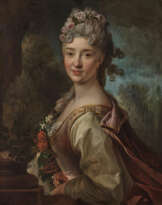ID 1336103
Lot 29 | NICOLAS DE LARGILLIERRE (PARIS 1656-1746)
Valeur estimée
€ 60 000 – 100 000
Portrait d'une femme en Uranie, de trois-quarts, près d'un globe céleste
signé 'peint par N de Largillierre' (au revers de la toile d'origine)
huile sur toile, sur sa toile d'origine
137 x 105 cm (5315/16 x 41 1/3 in.)
Provenance
Vente anonyme, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, 13 juin 1995 (Mes Loiseau, Schmitz & Digard), sans numéro de lot (p. 3) (comme école française du XVIIe siècle, atelier de Nicolas de Largillierre) ;
Acquis au cours de celle-ci par l'actuel propriétaire.
Exhibited
Perpignan, Musée d’art Hyacinthe Rigaud, Portraits en majesté. François de Troy, Nicolas de Largillierre, Hyacinthe Rigaud, 26 juin-7 novembre 2021, n°88 (comme Nicolas de Largillierre).
Further Details
NICOLAS DE LARGILLIERRE (1656-1746), PORTRAIT OF A WOMAN AS URANIA, THREE-QUARTERS, NEAR A CELESTIAL GLOBE, OIL ON CANVAS, UNLINED, SIGNED (ON THE REVERSE)
This Portrait of a Woman as Urania was painted by Nicolas de Largillierre (1656-1746) around 1718-1720, as evidenced not only by the model's hairstyle, but also by the work's execution - colour range and handling - characteristic of this period in the painter's career.
What is now considered to be a ricordo of the present painting, rediscovered in the catalogue of the sale of Madame Camille Lelong in 1903 (Galerie Georges Petit, Paris, 27-30 April 1903, lot 28), claimed that it was a representation of Gabrielle Emilie Le Tonnelier de Breteuil (1706-1749), Marquise du Châtelet, a famous woman of science and a great friend of Voltaire (1694-1778), who nicknamed her ‘la docte Uranie’. This identification of the sitter has been repeated ever since when describing the various known versions of this portrait, however, the dating of the painting, circa 1718-1720, makes this totally impossible: the supposed sitter was only between twelve and fourteen years old at the time.
We therefore need to look elsewhere for the identity of this woman, who was so interested in astronomy that she wanted to have herself painted in the guise of its muse, and who also had the financial means to buy a celestial globe of this size. Catherine Hofmann, curator at the Bibliothèque nationale de France and a specialist in astronomical globes, has identified this one (see D. Brême et al, Portraits en majesté. François de Troy, Nicolas de Largillierre, Hyacinthe Rigaud, [cat. exp.], Milan, 2021, p. 266) as the work of Willem Jansz. Blaeu (1571-1638), who produced a version 34 cm in diameter and in three different states (1598, 1603 and 1621) (fig. 1). As the globe represented by Largillierre is larger in size, it must be assumed that either a corresponding, very expensive model existed, or that the painter used poetic license to expand the smaller globe to the scale of his project.
During the first half of the 18th century, several women gave themselves or were given the nickname Uranie. The pseudonym was quite common in gallant literature of the period (Madeline Angélique de Gomez, Les journées amusantes dédiées au Roy, 1722; Soyez Destauvelles, Nouvelles lettres et œuvres galantes, 1724; Marie Huber, Le Monde fou préféré au Monde sage, 1731; etc.). Marie Marguerite d'Alègre (1688-1752), Countess of Rupelmonde, was honoured with an epistle by Voltaire in 1722, entitled Le pour et le contre, the first line of which reads: ‘Tu veux donc, belle Uranie...’.
However, in the context of the present painting, it is perhaps Louise Bénédicte de Bourbon Condé (1676-1753), Duchess of Maine, who most closely answers the necessary criteria of the sitter. Of all those who may have sat for Largillierre and his studio on more than one occasion, she was one of the most important, and we know that she was truly passionate about astronomy. Nicolas de Malézieu (1650-1727) had taught her the rudiments of this science, and the small learned society she brought together at her château in Sceaux included Fontenelle (1657-1757) - the author of the famous Entretiens sur la pluralité des mondes - and the Marquise du Châtelet, Voltaire's ‘docte Uranie’, with whom she debated the order of the universe.
During the many parties she gave at Châtenay, at Malézieu's house, or at Sceaux, the Duchesse du Maine was several times given the nickname Uranie. In a piece of verse dedicated to the princess, Nicolas de Malézieu calls her ‘adorable Uranie’, and elsewhere highlights his mistress's passion for astronomy by dedicating a song to her: ‘Pour Madame la Duchesse du Maine, un soir qu'elle vouloit observer l'étoile de Vénus’. He began another song, dedicated to the Duchesse d'Estrées, with ‘Près de la divine Uranie, // Dans son charmant Palais de Seaux...’. The famous Grandes Nuits de Sceaux (1714-1715) regularly featured celestial mechanics. On the Fifth Night (August 1714), the Duchess urged Malézieu to write her a few verses, beginning with the alexandrine ‘Daigne entendre la voix de ta chère Uranie’. But it was on the Seventh Night (September 1714) that astronomy was given pride of place at Sceaux, with the arrival - fictitious or real? - of the greatest scientists in the field. During the first interlude, Jacques Cassini (1677-1756), who would soon be credited with measuring the Paris meridian (1718); Philippe de La Hire (1640-1718) - son of the painter Laurent de La Hyre - author of a celestial planisphere (1705); and Jacques Philippe Maraldi (1665-1729), author of numerous discoveries and publications, all came to Malézieu to ask his opinion on the appearance of a new star. Cassini then addressed Malézieu, naming him ‘Worthy favourite of Urania’, and it was soon discovered that the new star that had recently appeared was none other than the Duchess of Maine.
As here, the princess was blonde and had blue eyes. She would have been about forty-five when Largillierre painted his Uranie, an age compatible with that of the model portrayed. But the identification of this muse of astronomy with the Duchess of Maine remains for the moment hypothetical. After being exiled in 1719 as part of Cellamare's conspiracy against Philippe d'Orléans (1674-1723), regent of France, the duchess returned to Sceaux in January 1720 and was keen to restore her image by leading a ‘second court of Sceaux’, which was once again very active intellectually, but much wiser politically. Largillierre's portrait may have been painted to mark this return to favour, and the princess had enough important friends and residences to ask a painter - then at the height of his fame - for two or three copies of his large allegorical portrait. Only a high-ranking person could afford to do so. However, there is as yet no documentary evidence to support this hypothesis.
All quotations are taken from the Suite des Divertissemens de Sceaux, contenant des Chansons, des Cantates & autres Pieces de Poësie. Avec la description des Nuits qui s'y sont données, & les Comedies qui s'y sont jouées, Paris, 1725, pp. 38, 93, 108, 142 and 162.
| Artiste: | Nicolas de Largillière (1656 - 1746) |
|---|---|
| Technique appliquée: | Huile sur toile |
| Style artistique: | Vieux Maître |
| Genre: | Portrait |
| Lieu d'origine: | Europe de l'Ouest, France, Europe |
| Catégorie maison de vente aux enchères: | Peintures, Aquarelles, Dessins, Peintures |
| Artiste: | Nicolas de Largillière (1656 - 1746) |
|---|---|
| Technique appliquée: | Huile sur toile |
| Style artistique: | Vieux Maître |
| Genre: | Portrait |
| Lieu d'origine: | Europe de l'Ouest, France, Europe |
| Catégorie maison de vente aux enchères: | Peintures, Aquarelles, Dessins, Peintures |
| Adresse de l'enchère |
CHRISTIE'S 8 King Street, St. James's SW1Y 6QT London Royaume-Uni | |
|---|---|---|
| Aperçu |
| |
| Téléphone | +44 (0)20 7839 9060 | |
| Commission | see on Website | |
| Conditions d'utilisation | Conditions d'utilisation |