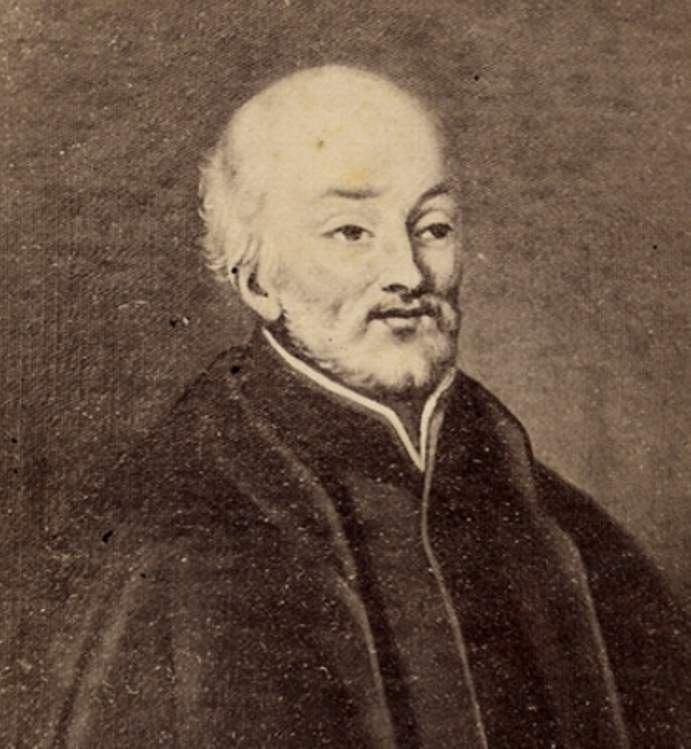






Geoffrey Chaucer was a medieval English poet and novelist, one of the founders of the literary English language.
Geoffrey Chaucer came from a wealthy family, in 1357 became a civil servant of Countess Elizabeth of Ulster and remained at the British court all his life. Later in his royal service, he traveled on diplomatic missions to France, Spain, and Italy. He made important contributions to the management of public affairs as a courtier, diplomat and civil servant. And very importantly, in these travels Chaucer was exposed to the works of Dante, Petrarch and Boccaccio, which later had a profound influence on his writing.
"The Canterbury Tales" became Geoffrey Chaucer's most famous and recognized work, although this voluminous work remained unfinished. He also wrote the popular science treatise "A Treatise on the Astrolabe", the historical poems "Troilus and Criseyde" and "Legends of Glorious Women", and many poems.
Geoffrey Chaucer is called the forerunner of the literature of the English Renaissance. He was the first to write works in his native language instead of Latin, for which he earned the title of "father of English poetry." Chaucer was buried in Westminster Abbey, and his grave became the first in the so-called "Poet's Corner", where Charles Dickens, Rudyard Kipling and Alfred Tennyson were later buried.


John Milton was a British poet and writer-publicist, intellectual and politician of the English Revolutionary period.
Milton first planned to become a priest, studied at Cambridge University, and then abandoned this activity. Several years he spent reading and self-education, learning many languages. In 1638 Milton traveled around the continent for about a year and a half, spending much time in Italy, primarily in Rome and Florence. He befriended young Italian literati, and his encounter with Galileo further influenced his writing.
Milton became best known for his poem Paradise Lost in Ten Books, which declares its purpose to justify the ways of God to man, but also touches on both universal and personal themes. Milton was the first author to use the word "cosmos" in our modern sense of "outer space," and his space epic takes place in a confidently Copernican universe.
In his prose works, Milton advocated the abolition of the Church of England and the execution of Charles I. From the outbreak of the English Civil Wars in 1642 and long after the restoration of Charles II as king in 1660, he spoke out against tyranny and state-sanctioned religion in all his works. As a Protestant, Milton was often in conflict with the Roman Catholic Church. As a civil servant, Milton became the voice of the English Commonwealth after 1649 and then under Oliver Cromwell, conducting international correspondence and defending the government against polemical attacks from abroad.
John Milton is considered the most important English writer after William Shakespeare. Author of political pamphlets and religious treatises, he is one of the most famous writers of the 1650s, the vibrant era of the English Revolution (Civil War).
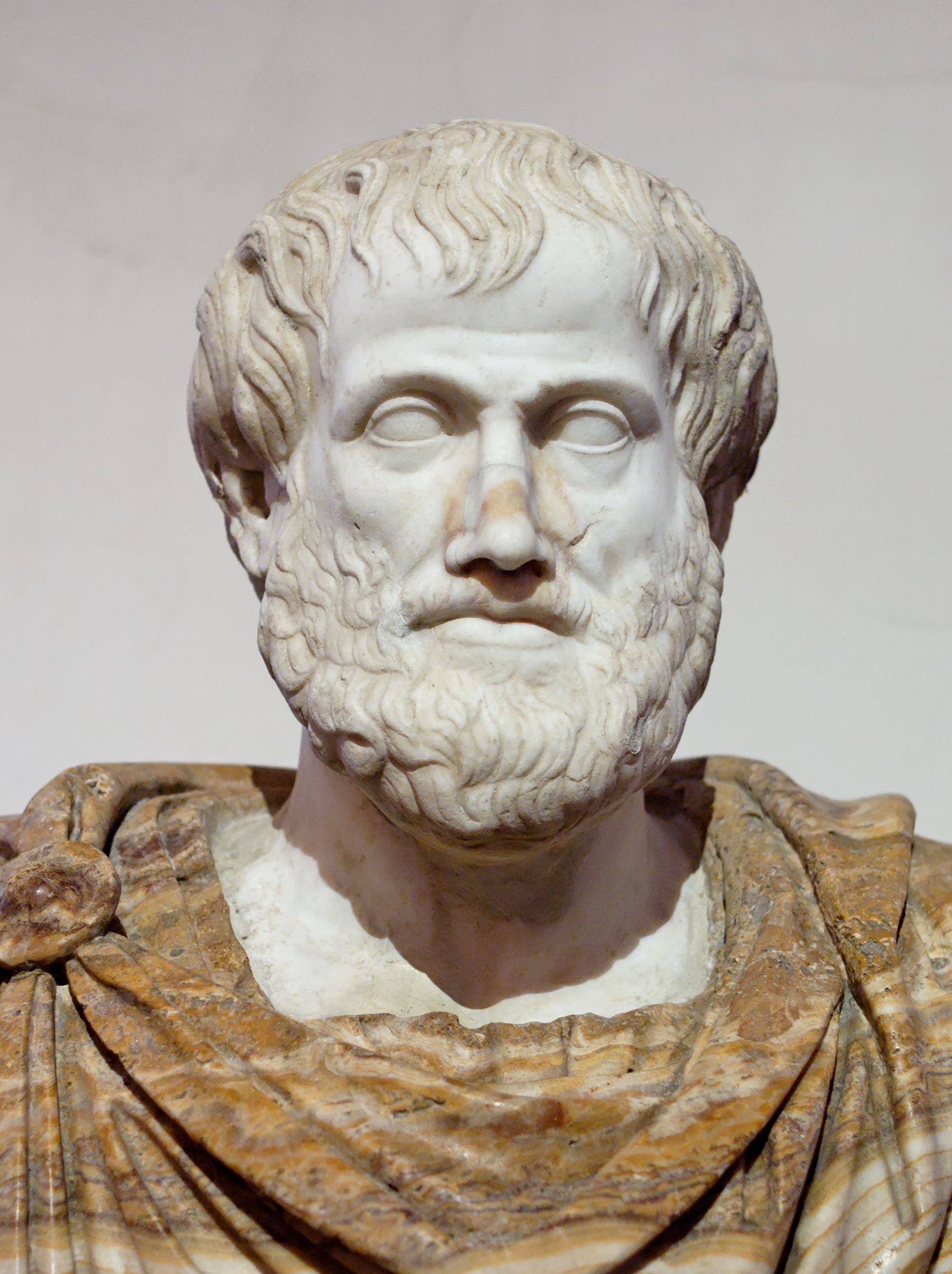


Aristotle (Greek: Ἀριστοτέλης) was an Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath, renowned for his profound impact on Western philosophy and science. Born in Stagira, Chalcidice, Aristotle's intellectual ventures spanned a multitude of subjects, including but not limited to physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology.
Educated in Plato's Academy in Athens, Aristotle distinguished himself as a scholar of vast knowledge and influence. His foundational works laid the groundwork for the development of modern science, while his teachings on logic and the syllogistic method continue to resonate in the realm of philosophy. As the tutor of Alexander the Great and the founder of the Lyceum in Athens, Aristotle's legacy extends beyond his prolific writings, with his teachings shaping medieval scholarship and influencing both Judeo-Islamic and Christian theologies.
Among Aristotle's notable works, his treatises such as "Nicomachean Ethics," "Politics," "Metaphysics," and "Poetics" have been studied for centuries. His concept of the "Golden Mean," advocating for a balanced and moderate approach to life, remains a cornerstone of ethical philosophy. His ideas on the "Prime Mover" and empirical evidence as a basis for understanding the world laid the foundation for scientific inquiry. Although only about a third of his original output has survived, Aristotle's contributions continue to be a subject of academic study and admiration.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, the philosophical and scientific principles of Aristotle's works are not just historical artifacts but living ideas that continue to shape our understanding of the world and our place within it. His insights into the "good life" and the pursuit of happiness are as relevant today as they were in ancient Greece.
If you wish to stay informed about new product sales and auction events related to Aristotle, sign up for updates. This subscription is your gateway to the latest scholarly works, collections, and auctions connected to the great philosopher's legacy.












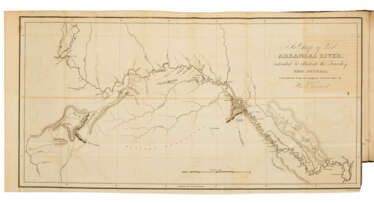
![[MARCHAND, Etienne (1755-1793)] and FLEURIEU, Charles Pierre Claret de (1738-1810).](/assets/image/picture_3615476/948e9/5adab94693e4ae36441ca19ea802e8991702422000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[MARCHAND, Etienne (1755-1793)] and FLEURIEU, Charles Pierre Claret de (1738-1810).](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3615476/948e9/5adab94693e4ae36441ca19ea802e8991702422000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)




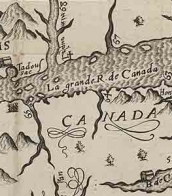
![[AURACH DE ARGENTINA, Georgius]](/assets/image/picture_3616055/bad31/b03c810ec12a6590da5b9da364e8fc261702422000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[AURACH DE ARGENTINA, Georgius]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3616055/bad31/b03c810ec12a6590da5b9da364e8fc261702422000jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)