early systems
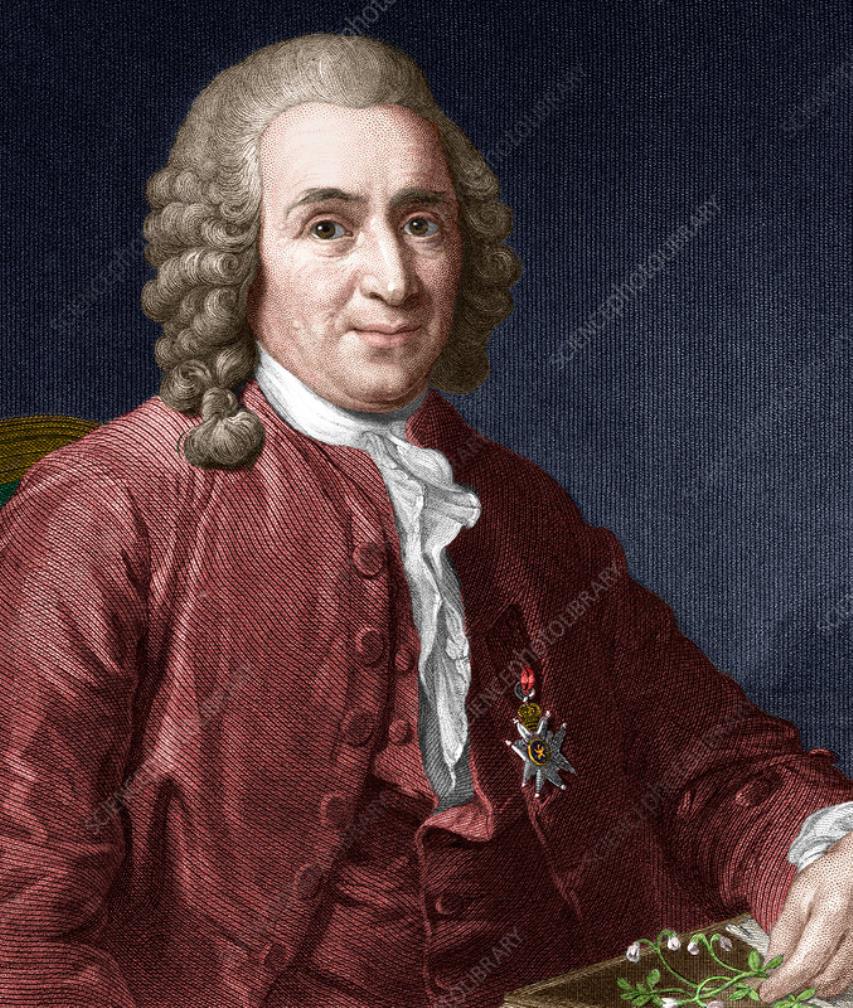

Carl Linnaeus was a Swedish naturalist, botanist and physician.
Carl Linnaeus created a unified system of classification of flora and fauna, in which he summarized and organized the knowledge of the entire previous period of development of biological science. He was the first to formulate the principles of definition of living beings of natural nature and created a unified system of their names, binary nomenclature. Linnaeus' book "The System of Nature", first published in 1735, is one of the most important books in the history of science and practically opened the classification of plants and animals.
Linnaeus was a professor at Uppsala University for many years, and he is also valued in Sweden as one of the creators of the literary Swedish language in its modern form. In addition to his work in botany and scientific classification, Linnaeus led many activities for the betterment of his native country. He was also involved in the establishment of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences.
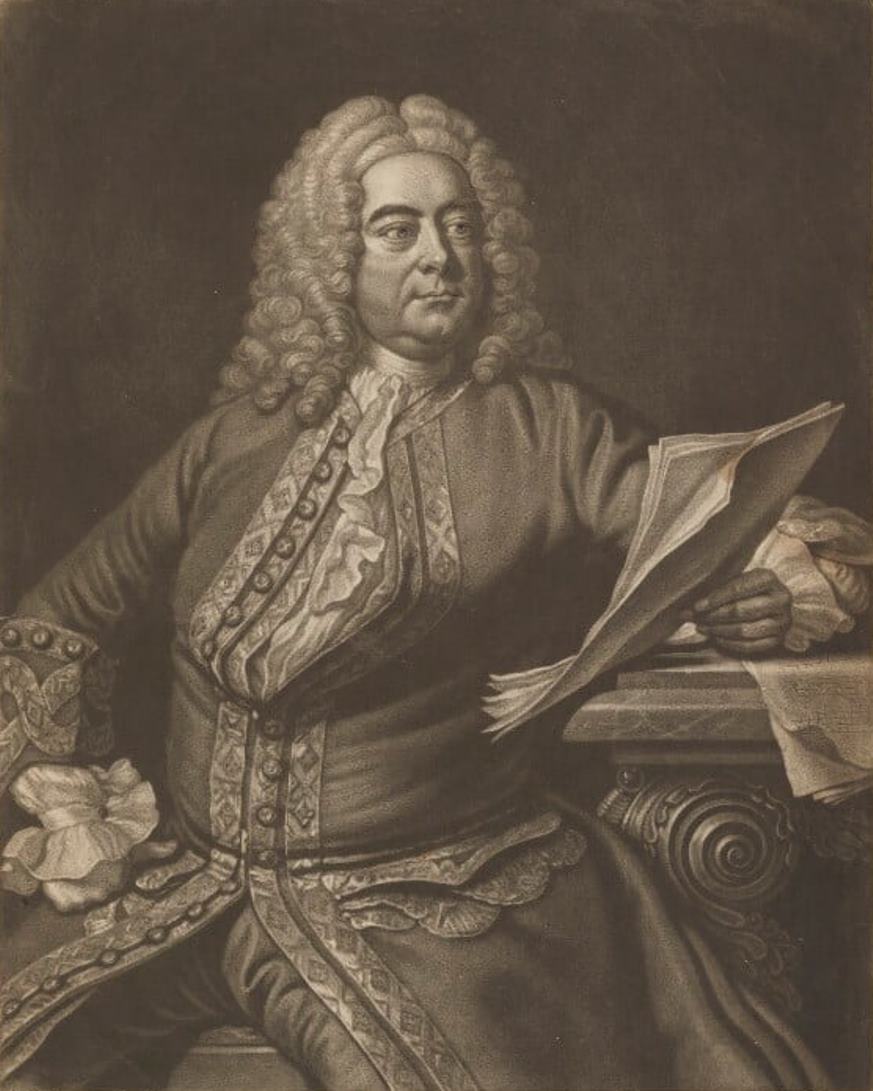




George Frideric Handel was a German-born English composer of the Baroque period.
After receiving a musical education, Handel worked briefly as an organist at the cathedral in Halle, then joined the violin section of the opera orchestra in Hamburg. After spending several years in Italy, he wrote many works there, including two operas. The style of Italian music permeated the composer's work throughout his life. Having become famous in Italy, in 1710 Handel was appointed Kapellmeister to the Elector of Hanover, the future King George I of England, and two years later he was already staging his operas in London.
In 1727 Handel became a British subject and was appointed composer to the Chapel Royal. In this capacity he wrote many musical works. From 1720 to 1728, operas at the Royal Theater in London were staged by the Royal Academy of Music, and Handel wrote the music for most of them.
In 1741, Handel wrote the most famous of his many oratorios, Messiah. Handel had a talent for musically portraying a human character in a single scene or aria - a gift he used with great dramatic power in his operas and oratorios. Although much of his music was vocal, Handel was also one of the recognized instrumental composers of the late Baroque era. Handel paid tribute to church music by composing many solemn hymns.
Handel's music has become an integral part of the national culture of England, and in Germany he is also honored as a major national composer.
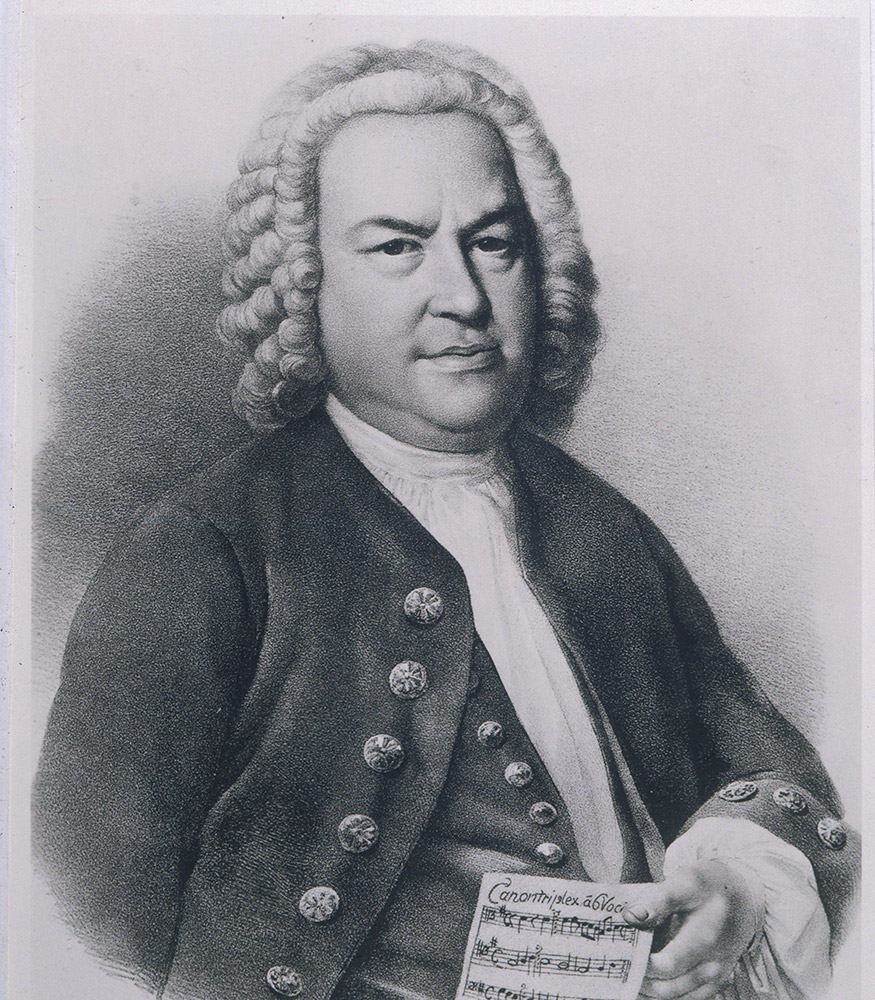


Johann Sebastian Bach was a German Baroque composer, Kapellmeister, organist and teacher.
Johann Sebastian Bach was the youngest child in the family of musician Johann Ambrosius Bach (1645-1695) and belonged to a large family of North German musicians whose dynasty he himself traced back to his great-great-grandfather Veit Bach, a Lutheran baker in the late 16th century. Johann was orphaned at an early age and was taken into care by his older brother, the organist Johann Christoph Bach. In August 1703 he was appointed official organist of the church in Arnstadt, then from 1714 he worked as Kapellmeister and concertmaster at the Weimar court, to which time his first compositions date. In 1736 he was appointed court composer to the King of Saxony, thus recognizing his merits as a composer and organist. While working as a concertmaster, Bach also mastered almost all the instruments in the orchestra.
In the last years of his life, Bach was nearly blind and living poorly, and his Baroque music was considered outdated as tastes changed. But in the 19th century, interest in Bach's works increased dramatically, and he became the favorite composer of many subsequent musicians. Johann Sebastian's sons Wilhelm Friedemann, Carl Philipp Emanuel and Johann Christian continued the family dynasty and also became musicians. And Johann Sebastian Bach himself was surrounded by students throughout his life.
Although his contemporaries admired Bach's playing on the harpsichord and organ, today it is his compositions that are considered some of the finest works of mature Baroque music. His most widely known works today include the Brandenburg Concertos, the Well-Tempered Clavier, the Masses in B minor, and many other masterpieces of church and instrumental music. Bach's rich legacy includes sacred and secular compositions, especially cantatas, organ pieces and concertos (Bach composed more than 1,000 musical works in all significant genres of his time, except opera), which influenced many later composers. Johann Sebastian Bach was able to encompass and unite the major styles, forms and national traditions developed in previous generations. Today he is considered one of the greatest composers of all time.


Ludwig van Beethoven was a German composer, pianist, and conductor, one of the most famous and celebrated composers in world history.
Beethoven showed an aptitude for music at a very early age; from the age of four his father began to teach him. Beethoven's early works - piano sonatas and symphonies - were composed under the strong influence of the music of the great classical composers Joseph Haydn and Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart. As Beethoven matured, however, he began to experiment with new forms and harmonic sequences, and his music became more complex and emotionally charged.
Unfortunately, at the height of his talent, Beethoven began to gradually lose his hearing, to the point of complete deafness by the end of his life. Despite this, he continued to compose and conduct, using special devices to feel the vibrations of the music.
Beethoven's work is considered pivotal in classical music and is a bridge between the classical and Romantic eras. His works vividly express a wide range of emotions, from triumph and joy to sadness and despair. Beethoven was also one of the first composers to include soloists and chorus in his symphonies. Beethoven's best-known works include nine symphonies, 32 piano sonatas, 16 string quartets and the heroic opera Fidelio. These and many other works have cemented Beethoven's place in music history as one of the greatest composers of all time. His music continues to be played and studied by musicians and music lovers around the world.


Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are together the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius".
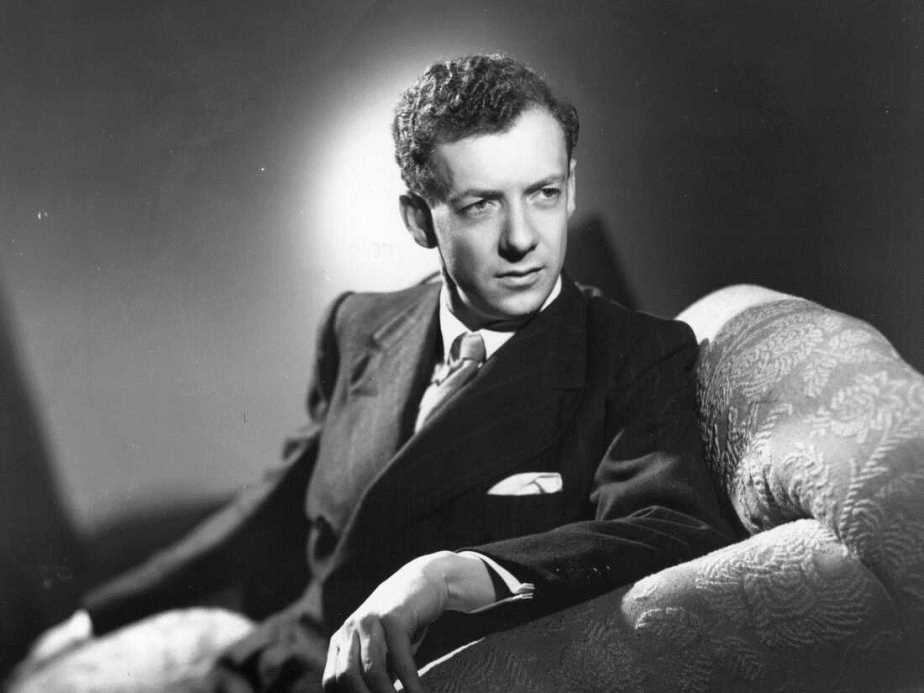



Benjamin Britten, full name Edward Benjamin Britten, Baron Britten, was a British composer, conductor and pianist.
Britten studied at the Royal College of Music in London, and had already written a set of choral variations, A Boy is Born (1933). He then worked as a composer for radio, theater and film, working closely with the poet W.H. Auden. His Variations on a Theme of Frank Bridge for string orchestra received international acclaim in 1937. Between 1939 and 1942 Britten worked in the United States, where he composed several significant works.
His later operas include The Rape of Lucretia (1946), the comic Albert Herring (1947), Billy Budd (1951), Gloriana (1953, written for the coronation of Queen Elizabeth II), and A Midsummer Night's Dream (1960). These and other works established his reputation as a leading British composer of the mid-20th century, whose operas are considered the best English works in the genre.
His song cycles occupy a significant place in Britten's oeuvre, and his largest choral work is War Requiem (1962) for chorus and orchestra. The composer wrote the Symphony in D major for cello and orchestra (1963) especially for the famous Russian cellist Mstislav Rostropovich. Britten's best-known works also include the opera Peter Grimes (1945) and the orchestral production The Young Person's Guide to the Orchestra (1945).
In addition to his work as a composer, Britten performed as a pianist and conductor, touring internationally and visiting the USSR on several occasions.
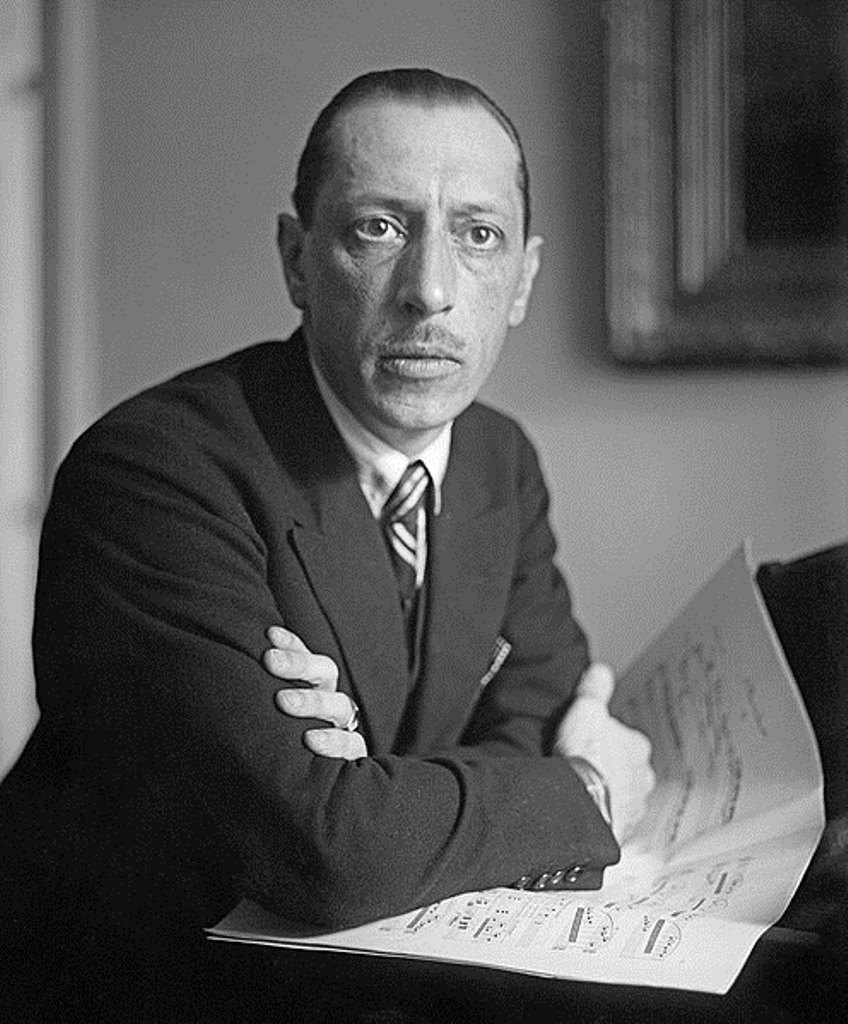


Igor Fedorovich Stravinskii (russian: Игорь Фёдорович Стравинский) was a Russian composer, a citizen of France and the United States. One of the greatest representatives of the world musical culture of the 20th century.
The future composer was born into a creative musical family. Igor Stravinskii's father was an opera singer, soloist of the Mariinsky Theater Fedor Stravinskii, and his mother was a pianist Anna Kholodovskaya. Igor studied music at home, the Stravinskiis were often visited by their friends: composers Caesar Cui and Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov, critic Vladimir Stasov and writer Fyodor Dostoevsky. For five years from 1902 Igor Stravinsky studied with the composer Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov. At the same time he became close to the impresario Sergei Diaghilev and the artists of the "World of Art" association.
Stravinskii 's first works were created under the influence of Rimsky-Korsakov and the French Impressionists, and his music bears a vivid imprint of the Russian cultural tradition. Igor Stravinskii's first ballet, The Firebird, was performed in June 1910 at the Paris Grand Opera House, and he later wrote music for Diaghilev's ballets Petrushka (1911) and Sacred Spring (1913). It was after the premiere of his ballets at Sergei Diaghilev's Russian Seasons in Paris that Stravinskii gained worldwide fame. The sets for his ballets were created by the artists Alexander Benois and Nikolai Roerich, the choreography was prepared by the famous dancers Vaclav Nijinsky and George Balanchine, and the costumes were designed by Coco Chanel herself.
In 1920 Stravinskii moved to France and in 1934 he took French citizenship. In Paris, the composer composed many works that became world-famous. In 1939 Igor Stravinskii moved to the United States and in 1945 he took American citizenship. During this period, he began to turn more to biblical themes and music of the pre-Brahmsian period.
From 1924 Stravinskii also performed as a pianist and conductor of his own works. In 1962, at the invitation of the USSR Ministry of Culture, Igor Stravinsky gave several concerts in Moscow and Leningrad (now St. Petersburg).
Critics believe that in recent years Stravinskii was moving further and further away from the Russian style, but the composer himself believed otherwise. On the basis of Russian folk songs, in 1965 he created a canon for orchestra, "Not a Pine Tree at the Gate Rocked". A year before his death, in 1966, the composer wrote the requiem "Funeral Chants", which he considered to be one of the major works of his life.
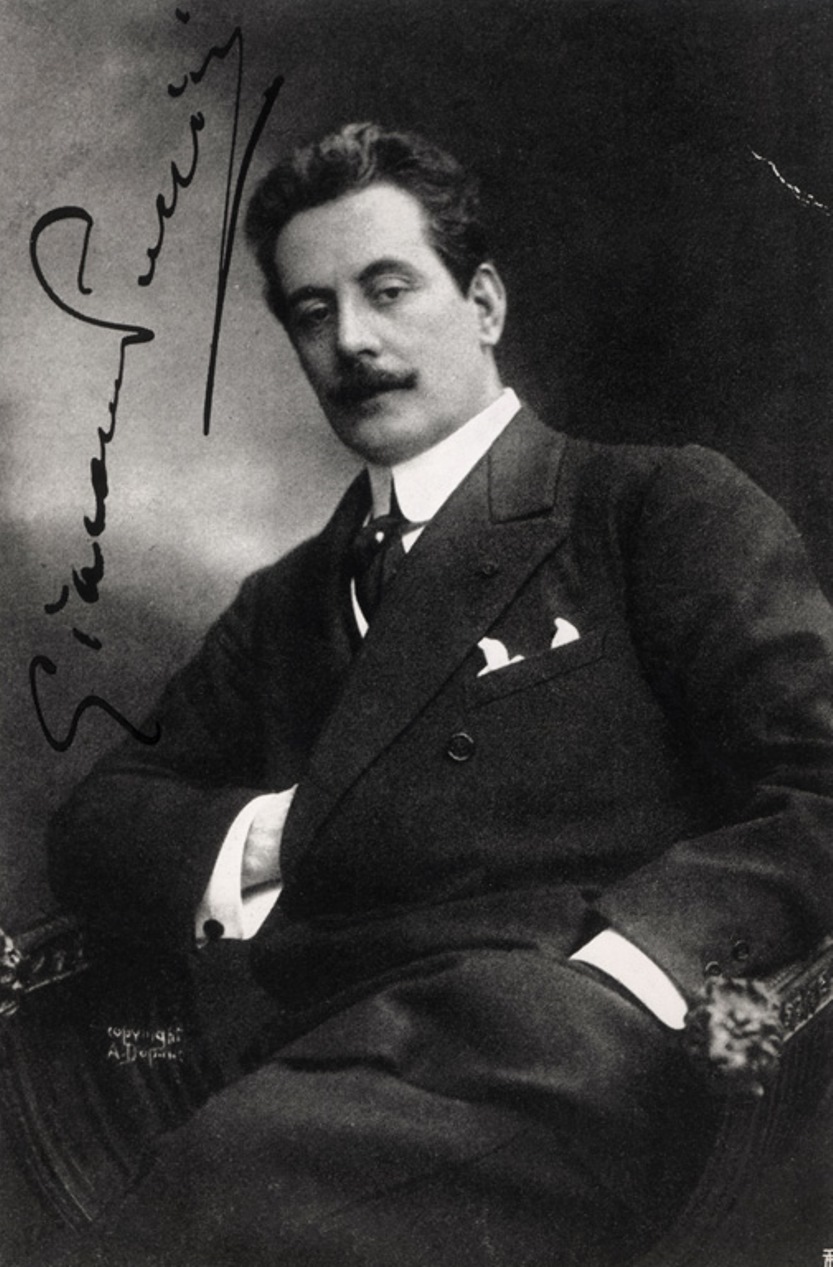


Giacomo Puccini, full name Giacomo Antonio Domenico Michele Secondo Maria Puccini, was an Italian opera composer, organist and choirmaster.
Puccini was born into the family that for two centuries directed the musical organization of the Cathedral of San Martino in Lucca, and the young musician inherited the position of cathedral organist until his adulthood. He also played organ in small local churches. Giuseppe Verdi's opera Aida, which he saw in Pisa in 1876, was a boost for him and he entered the Milan Conservatory in 1880.
Puccini carefully studied contemporary operatic compositions, particularly the work of Claude Debussy, Richard Strauss, Arnold Schoenberg, and Igor Stravinsky. Soon he wrote Triptych (1918), three one-act operas - the melodramatic The Cape, the sentimental Suor Angelica and the comic Gianni Schicchi. Puccini's other mature operas are La bohème (1896), Tosca (1900), and Madama Butterfly (1904).
The composer did not manage to finish his last opera, Turandot - he died of cancer with its score in his hands. This work is the only Italian opera in the Impressionist style. Puccini is also considered the greatest representative of opera realism, as well as the Verismo movement in music, attempting to faithfully portray the social and psychological conflicts of the new national-historical reality after the unification of Italy.


Giacomo Puccini, full name Giacomo Antonio Domenico Michele Secondo Maria Puccini, was an Italian opera composer, organist and choirmaster.
Puccini was born into the family that for two centuries directed the musical organization of the Cathedral of San Martino in Lucca, and the young musician inherited the position of cathedral organist until his adulthood. He also played organ in small local churches. Giuseppe Verdi's opera Aida, which he saw in Pisa in 1876, was a boost for him and he entered the Milan Conservatory in 1880.
Puccini carefully studied contemporary operatic compositions, particularly the work of Claude Debussy, Richard Strauss, Arnold Schoenberg, and Igor Stravinsky. Soon he wrote Triptych (1918), three one-act operas - the melodramatic The Cape, the sentimental Suor Angelica and the comic Gianni Schicchi. Puccini's other mature operas are La bohème (1896), Tosca (1900), and Madama Butterfly (1904).
The composer did not manage to finish his last opera, Turandot - he died of cancer with its score in his hands. This work is the only Italian opera in the Impressionist style. Puccini is also considered the greatest representative of opera realism, as well as the Verismo movement in music, attempting to faithfully portray the social and psychological conflicts of the new national-historical reality after the unification of Italy.
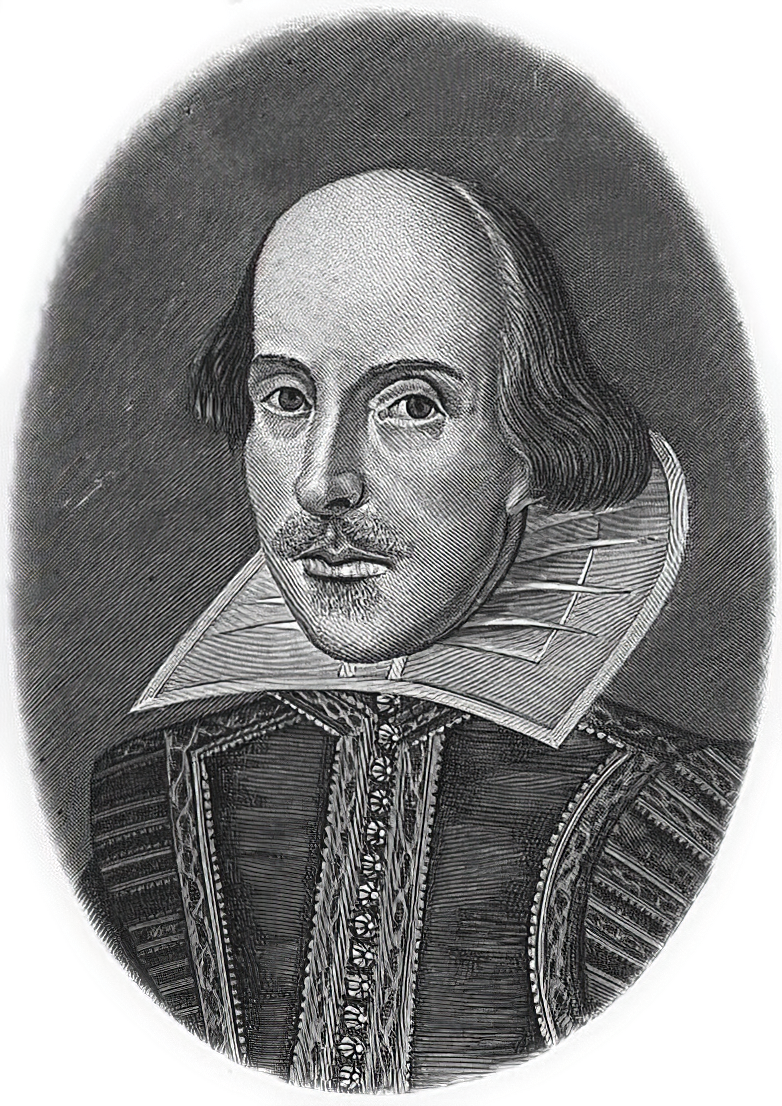


William Shakespeare was a British poet and playwright and writer.
William's father, John Shakespeare, was a merchant and official in Stratford. There are reports that he was a sailor for a time before joining a theater company in London. Beginning in the 1590s, Shakespeare began writing plays, and in 1593 he published a poem, Venus and Adonis, which became popular. He dedicated it to the Duke of Southampton, who was a philanthropist and patron of talent, and soon his business was booming.
From 1592 to 1600 Shakespeare wrote his dramas and romantic comedies "Richard III", "The Taming of the Shrew", "Romeo and Juliet", "A Midsummer Night's Dream" and "The Merchant of Venice", as well as the comedies "Much Ado About Nothing", "Twelfth Night" and the tragedy "Julius Caesar". The playwright's business was so successful that he even bought a large house in Stratford. In 1599, Shakespeare became one of the owners, playwright and actor of the new theater "Globe". In 1603 King James took Shakespeare's troupe under his direct patronage. In the mature period, the great playwright turned to tragedies, there were "Hamlet", "Othello", "King Lear", "Macbeth" and others.
Although in the 19th century researchers had some doubts about the authorship of many of these works, William Shakespeare is considered the greatest English playwright, one of the best playwrights in the world. His plays have been translated into all major languages and to this day form the basis of the world theatrical repertoire, most of them have been screened many times. According to the Guinness Book of Records, Shakespeare remains the world's best-selling playwright, and his plays and poems have sold more than 4 billion copies in the nearly 400 years since his death.
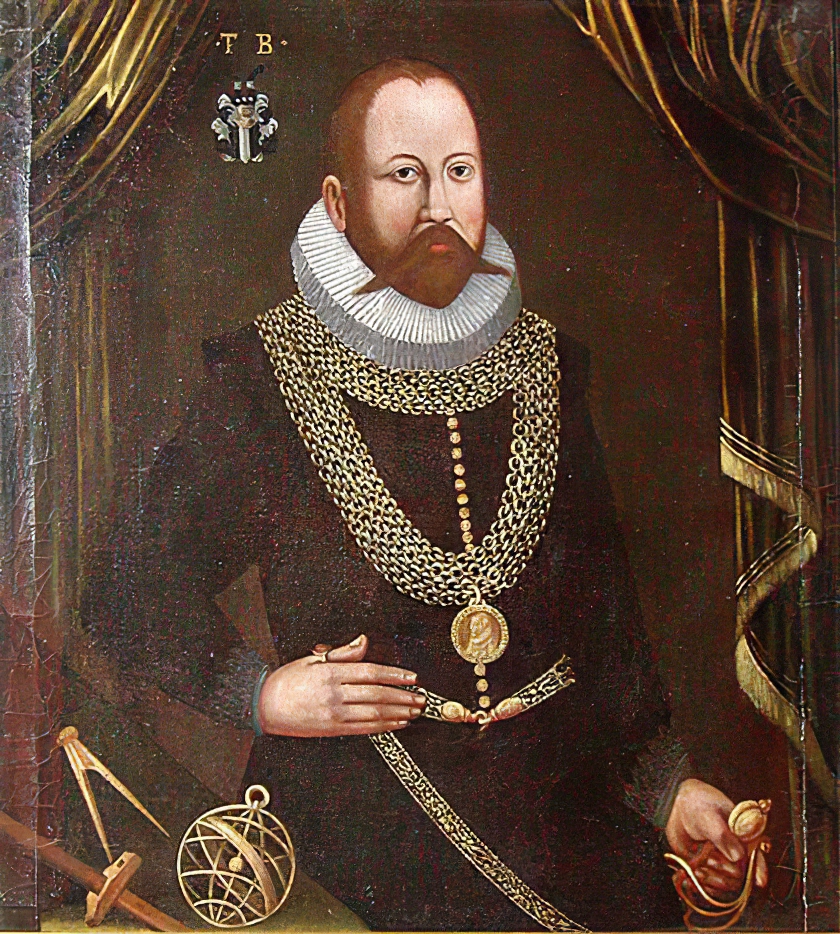


Tycho Brahe, born Tyge Ottesen Brahe, more commonly called Tycho, was a prominent Danish astronomer, astrologer, and alchemist of the Renaissance.
As a young man he traveled extensively throughout Europe, studying in Wittenberg, Rostock, Basel, and Augsburg and acquiring mathematical and astronomical instruments. In 1572 Tycho unexpectedly even for himself discovered a new star in Cassiopeia, and the publication of this turned the young Dane into an astronomer of European reputation. For further astronomical research he established an observatory and gathered around him modern progressive scientists.
Besides practicing astronomy, Tycho was an artist, scientist, and craftsman, and everything he undertook or surrounded himself with had to be innovative and beautiful. He even founded a printing house to produce and bind his manuscripts in his own way, and he perfected sanitary ware for convenience. His development of astronomical instruments and his work in measuring and fixing the positions of the stars laid a solid foundation for future discoveries.
Tycho's observations - the most accurate possible before the invention of the telescope - included a comprehensive study of the solar system and the precise positions of more than 777 fixed stars. What Tycho accomplished using only his simple instruments and intellect remains a remarkable achievement of the Renaissance.




Tycho Brahe, born Tyge Ottesen Brahe, more commonly called Tycho, was a prominent Danish astronomer, astrologer, and alchemist of the Renaissance.
As a young man he traveled extensively throughout Europe, studying in Wittenberg, Rostock, Basel, and Augsburg and acquiring mathematical and astronomical instruments. In 1572 Tycho unexpectedly even for himself discovered a new star in Cassiopeia, and the publication of this turned the young Dane into an astronomer of European reputation. For further astronomical research he established an observatory and gathered around him modern progressive scientists.
Besides practicing astronomy, Tycho was an artist, scientist, and craftsman, and everything he undertook or surrounded himself with had to be innovative and beautiful. He even founded a printing house to produce and bind his manuscripts in his own way, and he perfected sanitary ware for convenience. His development of astronomical instruments and his work in measuring and fixing the positions of the stars laid a solid foundation for future discoveries.
Tycho's observations - the most accurate possible before the invention of the telescope - included a comprehensive study of the solar system and the precise positions of more than 777 fixed stars. What Tycho accomplished using only his simple instruments and intellect remains a remarkable achievement of the Renaissance.
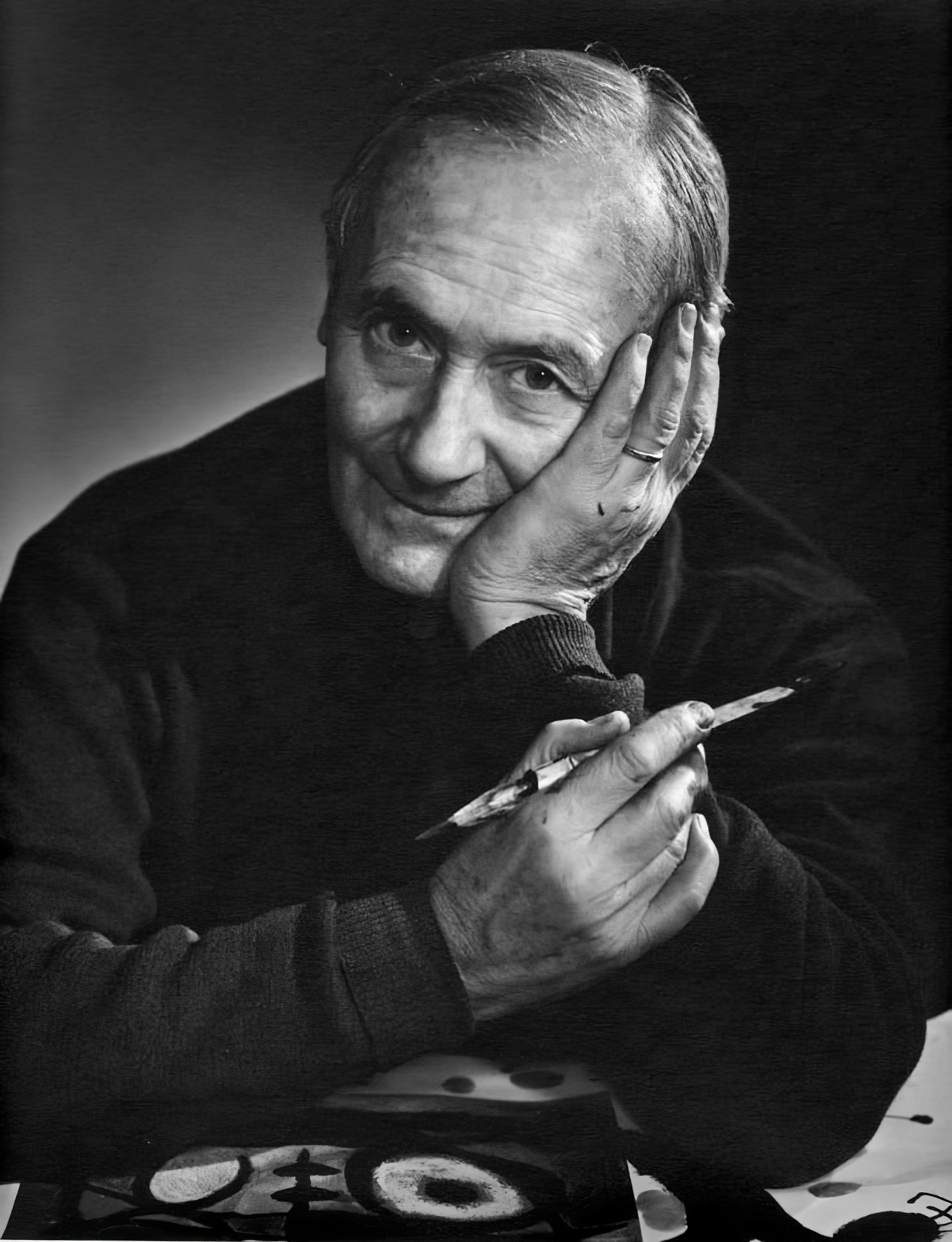


Joan Miró, a celebrated Spanish artist, was a master in painting, sculpture, and ceramics, renowned for his unique style that blurred the lines between Surrealism, Fauvism, and Expressionism. Born in Barcelona to a family of a goldsmith and a watchmaker, Miró grew up immersed in the rich cultural heritage of the Barri Gòtic neighborhood. His artistic journey began with drawing classes at the age of seven and continued at the prestigious La Llotja art academy. Despite an initial venture into the business world, Miró's passion for art prevailed, leading him to abandon his clerical career after a nervous breakdown.
Miró's work is noted for its exploration of the subconscious, often depicting a childlike perspective. This approach was both a critique of traditional painting methods and a means of expressing Catalan pride. His art, challenging to categorize, often featured symbolic elements and nationalistic qualities. One of his notable early works, "The Farm," reflects a transition to a more individual style, blending elements of his Catalan roots with broader artistic influences. This piece, later purchased by Ernest Hemingway, encapsulated the essence of Spain in its imagery.
In Paris, Miró joined the Surrealist movement in 1924, where his work began to reflect the influence of automatism, emphasizing spontaneous, automatic, or subconscious creation. He experimented with various mediums, including painting-poetry and collage, and even ventured into set and costume design for Sergei Diaghilev's Ballets Russes.
During World War II, Miró remained in Spain, and his work from this period, including the 22 Constellations series, reflected an interest in the night, music, and stars. His forms became increasingly abstracted, and he experimented with various techniques, often incorporating primary colors and evocative titles.
Miró's career spanned several decades, during which he continually evolved his style and explored new mediums. His contributions to art were recognized with numerous awards and retrospectives, including a major career retrospective at MoMA in 1941 and the Spanish Gold Medal for Fine Arts in 1980. Among his last major works was a tapestry for the World Trade Center in New York City, created in 1974.
For art collectors and enthusiasts, Joan Miró remains a figure of immense interest, not only for his distinct style and contributions to Surrealism but also for his ability to blend poetic imagery with political commentary. To stay updated on new product sales and auction events related to Joan Miró, sign up for our updates and immerse yourself in the world of this extraordinary artist.


George Frideric Handel was a German-born English composer of the Baroque period.
After receiving a musical education, Handel worked briefly as an organist at the cathedral in Halle, then joined the violin section of the opera orchestra in Hamburg. After spending several years in Italy, he wrote many works there, including two operas. The style of Italian music permeated the composer's work throughout his life. Having become famous in Italy, in 1710 Handel was appointed Kapellmeister to the Elector of Hanover, the future King George I of England, and two years later he was already staging his operas in London.
In 1727 Handel became a British subject and was appointed composer to the Chapel Royal. In this capacity he wrote many musical works. From 1720 to 1728, operas at the Royal Theater in London were staged by the Royal Academy of Music, and Handel wrote the music for most of them.
In 1741, Handel wrote the most famous of his many oratorios, Messiah. Handel had a talent for musically portraying a human character in a single scene or aria - a gift he used with great dramatic power in his operas and oratorios. Although much of his music was vocal, Handel was also one of the recognized instrumental composers of the late Baroque era. Handel paid tribute to church music by composing many solemn hymns.
Handel's music has become an integral part of the national culture of England, and in Germany he is also honored as a major national composer.
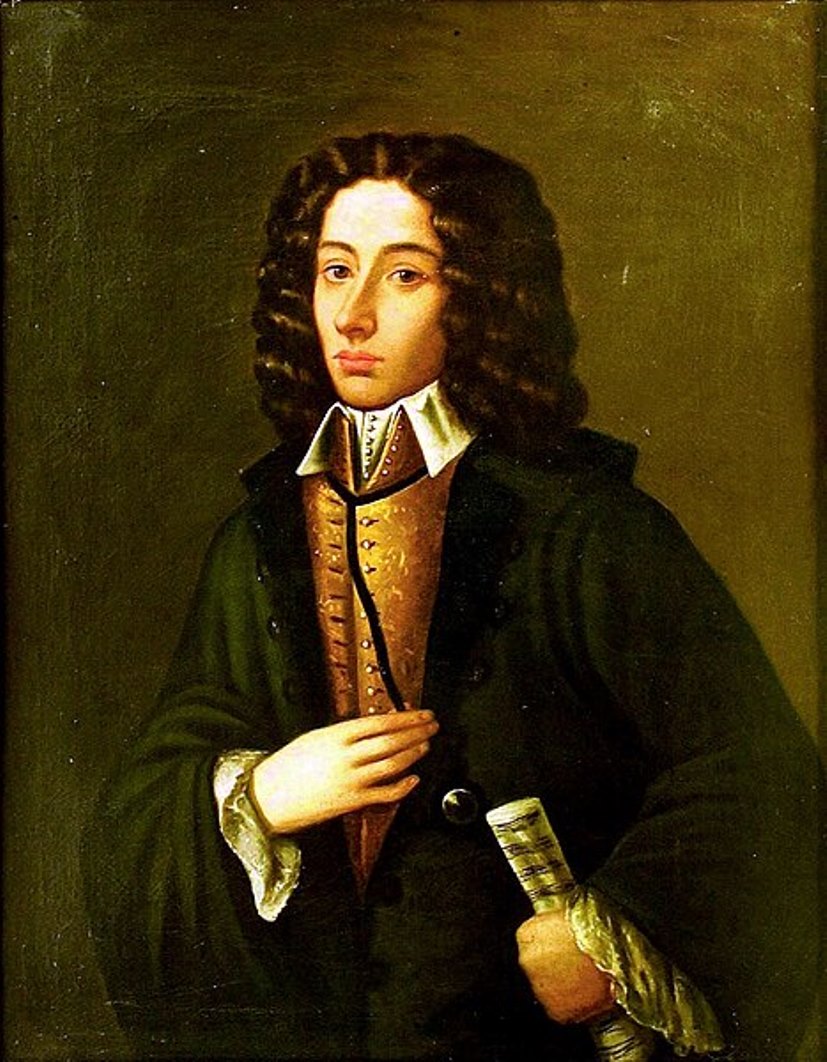


Giovanni Battista Pergolesi, born Giovanni Battista Draghi, was an Italian composer, violinist and organist, a leading representative of the Baroque and Neapolitan school.
Around 1720 he entered the Poveri Conservatory in Naples, where he earned a high reputation as a violinist. In 1732 Pergolesi was appointed maestro of the Prince of Stigliano's Chapel in Naples and soon composed his most successful work, the opera-buffa The Lady's Maid, which quickly gained popularity. His subsequent operas did not achieve the same success.
The Lady's Maid became much more popular when it was staged in Paris in 1752 after the composer's death. It also sparked fierce debate between conservatives, supporters of traditional French opera, and fans of the new Italian comic style. Pergolesi's opera-buffa became a forerunner of subsequent classical works: these are W. A. Mozart's The Marriage of Figaro, J. Rossini's The Barber of Seville, G. Verdi's Falstaff, I. Stravinsky's The Moor, and others.
Alongside secular music Pergolesi composed sacred music. His masses and hymns demonstrate the composer's ability to cope with large choral and instrumental forces, as well as with chamber music. Shortly before his death, he composed the cantata Stabat Mater, one of the composer's most inspired works, written for a small chamber ensemble (soprano, viola, string quartet and organ), filled with sublime, sincere and heartfelt lyrical feeling.
Fate, however, was not favorable to the young talent: Giovanni Battista Pergolesi died of tuberculosis in extreme poverty at the age of 26.

















































![Xiangyangfu Tu [Map of Xiangyang Prefecture]](/assets/image/picture_1696431/3fea0/60ef62d03130123a63c44dd3735a5c031633096800jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![Xiangyangfu Tu [Map of Xiangyang Prefecture]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_1696431/3fea0/60ef62d03130123a63c44dd3735a5c031633096800jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)


![FIBONACCI, Leonardo [c.1170-c.1250]; BOETHIUS, Anicius Manlius Severinus [c.480-524], GROSSETESTE, Robert [1175-1253]; [DE PULCHRO RIVO, Johannes, attrib.]](/assets/image/picture_2279440/69ac3/5672d49f6fe2176fe5b0465502ca1a9b1657663200jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![FIBONACCI, Leonardo [c.1170-c.1250]; BOETHIUS, Anicius Manlius Severinus [c.480-524], GROSSETESTE, Robert [1175-1253]; [DE PULCHRO RIVO, Johannes, attrib.]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_2279440/69ac3/5672d49f6fe2176fe5b0465502ca1a9b1657663200jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)












