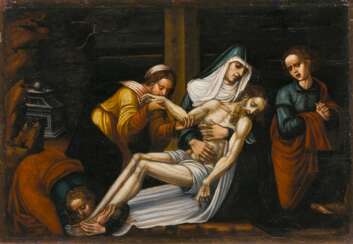
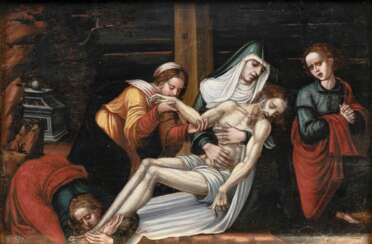
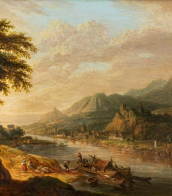manierismus
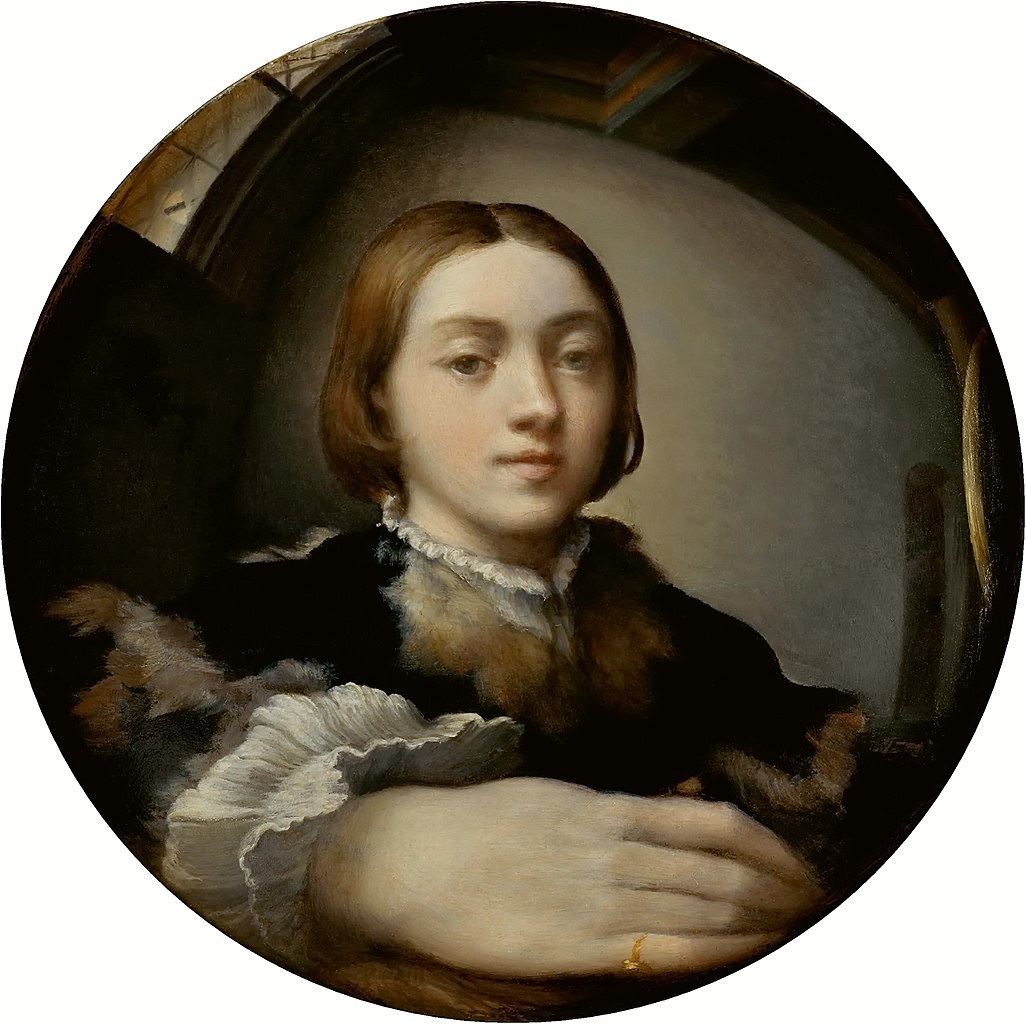

Parmigianino, an Italian Mannerist painter born Girolamo Francesco Maria Mazzola, was a pivotal figure in the development of the Mannerist style, known for his sophisticated and elegant approach to painting. He was a leading figure in Parma's art scene following Correggio and had a significant influence on the artistic developments during the post-High Renaissance period through his expressive and stylish works.
Parmigianino's journey as an artist took him from Parma to Rome and then to Bologna, with his last years spent in Parma. His works, including the renowned "Madonna with the Long Neck," display a unique blend of grace and elegance, coupled with an idiosyncratic use of elongation and distortion, typical of Mannerist aesthetics. This painting, in particular, is noted for its unusual composition and the elongation of figures, embodying the Mannerist style's departure from the proportional norms established during the Renaissance.
He was also an early Italian etcher, utilizing this technique to express the spontaneity of an artist's hand. His etchings and drawings had a considerable influence on printmaking and the visual arts in Italy and Europe. In addition to his paintings, Parmigianino's contributions to the arts include his work in the church of the Steccata in Parma and his innovative approach to integrating painting with architectural elements.
For art collectors and experts, Parmigianino's work represents a critical link between the High Renaissance and the emergence of Baroque and Rococo styles, offering a unique insight into the evolution of European art. His works continue to be celebrated for their originality and mastery, making him a subject of enduring interest in the study of art history.
For those interested in exploring Parmigianino's contributions to art further, subscribing to updates from art institutions or platforms specializing in Renaissance and Mannerist art could provide valuable insights into his life, works, and ongoing exhibitions or sales of his artworks.
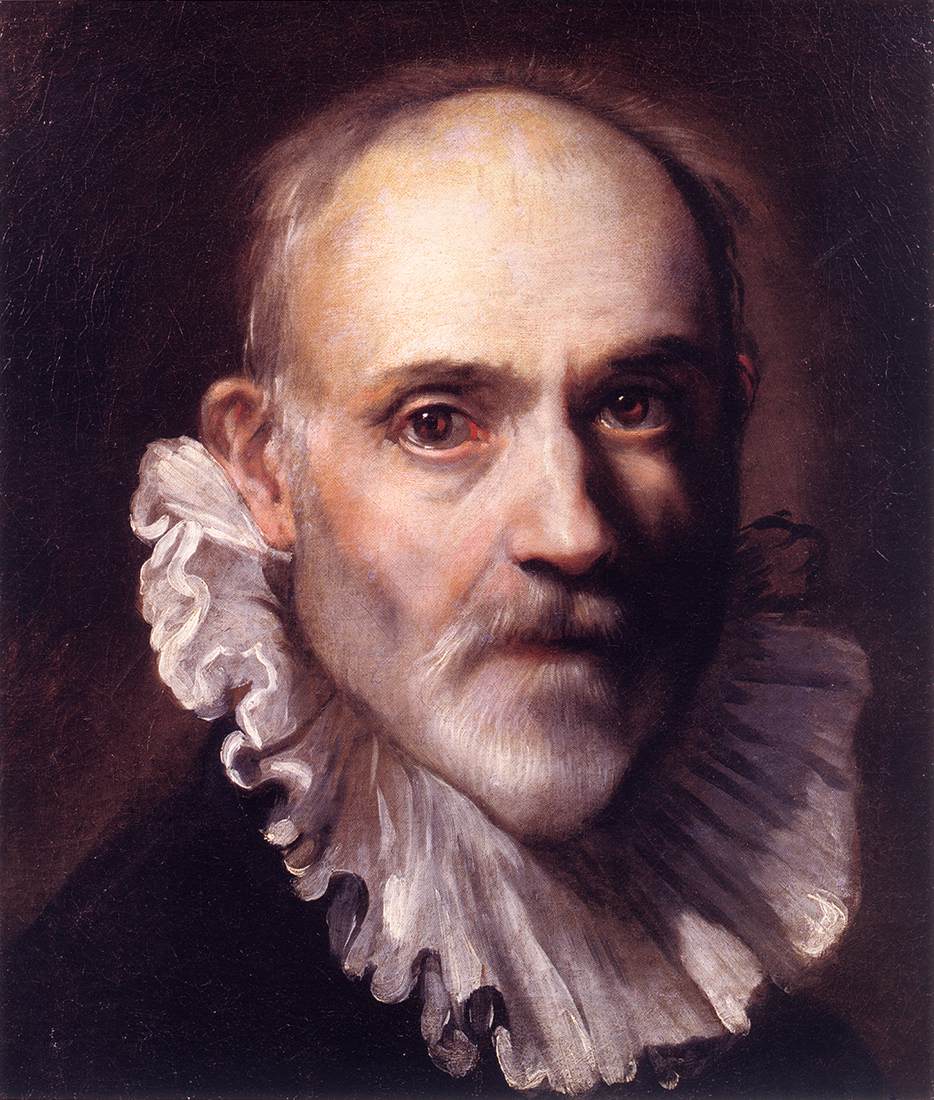



Federico Barocci, an Italian Renaissance painter and printmaker, was celebrated for his vibrant use of color and dynamic compositions. Born around 1533 in Urbino, Italy, a hub of Renaissance culture, Barocci's early life was steeped in the rich artistic heritage of the time. His training included an apprenticeship with his father, a sculptor, and later with notable artists such as Battista Franco Veneziano and Taddeo Zuccari.
Federico Barocci's work, known for its emotional intensity and use of light, positioned him as a critical link between the Mannerist style of the 16th century and the emerging Baroque period. His paintings often depicted religious scenes, imbued with a warmth and spirituality that resonated with viewers. His unique approach to color and composition had a significant influence on later artists, including the Baroque masters Peter Paul Rubens and Gian Lorenzo Bernini.
Despite suffering from chronic illness, possibly due to poisoning, Federico Barocci's output remained prolific and influential. His works can be found in several prestigious galleries, including the Uffizi in Florence, where his "Madonna del Popolo" and "Martyrdom of Saint Vitale" are displayed. These pieces, along with others like "The Deposition" in the Cathedral of Perugia and "Noli me Tangere" in Munich, showcase his mastery in portraying human emotion and divine radiance.
Collectors and experts in art and antiques will appreciate the depth and innovation of Federico Barocci's work. His legacy as a master colorist and draughtsman is undeniable, making his pieces a valuable addition to any collection.
To stay updated on sales and auction events related to Federico Barocci, sign up for our exclusive updates. This subscription ensures you're the first to know about new opportunities to acquire works connected to this remarkable artist.
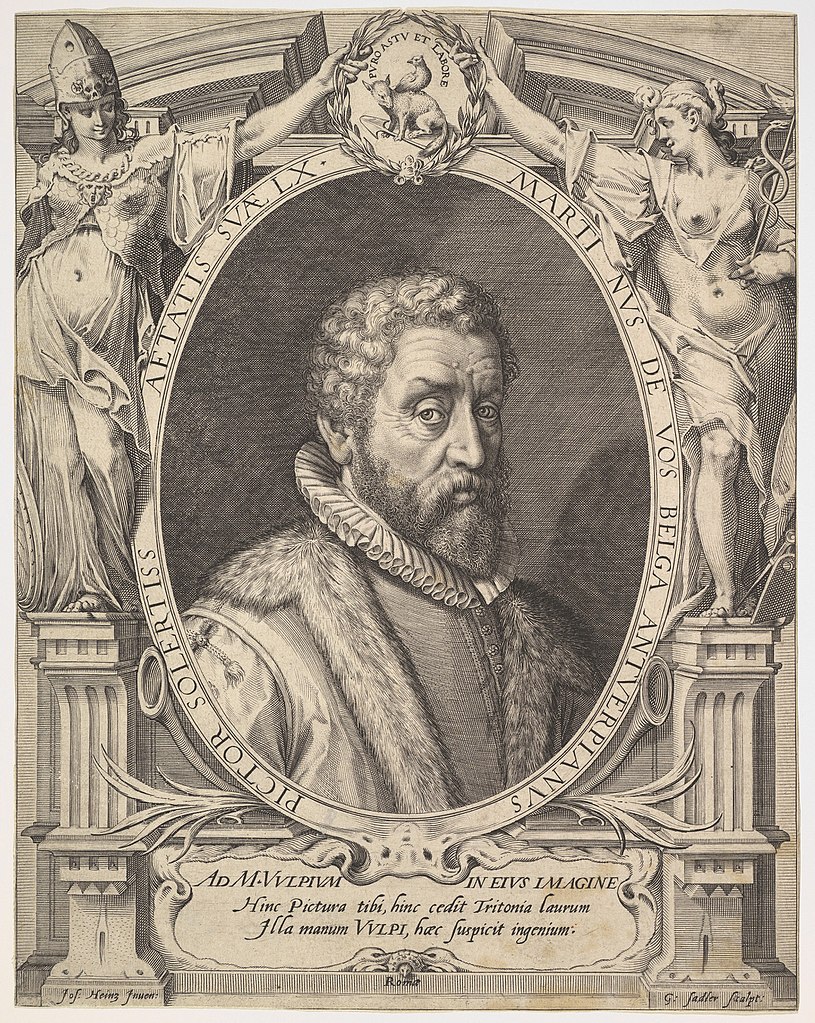


Marten de Vos (or Maarten de Vos, or Maerten de Vos) was a Dutch painter, draughtsman and graphic artist, dean of the Antwerp Guild.
After studying in Rome and Venice, de Vos returned to his native Antwerp in 1558 and became one of the city's leading artists. He created altarpiece images for many of Antwerp's churches. Many of his religious and historical paintings were later engraved, making him known throughout Flanders.
De Vos was also the founder of the Society of Romanists, whose members were famous artists and humanists of the time who appreciated the humanistic culture of Rome.

Joos de Momper the Younger was a Flemish landscape painter active in Antwerp between the late 16th century and the early 17th century. Brueghel's influence is clearly evident in many of de Momper's paintings. His work is situated at the transition from late 16th-century Mannerism to the greater realism in landscape painting that developed in the early 17th century. He achieved considerable success during his lifetime.
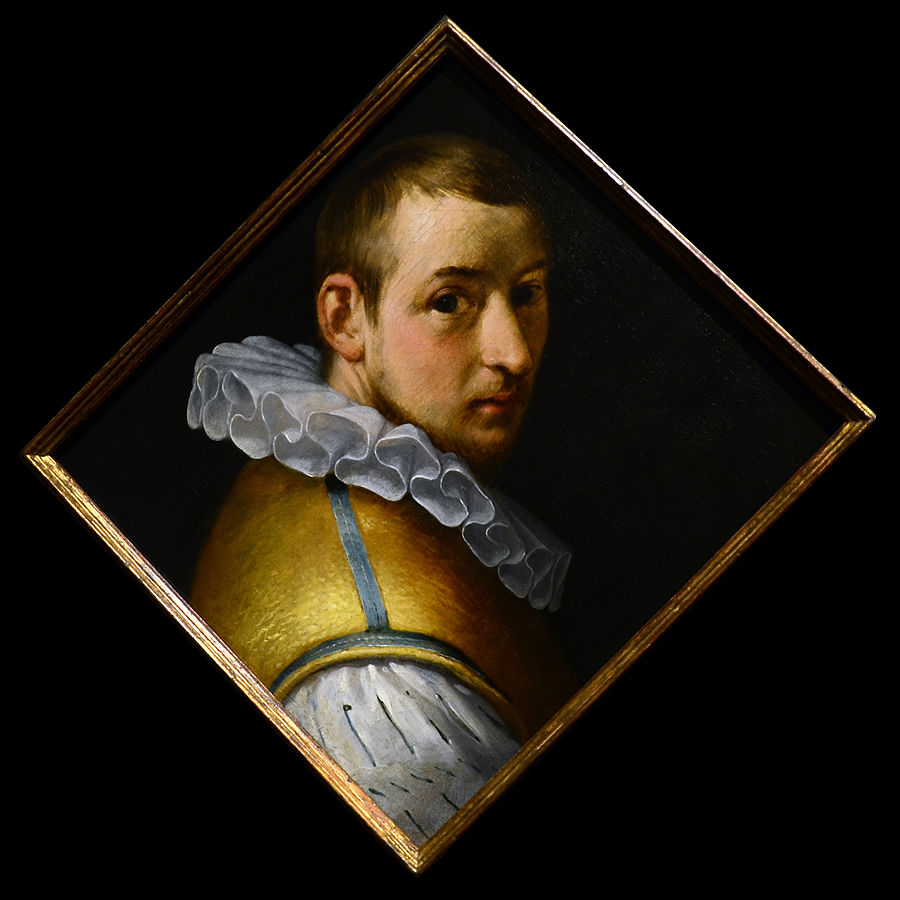

Cornelis Cornelisz. van Haarlem was a Dutch painter, draftsman, and architect. Along with Karel van Mander and Hendrik Goltzius, he is one of the leading artists of the Dutch Mannerism of the Haarlem School, more commonly referred to as Cornelis van Haarlem.
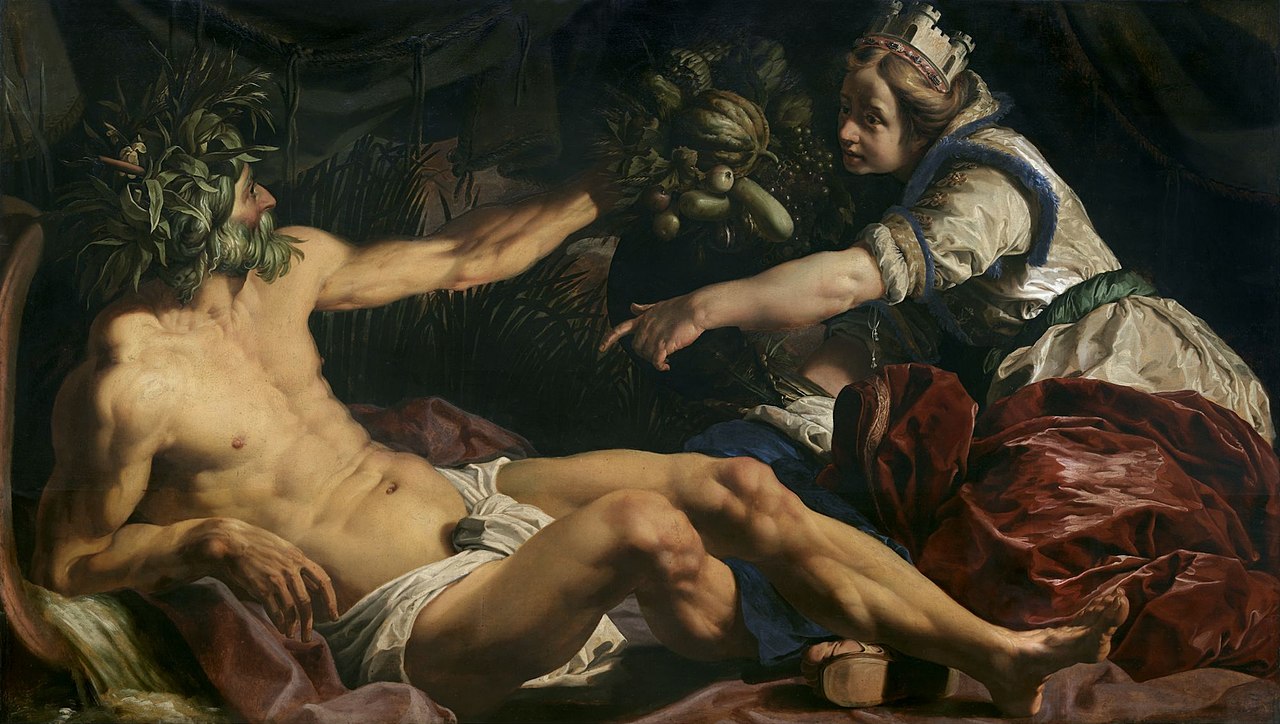

Abraham Janssens was a Flemish painter, who is known principally for his large religious and mythological works, which show the influence of Caravaggio. He was the leading history painter in Flanders prior to the return of Rubens from Italy.


Abraham Janssens was a Flemish painter, who is known principally for his large religious and mythological works, which show the influence of Caravaggio. He was the leading history painter in Flanders prior to the return of Rubens from Italy.
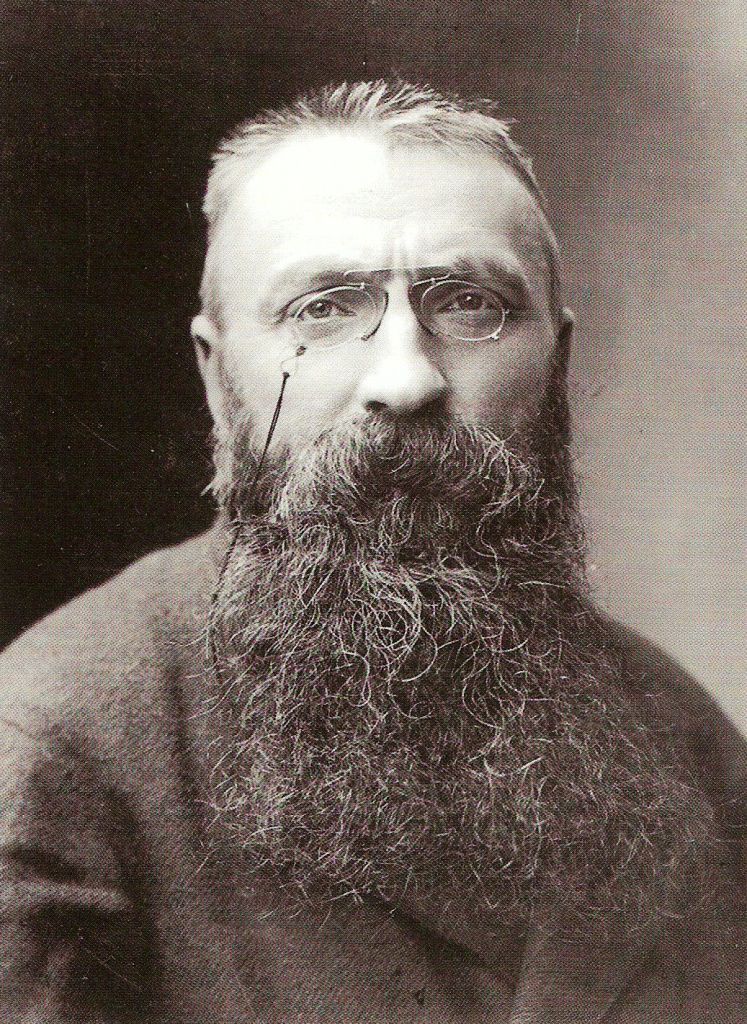


François Auguste René Rodin was a French sculptor, generally considered the founder of modern sculpture. He was schooled traditionally and took a craftsman-like approach to his work. Rodin possessed a unique ability to model a complex, turbulent, and deeply pocketed surface in clay. He is known for such sculptures as The Thinker, Monument to Balzac, The Kiss, The Burghers of Calais, and The Gates of Hell.
Many of Rodin's most notable sculptures were criticized, as they clashed with predominant figurative sculpture traditions in which works were decorative, formulaic, or highly thematic. Rodin's most original work departed from traditional themes of mythology and allegory. He modeled the human body with naturalism, and his sculptures celebrate individual character and physicality. Although Rodin was sensitive to the controversy surrounding his work, he refused to change his style, and his continued output brought increasing favor from the government and the artistic community.
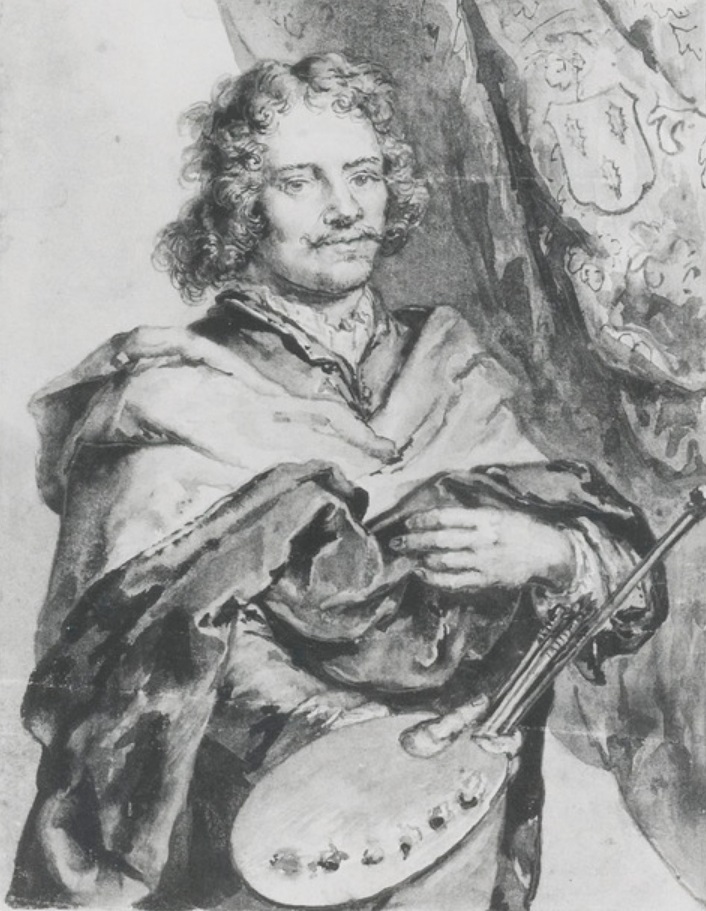


Hendrick Jansz ter Brugghen was a Dutch painter of genre scenes and religious subjects. He was one of the Dutch followers of Caravaggio – the so-called Utrecht Caravaggisti. Along with Gerrit van Hondhorst and Dirck van Baburen, Ter Brugghen was one of the most important Dutch painters to have been influenced by Caravaggio.
Ter Brugghen's favourite subjects were half-length figures of drinkers or musicians, but he also produced larger-scale religious images and group portraits. He carried with him Caravaggio's influence, and his paintings have a strong dramatic use of light and shadow, as well as emotionally charged subjects. His treatment of religious subjects can be seen reflected in the work of Rembrandt, and elements of his style can also be found in the paintings of Frans Hals and Johannes Vermeer. Peter Paul Rubens described ter Brugghen's work as "...above that of all the other Utrecht artists".


Jan Gossaert was a French-speaking painter from the Low Countries also known as Jan Mabuse (the name he adopted from his birthplace, Maubeuge) or Jennyn van Hennegouwe (Hainaut), as he called himself when he matriculated in the Guild of Saint Luke, at Antwerp, in 1503. He was one of the first painters of Dutch and Flemish Renaissance painting to visit Italy and Rome, which he did in 1508–09, and a leader of the style known as Romanism, which brought elements of Italian Renaissance painting to the north, sometimes with a rather awkward effect. He achieved fame across at least northern Europe, and painted religious subjects, including large altarpieces, but also portraits and mythological subjects, including some nudity.







































![Schule von Fontainebleau Ende 16. Jahrhundert. Gabrielle d'Estrées (um 1570 Schloss Coeuvres [Picardie] - 1599 Paris)](/assets/image/picture_214508/ed584/rhcygwoxvgwkbsr1etliaemrqvcqwe1dqvvjf67329tiatmsu76kvkbiq1lv0y1529445046jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![Schule von Fontainebleau Ende 16. Jahrhundert. Gabrielle d'Estrées (um 1570 Schloss Coeuvres [Picardie] - 1599 Paris)](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_214508/ed584/rhcygwoxvgwkbsr1etliaemrqvcqwe1dqvvjf67329tiatmsu76kvkbiq1lv0y1529445046jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)