Historians 19th century


Paul Allen is an American editor, historian, and poet.
He attended Brown University and later moved to Philadelphia, where he was editor of The Port Folio, The Gazette of the United States, and The Federal Republican. Success came to Allen in Baltimore, where he served as editor until his death at the Baltimore Morning Chronicle newspaper. Paul Allen also joined the Delphic Club, and his epic poem Noah (1821) was a success.


Rodolphe Auguste Bachelin was a Swiss landscape, history and portrait painter as well as a writer, historian and art critic.
He was interested in the Lombardy War of 1859 and in particular in the Franco-Prussian War of 1870 to 1871, which provided him with several subjects with its troop surge at Les Verrières. The Neuchâtel painter was greatly influenced by the writings of Rodolphe Töpffer and aspired to become a Swiss national painter.


Pierre-François Hugues d'Hancarville, better known as Baron d'Hancarville, was an art historian, writer, and adventurer who lived most of his life in Italy.
To advance from the merchant class to high society, he studied mathematics, physics, history, literature, ancient languages, and English, Italian, and German. Traveling in Europe, he presented himself as an aristocrat under various names. Under the name Baron d'Hancarville, he was known as a connoisseur and art dealer, which is apparently why he was approached by Sir William Hamilton (1731-1803), who was ambassador to the British embassy in Naples and had amassed a large collection of ancient vases. Before selling this collection to the British Museum in 1772, Hamilton asked d'Hancarville for help in creating a complete catalog of it in descriptions and illustrations. The baron also wrote a detailed essay.
This catalog, entitled The Complete Collection of Antiquities from the Cabinet of Sir William Hamilton, is itself a neoclassical masterpiece in French and English. Antique vases have never before been depicted with such precision and aestheticism.


Platon Petrovich Beketov (Russian: Платон Петрович Бекетов) was a Russian publisher, book printer, historian and collector.
Platon Beketov was born into an old Russian landowning family, from 1798 he lived in Moscow, where he became interested in collecting and in 1801 opened his own printing house, which was considered one of the best in Moscow. Beketov raised the national printing industry to a worthy level. His books were made with great artistic taste and elegance, more than a hundred beautiful editions in all. A number of editions of Russian authors were printed here, among them Vasily Andreyevich Zhukovsky, Alexander Nikolayevich Radishchev, Mikhail Matveyevich Kheraskov and others. The printing house also printed the magazines "Friend of Enlightenment" (1805) and "Inventory of Books Printed at the Dependence of Platon Beketov's Printing House" (1806).
Beketov was passionate about old manuscripts, especially with portrait miniatures and autographs, and portraits of famous contemporaries. He collected an entire picture gallery, which formed the basis of two of his major projects - the publication "Pantheon of Russian Authors" (1801-1802) and the collection "Collection of Portraits of Russians, famous..." (1821-1824). (1821-1824). The texts for them were written by the publisher's friend and distant relative N.M. Karamzin.
Platon Petrovich Beketov was widely known in the circles of the Russian intellectual elite of the first half of the XIX century. In 1811 he was elected chairman of the Moscow Society of Russian History and Antiquities, a position he held until 1823.


Alexandre Nikolayevich Benois (Russian: Алекса́ндр Никола́евич Бенуа́) was a distinguished Russian artist, art critic, and historian, celebrated for his pivotal role in the art world, particularly in painting and stage design. Born into a family deeply embedded in the cultural fabric of Russia, Benois was instrumental in the development of the Russian artistic movement at the turn of the 20th century. His contributions to art and culture extend beyond his vivid paintings; he was a founding member of the World of Art (Mir iskusstva), a significant art movement and magazine that sought to elevate Russian artistry on the global stage.
Benois' work is notable for its intricate detailing, vibrant use of color, and the ability to convey deep narratives within each piece. His designs for ballets such as "Petrushka" and "The Sleeping Beauty" remain iconic, showcasing his mastery over the fusion of visual art and performance. This synthesis not only enhanced the ballets’ visual appeal but also deepened the audience's engagement with the narrative. Museums and galleries around the world, including the Russian Museum in St. Petersburg and the Tretyakov Gallery in Moscow, house his works, underscoring his global recognition and the enduring appeal of his artistic vision.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Benois' oeuvre represents a fascinating exploration of early 20th-century Russian culture, art, and the avant-garde movement. His ability to blend traditional Russian themes with the modernist trends of his time makes his work a valuable study in the evolution of modern art. Those interested in the rich tapestry of Russian cultural history and the interplay between art and performance will find Benois' contributions invaluable.
To stay informed about new discoveries, sales, and auction events related to Alexandre Nikolayevich Benois, we encourage you to sign up for updates. This subscription is tailored specifically for enthusiasts eager to deepen their appreciation and understanding of Benois' legacy, ensuring you're the first to know about opportunities to acquire pieces connected to this luminary of Russian art.


Edward Wedlake Brayley was a British writer, historian, archaeologist and topographer.
Notable among Brayley's works are A Topographical History of Surrey, Lambeth Palace, Topographical Sketches of Brighthelmston, and Londiniana. Braley often collaborated with the topographer and antiquarian John Britton in the creation of his books. The text in his books was illustrated with woodcuts and engraved steel plates.
Britton and Brayley's long-standing collaboration also resulted in the popular series "Beauties of England and Wales," published from 1801 to 1818. Several volumes were planned, dealing with the history and topography of England and Wales, illustrated with views of picturesque scenes and important places. The series eventually expanded to twenty-five large volumes, published over a period of nearly twenty years.
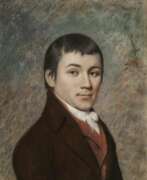

Charles Brockden Brown was an American writer, historian, and editor.
Brown took up literary endeavors early in life. In 1798, his first mystical and psychological novel, Wieland, was published. Brown also wrote the novels Ormond (1799), Edgar Huntley (1799), and Arthur Merwin (1799-1800).
Brown's works interweave fiction, history, fantasy, psychology, and liberal politics. Brown is considered the father of the American novel. His American-style Gothic novels pioneered and paved the way for two of the greatest early American writers, Edgar Allan Poe and Nathaniel Hawthorne.
Charles Brown also wrote a great deal of journalism on political, educational, and historical topics.




Victor Yakovlevich Bunyakovsky (Russian: Ви́ктор Я́ковлевич Буняко́вский) was a Russian mathematician, teacher, historian of mathematics, vice-president of the Academy of Sciences in 1864-1889. He made a significant contribution to number theory.


Théodore-Joseph Canneel was a Belgian portrait and genre painter, lithographer and art teacher. From 1830, Theodore Canneel learned the craft of lithography in the printing shop where his father worked. He then became a student of the painter Pieter van Hanselaere. From 1838 to 1841 he combined his profession with an education at the Koninklijke Acaďemie voor Schone Kunsten van Gent. He taught there from 1843. From 1848 to 1850 he undertook a study trip to France and Italy. On his return in 1850 he was appointed director of the Ghent Academy. In 1869 he became inspector at the Belgian drawing schools and academies. He also became a corresponding member of the Royal Academy of Sciences and Fine Arts of Belgium, the Koninklijke Academie voor Schone Kunsten van Antwerpen and an honorary member of the Philadelphia Academy. For the services rendered, he was appointed officer of the Belgian Order of Leopold.


Alfred Jean Andre Cluysenaar was a Belgian Portrait painter. Jean Alfred was a member of the Cluysenaar family, an artistic family from Brussels. He became the father of the painter André Cluysenaar. He studied in the Académie Royale des Beaux-Arts of Brussels in the atelier of Joseph Jaquet and François-Joseph Navez. He painted some important decorations in the Royal Zoo of Antwerp and in 1861-1876 he ornated the Aula in Ghent. Cluysenaar was famous for his monumental decorations of high quality. Awarded in the expositions of Brussels, Ghent, Paris Vienna and London. Some of his paintings are kept in the Royal Museum of Fine Arts Antwerp.


James Fenimore Cooper is an American writer and the founder of the Western genre.
Cooper is the first major American novelist, he wrote a whole series of novels from American life: "The Pioneers" (1823), "The Last of the Mohicans" (1826), "The Prairie" (1827), "The Pathfinder" (1840), "The Beastmaster, or the First Warpath" (1841). The author fascinatingly and vividly describes how Europeans waged wars among themselves on the American continent, involving Indian tribes in these strife. All of these works were a huge success in 19th century Europe and are still being reprinted today.
At the height of his popularity, Cooper spent seven years in Europe, and then returned to the United States, where he wrote works on military-historical and maritime themes until his advanced old age. Among them are "The Pilot, or Maritime History" (1823), "The Red Corsair" (1827).


Francesco de Bourcard was a Swiss-born Italian scholar, historian and publisher.
De Bourcard devoted about twenty years, from 1847 to 1866, to the production of a voluminous work, The Uses and Customs of Naples, to which he engaged a large number of contributors, both writers, artists, and engravers.
The first of the two volumes was published in 1853. The books depict the customs of the time, the typical characters of the people, their daily lives, and a wide range of popular and religious festivals. Hundreds of lithographs are accompanied by explanatory texts.


Charles Corneille Auguste de Groux or Charles Degroux was a French painter, engraver, lithographer and illustrator. As he moved to Belgium at a young age and his whole career took place in Belgium he is usually referred to as a Belgian artist. His depictions of scenes from the life of the disadvantaged and lower-class people of his time mark him as the first Belgian social realist painter. These works made him the precursor of Belgian Realist artists such as Constantin Meunier and Eugène Laermans. De Groux worked in different media, including oil painting, watercolor, pastel, engraving and lithography. He started out as a painter of history and religious scenes in the Romantic style then prevalent in Belgium. He later developed his own realist style which shows the influence of Courbet as well as genre painters of the 17th century. De Groux' social realist works contain many religious overtones and references.


Edouard de Jans was a Flemish portrait and genre painter. Although he specialized in portraits, he also did Biblical scenes, history paintings and landscapes. In 1876, he received a scholarship from the Prix de Rome for his painting "Return of the Prodigal Son", which enabled him to travel throughout Europe, visiting France, Italy, Germany and Austria. When he returned to Antwerp in 1889, he was appointed a Professor at the Academy and held that position until his death.


Jacques de Lalaing was an Anglo-Belgian painter and sculptor, specializing in animals. Lalaing was raised in England until 1875, when he moved to Brussels. He trained as an artist under Jean-François Portaels and Louis Gallait at the Académie Royale des Beaux-Arts in Brussels. With the encouragement of Thomas Vinçotte and Jef Lambeaux, Lalaing began to sculpt in 1884. As a painter he continued to work in a realistic, naturalistic style, as a portrait painter and producing historical scenes. As a sculptor he produced allegorical bronzes and memorial art. Along with his fellow animalier sculptors Léon Mignon and Antoine-Félix Bouré Lalaing established a distinctively Belgian tradition of animal art, to which the flourishing Antwerp Zoo contributed inspiration. In 1896 Lalaing became a member of the Royal Academy where he had studied, and from 1904 through 1913 he served as its director. His works are represented in the collections of museums in Antwerp, Bruges, Brussels, Ghent and Tournai.


Alfred de Marbot, full name Baron Alfred-Charles-Adolphe de Marbot, was a French writer, historian and illustrator, a specialist in military uniforms.
He was born into the family of Lieutenant General Baron Marcelin Marbot (1782-1854). As a historian of the post-Napoleonic era, Marbot did extensive research and illustrated many types of infantry and cavalry uniforms, uniforms of the National Guard, volunteer and allied French Legions.
From 1836 to 1860, together with Baron Dunoyer de Noirmont (1816-1896), Alfred de Marbot published in Paris a series of "French military costumes from the organization of the first regular troops in 1439 to the present day", and in 1854 published the work "Synoptic tables of French infantry and cavalry and foreign regiments in the service of France from 1720 to 1789".


Dunoyer de Noirmont, full name Baron Joseph-Anne-Emile-Edouard Dunoyer de Noirmont, was a French writer, historian, and draftsman.
Baron Dunoyer de Noirmont wrote books on the history of hunting in France. Among his other famous works is the voluminous tome French Military Costumes, which describes the organization, arms, clothing, and equipment of the various army corps. It is the joint work of Dunoyer de Noirmont and the historian and artist Alfred de Marbeau (1812-1865). This monument to French military costume from 1439 to 1815 consists of hand-colored lithographed plates with explanatory texts.


Maximilien de Ring was a nineteenth-century German artist of French descent. He is known as a painter, graphic artist, landscape painter, illustrator, lithographer, historian and archaeologist.
Maximilien de Ring was born in Bonn and worked in Paris, but concentrated on studying the history and culture of Southwest Germany and Alsace. He became famous for his paintings of scenic views of German castles, as well as his publications on history, archaeology, and architecture. He also illustrated his publications, including albums on Celtic and Roman settlements.


Maurice Denis, a French painter and writer, was an influential figure in the transition from impressionism to modern art. Born on November 25, 1870, in Granville, France, Denis's artistic journey began at the Académie Julian in Paris. Here, he met future collaborators like Paul Sérusier and Pierre Bonnard, with whom he later formed the Nabis group, a collective deriving its name from the Hebrew word "Nabi," meaning "Prophet".
Denis's style evolved from neoimpressionism, influenced by artists like Seurat, to a more decorative and colorful approach under the influence of Gauguin. This shift is evident in works like "Taches du soleil sur la terrace" (1890). He famously stated, "Art is no longer a visual sensation... it is a creation of our spirit," highlighting his belief in art as an idealistic expression, transcending mere imitation of nature.
Denis was also impacted by Japanese art, which influenced his compositions and styles, contributing to his unique and recognizable approach. His philosophy on art, encapsulated in his 1890 essay published in "Art et Critique," emphasized the importance of color and form in creating emotional depth, a notion that laid the groundwork for modernism. He argued that a painting's essence lies in its colors and composition, rather than its subject matter.
Throughout his career, Denis's work evolved towards a more classical approach. His involvement with the Ateliers d'Art Sacré, founded in 1919, demonstrated his interest in religious art and decoration. His notable works include "The Legend of Saint Hubert" (1897) and "The History of Music" for the Théâtre des Champs Elysées (1912-1913).
Tragically, Maurice Denis's life ended on November 13, 1943, when he was struck by a truck during the German occupation of Paris. However, his legacy endures through his contributions to modern art and symbolism, his influence on fellow artists, and his works displayed in various museums and galleries.
For collectors and art experts, Denis's work offers a unique glimpse into the evolution of modern art. His blend of symbolism, color, and form marks a significant shift in art history. To stay updated on new sales and auction events related to Maurice Denis's work, sign up for our newsletter. This subscription will keep you informed about the latest developments in the world of this remarkable artist.


Ludwig des Coudres was a German history and portrait painter. He also served as a Professor at the Academy of Fine Arts, Karlsruhe. His son, Adolf Des Coudres, was a well-known landscape painter. In 1836, he began studying architecture at the new polytechnic school. The following year, he was able to begin studies at the Kunsthochschule. Dissatisfied with the school's emphasis on the Nazarene style, he and two of his friends left to start their own studio and teach themselves. Shortly after, he went to study at the Academy of Fine Arts, Munich. In 1843, he went to spend two years in Rome. Then he studied at the Kunstakademie Düsseldorf. It was there he turned to portrait painting. In 1854 he became the first Director of the Academy in Karlsruhe, organizing its operations and establishing the curriculum.


Francis Douce was a British antiquarian and curator of the British Museum, historian and writer.
Francis Douce studied law, but he loved books much more. He became a prominent member of the Society of Antiquaries and served as Keeper of Manuscripts at the British Museum from 1799 to 1811, but was forced to resign because of a quarrel with one of the trustees.
Francis Douce was an avid book collector and bibliophile. After leaving his post at the museum, he concentrated on adding to his collection of antiquarian books and manuscripts. And he also wrote scholarly works, most notably Illustrations of Shakespeare and Ancient Manners (1807) and A Dissertation on the Various Variants of the Dance of Death (1833). When Douce died in 1834, he left his extensive and valuable book collection of over 19,000 printed works to the Bodleian Library in Oxford.


Edward Dujardin was a Belgian painter and art teacher. He began his studies at the Royal Academy of Fine Arts (Antwerp), under Gustaf Wappers. From 1841, he taught figure drawing and placement at the Academy. He painted historical events, Biblical scenes, and portraits, and was in great demand for decorating public celebrations.


William Dunlap was an American playwright, theater director, artist, and historian.
William Dunlap was a pioneer of the young country's theater. He directed two of New York City's earliest and most famous theaters, the John Street Theater and the Theater in the Park. During his lifetime he directed over sixty plays, most of which were adaptations or translations of French and German works. But among them were some original ones based on American themes with American characters.
In 1832 Dunlap published A History of the American Theater in two volumes. In 1825, Dunlap co-founded the National Academy of Design and taught at its school. Even today, Dunlap is best known for his encyclopedic three-volume History of the Origin and Progress of the Art of Design in the United States. The book was published in 1834 and is now an invaluable source of information about artists, collecting, and artistic endeavors in the country of that historical period.


Johannes Hinderikus Egenberger was a Dutch painter, photographer and art educator. From 1840 to 1848, he studied at the Royal Academy of Fine Arts in Amsterdam with Jan Willem Pieneman. During these years, he focused on painting scenes from Dutch history. In 1854, he collaborated with Barend Wijnveld to produce a massive canvas depicting the heroic defense of Haarlem led by Kenau Hasselaer in 1573. Later, he would turn to landscapes, domestic scenes and portraits, including a series for the Rijksuniversiteit. In 1857, he was appointed Headmaster of the Academie Minerva in Groningen. In addition to his work there, he became a photographer and, in 1864, opened the first photography studio in Groningen. The following year, he resigned his position as Headmaster to devote himself entirely to photography.


Otto Clemens Fikentscher the Elder was a German painter, draughtsman and illustrator of the Düsseldorf School. Although it is unclear whether he is related to the artist Otto Fikentscher, who was married to Jenny Fikentscher, Otto Fikentscher (the Elder) studied at the Düsseldorf Art Academy and specialised in historical painting and the depiction of horses in battle scenes. He was a member of the artists' association Malkasten and served as a war correspondent during conflicts such as the German-Danish War and the Franco-Prussian War. Fikentscher's works were reproduced in popular magazines and showed his lively and dynamic style.


Joseph Fourier, full name Jean-Baptiste Joseph Fourier, was a French mathematician and physicist and historical Egyptologist.
Fourier famously accompanied Napoleon Bonaparte on his Egyptian expedition in 1798 as a scientific advisor and was appointed secretary of the Institute of Egypt. During the occupation of Egypt, Fourier worked in the French administration, supervised archaeological excavations, and worked to shape the educational system.
But the main thing in Fourier's life was science. Back in France, he studied the mathematical theory of heat conduction, established the partial differential equation governing heat diffusion, and solved it using an infinite series of trigonometric functions. Fourier showed that heat diffusion obeyed simple observable physical constants that could be expressed mathematically. His work The Analytic Theory of Heat (1822) had a great influence on the development of physics and pure mathematics.
Joseph Fourier was a member of the Paris Academy of Sciences, the French Academy, a foreign honorary member of the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences, and a member of the Royal Society of London.


Alois Gabl, an Austrian painter and draftsman, came from a baker's family and taught himself drawing. He received a scholarship from the Prince-Bishop of Brixen, allowing him to attend the Munich Academy of Fine Arts. Initially focused on church painting, Gabl later shifted to historical and genre painting. He gained attention with his work "Haspinger, die Tiroler zum Kampfe anfeuernd." Gabl became a professor at the academy but had to resign due to illness.




Johann Gottfried Gruber was a German critic and literary historian.
A graduate of the University of Leipzig, Gruber was later appointed professor at the University of Wittenberg, and in 1815 he became professor of philosophy at Halle. Gruber is the author of numerous historical and philosophical works.


Willem Jacob Herreyns, the Younger, was a Flemish painter of history subjects and portraits. He is regarded as one of the last painters in the tradition of the Flemish Baroque and the last follower of Peter Paul Rubens. Herreyns’ work was very highly regarded in his time. His religious compositions stand in the Rubens tradition. Herreyns is considered a draughtsman with a precise line, but his work shows a certain coldness and lacks originality.


John Camden Hotten was a British publisher, writer, linguist and bibliophile.
By mid-1855, Hotten had opened a small bookstore in London and then established his own publishing business, which after his death became Chatto & Windus. Hotten's publishing house published many works by classic and contemporary writers. After spending about six years in America, he was the first to introduce a number of American writers to the British public, including James Russell Lowell, Oliver Wendell Holmes, and Bret Harte.
Hotten compiled The Dictionary of Modern Slang, Slang, and Vulgar Words, first published in 1859 and reprinted many times thereafter. His other major work is A Handbook of Topography and Family History of England and Wales (1863). Hotten also wrote and edited literary and biographical material in various periodicals.
Hotten was a collector, author, and secret publisher of erotic works, which were illustrated, among others, by the famous caricaturist Thomas Rowlandson (1757-1827).


Armand-Gustave Houbigant was a French painter, illustrator, historian, politician and perfumer.
Armand-Gustave was the son of the famous Parisian perfumer Jean-François Houbigant (1752-1807). He took lessons in the atelier of David's pupil A.C. Caraffe and was a close friend of the archaeologist and collector Aubin-Louis Millin. Ubigan was a prolific painter and illustrator. As a young man, he became famous for his drawings for the card game Women of France (1816).
Later, from 1850 to 1855, Houbigant traveled to the Bas-Pyrenees (today the Atlantic Pyrenees), collected materials for an album about the youth of King Henry IV, and made sketches and engravings.
After his father's death, Armand-Gustave Houbigant continued his family's perfumery business.


David Humphreys was an American soldier, statesman, diplomat, writer, poet, and biographer.
He received his bachelor's degree from Yale University, where he became a member of the Hartford Witters and taught, and went to serve in the Continental Army in the summer of 1776.
A close friend and aide to George Washington, Humphreys was an eyewitness and active participant in the early years of the United States. During his long career, Col. David Humphreys served as a soldier, secretary, diplomat, and was a writer, poet, orator, biographer, and industrialist. His speeches, poems, literary works, and correspondence with Washington and others of the founding generation serve as a valuable source for historians of the early republic in the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries.
Because of his intelligence and diligence, David Humphreys had a long record of service and held many public offices, among others serving as U.S. minister to Spain from 1797 to 1801. He was a member of the Royal Society of London and the American Antiquarian Society.


Henry Noel Humphreys was a British artist, illustrator, naturalist, entomologist and numismatist.
He was educated at King Edward's School and studied medieval manuscripts in Italy, and became a distinguished scholar in many fields of science. In addition to publications on entomology, Humphreys wrote works on ancient Greek and Roman coins, archaeology, and the art of writing and printing.
Humphreys was a successful book illustrator, and is also known for publishing sumptuous books whose design is reminiscent of medieval carved and jeweled bindings.


Washington Irving was an American Romantic writer, historian, and diplomat.
Irving has been called "the first American writer" to be recognized in Europe. In 1815, he traveled to England on family business. A huge success in England and the United States was The Sketch Book, published in several installments during 1819-1820, which contained two of the author's most famous works, Rip Van Winkle and The Legend of Sleepy Hollow, and which made him a literary star in both England and the United States.
He continued his literary endeavors and worked at the U.S. Embassy of Great Britain. Returning to the United States in 1832, Irving visited some little-known territories near the western fringes of the country, and this journey inspired his works Journey on the Prairie (1835), Astoria (1836), and The Adventures of Captain Bonneville (1837). Late in life he published several historical and biographical works, including the five-volume Life of George Washington (1855-1859).


Thomas Jefferson was an American politician and statesman, the third President of the United States (March 4, 1801 - March 4, 1809).
Jefferson was the son of a planter and received a law degree. In 1774, he wrote A Summary of the Rights of British America, which attracted public attention, and he soon gained a reputation as one of the first advocates of American independence from the authority of the British Parliament. In the spring of 1775, the Virginia legislature appointed him a delegate to the Second Conference of the Continental Congress. A year later he was appointed to a committee of five, which also included Adams and Benjamin Franklin, to draft a formal statement of reasons to justify a break with Great Britain. Jefferson thus became one of the authors of the Declaration of Independence. Jefferson succeeded Benjamin Franklin as minister to France in 1785, was secretary of state (1790-1793) under Washington, and vice president (1797-1801) under John Adams.
A Democratic-Republican, Jefferson, who believed that the national government should play a limited role in the lives of citizens, was elected president in 1800. One of the most significant accomplishments of Jefferson's first administration was the purchase of the Louisiana Territory from France for $15 million dollars in 1803 (from the Gulf of Mexico to present-day Canada), effectively doubling the size of the United States. During his second term, Jefferson was focused on trying to keep America out of the Napoleonic Wars in Europe. After his second term as president, he was succeeded by James Madison in 1808.
Upon leaving office, Jefferson retired to his plantation in Virginia, pursued his favorite pastimes, and helped found the University of Virginia. In addition to politics, he is known as a writer, farmer, horticulturist, inventor, book collector, art historian, architect, and scientist. He died at the age of 83 on July 4, 1826, the 50th anniversary of the Declaration of Independence.




Jacob Johann Kirchhoff was a German artist. Known for his detailed and captivating watercolors and lithographs, Kirchhoff's artwork primarily captures the historical and cultural essence of his time. He is especially noted for his portrayals of important military figures and scenes from the Prussian wars, contributing significantly to the visual documentation of 19th-century German history.
Among his notable works are "Portraits of Prussian Generals of the Liberation Wars" and "The King's Parade at Tempelhofer Field," both of which showcase his skill in capturing the grandeur of military attire and the solemnity of historical events through watercolor. His artworks are recognized for their historical value and meticulous attention to detail, making them significant pieces for collectors and historians alike.
Some of Kirchhoff's works have been kept in prestigious collections, including a commissioned piece representing Martin Luther, which is housed in the Royal Collection in the UK. His contributions to illustrated books and periodicals further underscore his versatility and importance in the art and culture of his era.
Collectors and experts in art and antiques may find the ongoing auctions and exhibitions of Jacob Johann Kirchhoff's work an excellent opportunity to acquire pieces of notable historical significance. For those interested in staying updated on Kirchhoff's artworks and auction events, subscribing for updates can be a valuable resource.


Fernand Khnopff, full name Fernand-Edmond-Jean-Marie Khnopff, was a Belgian Symbolist painter, graphic artist, sculptor and art historian.
Born into a wealthy family, Fernand attended the Royal Academy of Fine Arts in Brussels, where he studied painting with Xavier Mellerie. Throughout his years at the academy, Khnopff spent summers in Paris studying art, and at the 1878 World's Fair he saw the works of Pre-Raphaelite Edward Burne-Jones and Symbolist Gustave Moreau, which had a decisive influence on his work.
In the early 1880s Khnopff began to exhibit his Symbolist works, often inspired by literary works, particularly by Gustave Flaubert. His paintings combined precise realism with an ethereal fairy-tale atmosphere, and he also painted portraits.
In 1883 Khnopff co-founded Les Vingt, a group of Belgian avant-garde artists. From the early 1990s, he collaborated regularly with the Brussels opera house Royal de la Monnaie, designing costumes and sets for many productions. He also designed the interiors of Brussels' landmark buildings: the Maison Stoclet and the Hôtel de Ville in Saint-Gilles.


Victor Lagye (1825–1896) was a Belgian 19th-century painter known for his genre scenes, historical and religious works. Born in Antwerp, he studied at the Royal Academy of Fine Arts there. He collaborated closely with the artist Henri Leys, contributing to large-scale murals and the restoration of historic buildings. His works are characterized by meticulous detail and attention to historical costumes and interiors.
Though talented, he remained overshadowed by more famous contemporaries. Some of his pieces are housed in the Royal Museum of Fine Arts Antwerp. Details about his birth and death locations, as well as his biography, are less documented compared to leading artists of his time.




Arsène Lacarrière Latour, full name Géraud Calixte Jean Baptiste Arsène Lacarrière Latour, was a French-born American engineer and military officer, architect and surveyor, and writer.
He studied architecture and engineering at the Académie des Beaux-Arts in Paris and served briefly in the French Army Corps of Engineers. In 1805 Latour came to New York, where he worked first as a merchant, then as an architect and surveyor, and opened an architectural firm in New Orleans. In 1812. Latour became a U.S. citizen.
In 1814. Latour became Andrew Jackson's military engineer and made an important contribution to the American victory at the Battle of New Orleans. After the war ended, Latour published a book, Historical Memoirs of the War in West Florida and Louisiana, 1814-1815, which is still valued for its eye-witness view of the war.
In 1816. Latour traveled with Jean Lafitte on an expedition to survey and map the Southwest as an agent for Spain. From 1818 to 1834 he worked as an architect in Havana. His manuscripts include an extensive report describing Havana's thriving economy in 1815-1821, local agricultural production (sugar cane, coffee, tobacco), trade with Europe, the United States, and the colonies of South America; statistics; and a section on the city's possible future expansion and growth. Latour subsequently returned to France, where he died.




Joseph Henri Hubert Lies was a Belgian Romantic painter, draughtsman and engraver. He worked in a wide range of genres including history painting, landscapes, genre scenes and portraits. He enjoyed a European-wide reputation during his lifetime.


Felix Joseph Lipowsky was a Bavarian lawyer, historian and archivist.
Lipowsky studied law in Munich and entered the Bavarian civil service. During the Napoleonic Wars he was assigned diplomatic duties and was also commandant of Munich for a time.
Lipowski was the author of published biographical encyclopedias on Bavarian history, containing a wealth of information on Bavarian art and cultural history. Between 1822 and 1830 he published a collection of Bavarian national costumes, which became the basis for the development of the costume movement in Bavaria.


Edmund Lodge was a British officer, historian, heraldic writer and biographer.
Edmund Lodge was a historian and writer on heraldic subjects. His works included Illustrations of British History, Biography, and Manners in the Reigns of Henry VIII, Edward VI, Mary, Elizabeth, and James I (3 vols., 1791), which consisted of excerpts from the Howard, Talbot, and Cecil Family manuscripts. He also wrote The Life of Sir Julius Caesar (1827). Lodge contributed to Portraits of Eminent Persons of Great Britain (1814). And his most important work on heraldry was Genealogy of the Existing British Peers (1832).


James Logan is a Scottish writer.
Logan studied at the Royal Academy in London, worked as a journalist, and then began to study Gaelic culture. Logan's major work was The Scottish Gael, or Celtic Manners Preserved among the Highlanders (2 volumes), published in 1831, it was dedicated to William IV. He also wrote the texts for The Clans of the Scottish Highlands, published in 1845, with colorful illustrations by Robert McIan (1803-1856).


John Marshall was Chief Justice of the United States Supreme Court from 1801 to 1835, Secretary of State, and one of the founders of the American legal system.
During the Revolutionary War, Marshall served first as a lieutenant and after July 1778 as a captain in the Continental Army. In 1781 he left the service, studied law, and began practicing law in Virginia, in Fauquier County, and then in Richmond. He soon became head of the Virginia bar and was a member of the Virginia assembly. In 1788 he took a leading part in the Virginia convention convened to discuss the proposed U.S. Constitution. In 1797-98, along with Charles Cotesworth Pinckney and Elbridge, Gerry Marshall was appointed by John Adams to negotiate with France.
He was Secretary of State under President Adams from June 6, 1800 to March 4, 1801. At the same time he was appointed Chief Justice of the Supreme Court in 1801 and served in that position until 1835.
John Marshall was a personal friend of Washington, he announced his death in 1799, organized his funeral, and delivered his eulogy. Washington's relatives soon asked Marshall to write a biography of the late president. "The Life of George Washington" was published in London in 1804-1807. It includes illustrations, portraits, facsimile letters, and folding maps.


Thomas Martyn was a British zoologist, conchologist and entomologist.
Thomas Martyn was the founder of the Academy of Painted Natural History in London - for young men "possessing a natural talent for drawing and painting, to be developed under his immediate sole direction" in the art of describing natural history. He published several illustrated volumes on botany, entomology, and history.
In 1784 Martyn began his major work, The Universal Conchologist. He acquired a large number of shells brought back from Cook's third voyage, many of which are illustrated in the book along with specimens from other famous collections. Originally publishing the work in 1784 as two volumes devoted mainly to shells from the South Seas, Martyn later expanded the work to a four-volume set in French and English containing 160 plates.


Karl Marx, full name Karl Heinrich Marx, was a German philosopher, sociologist, historian and economist, social activist, and journalist. One of the most significant political figures in the world, his works have had a great influence on the course of human history.
Karl Heinrich Marx was born into a large Jewish family of rabbinic dynasty, but his father and Karl himself were baptized. The young Karl received a liberal arts education at the University of Bonn and the University of Berlin and was actively involved in the turbulent political life of Germany and France in the 19th century. For his political activities in 1849 he was expelled from Germany, moved with his family to Paris and then to London, where he lived and worked until the end of his life.
In 1844 he met the German socialist Friedrich Engels, who became his friend and collaborator for the rest of his life. Together they had already published the Manifesto of the Communist Party (1848), the most famous pamphlet in the history of the socialist movement. Karl Marx was also the author of the movement's most important book, Das Kapital (Capital). These and other writings of Marx and Engels formed the basis of the system of views and beliefs known as Marxism.
Marx examined the very different versions of socialism that existed in the early nineteenth century and combined them into a doctrine that remained the dominant version of socialism for half a century after his death. His emphasis on the influence of economic structure on historical development was of enduring importance.


Johan Hendrik Louis Meijer was a Dutch painter, etcher, lithographer, and draftsman. He painted in the Romantic tradition and is best known for his seascapes. Meijer received his first training in painting from Westenberg and then continued his studies under JW Pieneman. He went through all the classes at the Royal Academy of Art in Amsterdam. In 1827 he left for France where he practiced landscape painting. In 1831 he returned to Holland. It was there that he first occupied himself with the profession of sea painting with the happy result that he devoted himself entirely to it.


Johann Heinrich Meyer was a Swiss artist and art critic, renowned for his significant contributions to the art and culture of his time. Meyer, born in Stäfa, Switzerland, embarked on an artistic journey that led him to Italy, where he immersed himself in studying Roman sculpture and the works of Raphael. His path crossed with Johann Wolfgang von Goethe in 1787, marking the beginning of a lifelong collaboration and friendship.
Johann Heinrich Meyer's expertise in painting and art history found a prominent platform in Weimar, where he became a key figure at the Weimar Princely Free Drawing School. His involvement with Goethe extended to publishing the art journal Propyläen and managing the art collections at Schloss Weimar. His scholarly pursuits included contributions to Goethe's "Winckelmann and His Century" and a comprehensive History of Art, showcasing his deep engagement with the artistic discourse of his era.
For art collectors and experts, Johann Heinrich Meyer's legacy offers a fascinating glimpse into the intersection of art, culture, and intellectual camaraderie in 18th and 19th-century Europe. His works and scholarly contributions remain a testament to his profound influence on the art world and his pivotal role in the cultural milieu of Weimar.
Stay updated on upcoming sales and auction events featuring Johann Heinrich Meyer's works. Sign up now for exclusive insights and opportunities in the realm of art and antiques.


Benoît-Hermogaste Molin, a 19th-century French painter, distinguished himself in the art world for his unique talent and his contribution to culture. Specialising in painting, Molin left his mark on artistic history with works that still captivate art lovers and collectors.
His paintings, often characterised by emotional depth and impeccable technique, reflect his commitment to artistic expression and visual storytelling. His distinctive style and mastery of colour and form established his reputation in the artistic circles of his day.
The works of Benoît-Hermogaste Molin, preserved in museums and private collections, continue to inspire and intrigue. They bear witness to his enduring legacy in the world of art and painting, illustrating his importance in French cultural history.
For art enthusiasts and antiques experts, Benoît-Hermogaste Molin's creations offer a window into the artistic past and an inexhaustible source of inspiration. By subscribing to our updates, you will be informed of the latest product sales and auction events related to Benoît-Hermogaste Molin. Don't miss this opportunity to explore his artistic world.


Frans Mortelmans was a Belgian painter, draughtsman and engraver. He initially produced portraits, history paintings, marines and genre scenes. From 1892 onwards, he almost exclusively painted very decorative and harmoniously composed still lifes and flower pieces. It is through these works that he established his reputation. His compositions with pink roses are in particular highly valued. His work situates itself between impressionism and realism with some luminist touches. He produced many pastel works. Frans Mortelmans was a very prolific painter. To date, more than 850 of his works have been inventoried.


Franz Hubert Müller was a German painter, historian and art historian.
Until 1814 he worked as a court painter in Kassel, where he copied works from the Kassel gallery. Later he visited St. Petersburg and Moscow, where he painted portraits of Russian military figures. In 1823 Franz Hubert Müller was appointed director of the gallery in Darmstadt.




Clara Wilhelmine Oenicke was a German history, portrait, and genre painter. She was a student of Marie Remy in 1837, then employed by Carl Joseph Begas and later in the studio of Eduard Magnus. From 1840 she worked independently, and in 1848 she also offered drawing and painting lessons for women in her apartment. In 1867, together with Marie Remy, Rosa Petzel, and Clara Heinke, she founded the Verein der Berliner Künstlerinnen. In 1870 she was listed in the Berlin address book as a portrait and history painter.


Mercy Otis Warren was an American poet, satirist, playwright, historian, and essayist of the American Revolution.
Mercy Otis was born into a prosperous Cape Cod Island family and was immersed early in the tumultuous political events taking place in the country at the time. One of her brothers was political activist James Otis, who was involved in the American Revolution from the beginning. In 1754, Mercy Otis married farmer James Warren, who later served in the Massachusetts legislature (1766-78). Through her husband's political connections, Warren was personally acquainted with most of the leaders of the Revolution and was constantly at the center of events for more than two decades.
Combining her own convictions with her writing talent, Warren became a poet and historian of the revolutionary era. Her first incisive and polemical pieces in verse were published in a Boston newspaper. This was followed by the prophetic novel Defeat and other works. In 1790 she published a collection of her works, Poems, Dramatic and Miscellaneous, which included two new plays, The Sack of Rome and The Ladies of Castille. For a woman of the time, such publications were very daring, as female writers usually hid under pseudonyms.
Warren also corresponded extensively with politicians, including George Washington and Thomas Jefferson. In 1805, she completed a three-volume work entitled A History of the Rise, Progress, and Termination of the American Revolution. This book was the earliest work on historical events in the country. Its proximity to political leaders and major national events makes Mercy Warren's writings on the American Revolutionary period especially valuable.


Charles-Pierre Victor Pajol, known as Count Pajol, was a French cavalry soldier, historian, painter and sculptor.
Pajol commanded the French cavalry during the Crimean War of 1853-1856, becoming a division general in 1870. He was the author of several sculptural monuments and historical works. Pajol also left beautiful sketches of Russian military costume and portraits of Tsar Nicholas I and his sons.
Charles Pajol's father, Count Claude-Pierre Pajol (1772-1844), was a Napoleonic general who led the French advance guard in Moscow.


Wilhelm Ferdinand Pauwels was a Belgian history painter who lived and worked in Germany. From 1842 to 1850, he studied at the Royal Academy of Fine Arts (Antwerp). In 1852 he won the Prix de Rome (Belgium) for his painting Coriolanus at Rome and was able to spend four years studying in Italy. From 1862 to 1872, he was the Professor of History Painting at the Weimar Saxon-Grand Ducal Art School. This period was especially productive for him and he completed seven large wall panels at the Wartburg, depicting the life of Martin Luther. After a short stay in Belgium, he returned to Germany, where he became a Professor at the Dresden Academy of Fine Arts. During this period he also executed six large historical wall panels at the Fürstenschule in Meissen. From 1870 to 1881, he produced what was considered his greatest work: twelve frescoes in the upper part of the Ypres Cloth Hall, which had been left incomplete by Charles de Groux. They depicted scenes of Ypres' history from 1187 to 1383.


Nicolaas Pieneman was a Dutch painter, art collector, lithographer, and sculptor. He was the son of painter Jan Willem Pieneman. Pieneman studied under his father and also at the Royal Academy of Fine Arts in Amsterdam; he was a pupil of Jean Baptiste Madou. He specialised in paintings of recent history and in portraits. He was a friend of William II of the Netherlands; he painted the king's inauguration in 1840, and many members of the royal family. He was a member fourth class of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences and by virtue of this, from 1852 of Natura Artis Magistra. He was a member of the Society Arti et Amicitiae. He was a knight of the Order of the Netherlands Lion, a Commander of the Order of Adolphe of Nassau and appointed to the Order of the Polar Star.


Jan Willem Pieneman was a painter from the Northern Netherlands. In 1805 he was appointed as drawing instructor at the artillery and engineering training centre in Amersfoort. He was particularly noted for his paintings depicting events from the history of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands. His fame was established by a painting he did at the Villa Welgelegen, depicting the heroic acts of the Prince of Orange at the Battle of Quatre Bras, followed by a painting of the Battle of Waterloo. The latter found favor with the Duke of Wellington, who invited him to England, on several occasions, to do portraits. In 1820 he was appointed as first director of the Royal Academy of Fine Arts (Koninklijke Academie voor Schone Kunsten) in Amsterdam. He played an important role as mentor and tutor to a group of young artists.


André Ploumo was a Belgian realist painter who specialized in genre scenes, antique interiors, landscapes and images of poultry. He studied at the Royal Academy of Fine Arts in Antwerp and worked for some time in the workshop of Nicaise de Keyser on the Ossenmarkt. At the age of 20, he completed his studies, left the Academy and mainly painted paintings with interiors and figures, inspired by the painting of the 16th-17th centuries. A lucrative genre practiced by many Antwerp artists at the time. In the 1860s, Plumo painted mainly historical genre scenes. In the 1860s he met Jacques Rossels, Isidore Meyers and other landscape painters in Kalmthout. He traveled through the Ardennes, where he painted the Meuse valley and forest scenes several times. Due to his frequent stay in Kalmtaut and its environs, he began to show an increasing interest in nature and animals, he painted pictures depicting livestock and birds. In 1872 he was awarded a diploma and a medal at an exhibition in London.


Aleksandr Sergeevich Pushkin (Russian Александр Сергеевич Пушкин) was a Russian poet, playwright and prose writer who laid the foundations of the Russian realist movement, literary critic and literary theorist, historian, publicist and journalist.
Pushkin was born in Moscow into an aristocratic family. From childhood he showed a unique literary talent and passion for words. His first poems were written in his school years, and since then his path became inseparable from the world of literature.
One of Pushkin's most famous works is Eugene Onegin, a magnificent novel in verse that plumbs the depths of the human soul and explores many themes such as love, friendship, art and society. In this work, Pushkin created an unrivaled image of the Russian aristocrat and poet, Eugene Onegin. Pushkin was also a master of lyric poetry, writing many ineffably beautiful poems that expressed the feelings and emotions of people in a variety of situations. His poems about love, nature and homeland remain eternal and inspire new generations of poets.
Aleksandr Sergeevich Pushkin was a Russian poet, playwright and was also a public figure and a man with a wide outlook. He published articles in which he expressed his opinion on social and political issues of his time. His passion for freedom and justice was always evident in his works and in his life.
Aleksandr Sergeevich Pushkin died on February 10, 1837 as a result of a duel, but his work remains alive and eternal. His literary legacy has left an indelible mark on world literature, and his work continues to inspire fans around the world.




Aloys Wilhelm Schreiber was a German historian, professor of aesthetics, and writer.
Schreiber was a versatilely gifted intellectual-humanitarian, with interests ranging from aesthetics to court, theater, and travel history. He collected folkloric sagas and songs, published journals, and tried his hand at various literary genres, but readers especially loved his descriptions of his travels along the Rhine and its environs. In 1806 the book "Picturesque Views of the Rhine from Mainz to Düsseldorf" was published. Of particular value is Alois Schreiber's descriptive and illustrative work on the costumes, folk festivals and typical occupations of the inhabitants of the Grand Duchy of Baden. In 1813.
In 1813, Schreiber was appointed court historian of Karlsruhe, and in this capacity he contributed not only to the cultural but also to the political recognition of the region with his illustrated books.




William Milligan Sloane is an American educator and historian.
Sloane graduated from Columbia College, then taught history and chaired departments at Princeton and Columbia. He subsequently earned a doctorate from the University of Leipzig. William Sloane wrote several books on European history. The best known of these was Napoleon Bonaparte (4 vols., 1895-97), a monumental work of biographical and historical literature.
He later served as president of the American Academy of Arts and Letters (1920-28), the American Historical Association, and the National Institute of Arts and Letters. Sloane was also an officer of the French Legion of Honor and a Commander of the Order of the Polaris of Sweden. William Sloane was also a founding member of the IOC and served on its board from 1894 to 1924.


Joseph Stallaert was a Belgian painter; best known for his scenes from antiquity. In 1847, he was awarded the Prix de Rome and stayed in Italy until 1852. Upon his return, his mentor Navez exerted some influence to obtain a contract for him to do a painting for the Brussels Town Hall ("The Death of Everard 't Serclaes"). That same year, he became Director of the Academy of Fine Arts in Tournai. In 1865, he was selected to be the first teacher of "Drawing and Painting from Nature" at the Brussels Academy and held several important positions there over the next thirty years.


Willem Steelink Jr. was a Dutch painter and graphic artist, associated with the Laren School. He initially focused on portraits, genre scenes and historical paintings, done in a style influenced by the Romantic style of his father. In 1880, he visited the moors around Gooi and began to paint in the style of the Hague School. Together with his friend, Hein Kever, he spent several summers in Laren where he came under the influence of the Laren School, inspired by Anton Mauve. The picturesque village of Heeze became one of his favorite places to work. Sheep, and their shepherds, was his favorite subject. He was also known for his graphic work and etchings, and made copies of famous works by Jozef Israëls and Johannes Bosboom. Later, he did illustrations, mostly for historical works and children's books, but also for an edition of the New Testament in Sundanese. His works were popular and sold well in Germany, England and Canada. He was a member of many artistic organizations, including Arti et Amicitiae and the Pulchri Studio, and received the Belgian Order of the Crown and the French Order of Saint Lazarus.


Sophia Hermine Stilke, née Sophia Hermine Peipers was a German illustrator and painter of the Düsseldorf school. She studied painting at the Düsseldorf Art Academy. After initially trying out history painting, she switched to painting flowers and arabesques. She went to Berlin with her family in 1850, where she ran a private drawing school. One of her students was Marie Remy. In 1848, 1856, and 1860, Stilke was at the art exhibitions of the Berlin Art Academy as well as 1867 and 1870 represented at those of the Verein der Berliner Künstlerinnen. In addition to watercolours, Hermine Stilke primarily created illustrations, initials, and other elements of decorative prints. Her works found their way into numerous albums, collections of poems, sayings and songs, travelogues, and luxury volumes as book decorations. They played an important role in the decorative arts of the 19th century. In many of her works, Stilke used the new medium of photography based on chromolithography. She is considered one of the most important German artists of the 19th century.


Anton Hermann Stilke, a German painter associated with the Düsseldorf School of Painting, is renowned for his depictions of Joan of Arc's life. Originally interested in agriculture, he pursued art and studied under Carl Wilhelm Kolbe and Peter von Cornelius. Stilke worked on various projects in Düsseldorf and Munich, including frescoes in the Munich Hofgarten. He also decorated Stolzenfels Castle's Great Hall with murals depicting the "Six Knightly Virtues." Stilke became a professor at the Berlin Academy. His wife, Hermine Peipers, was an accomplished watercolorist.


John Addington Symonds was an English poet and literary critic. A cultural historian, he was known for his work on the Renaissance, as well as numerous biographies of writers and artists. Although married with children, Symonds supported male love (homosexuality), which he believed could include pederastic as well as egalitarian relationships, referring to it as l'amour de l'impossible (love of the impossible). He also wrote much poetry inspired by his same-sex affairs.


Pieter (Pierre) van Hanselaere was a Belgian painter in the neoclassical style, who specialized in portraits and religious and historical scenes. In his early days he specialized in portraiture and achieved a high level of technical perfection. Due to the Napoleonic wars he was not able to leave for Italy until 1816; when he did, he first stayed in Rome and painted portraits of some high-ranking officials, before moving to Naples and achieving success there as well, becoming the painter for the royal court.


Pieter Van Huffel was a Belgian portrait and history painter and industrialist. He received his first drawing training from his uncle Pierre Canivé, a painter and restorer in his hometown. Courses at the Royal Academy of Fine Arts in Ghent followed. Here he already won first prizes in 1786 and 1788. After his student years Pieter Van Huffel settled in Ghent. In 1796 he was first represented at the Ghent Salon with two religious works. After that he regularly exhibited there until 1832. In 1805 he was appointed artistic director and in 1814 professor at the Academy in Ghent. In 1811 he was appointed permanent president of the Société des Arts in Ghent, which he had founded with other artists in 1808. Pieter Van Huffel's oeuvre consisted mainly of portraits and historical motifs; he also produced several Christian religious works for various churches in Ghent.


Joseph Henri François Van Lerius was a Belgian painter in the Romantic-Historical style. Van Lerius painted mythological and biblical scenes as well as portraits and genre pictures. Much of his work is didactic in nature. Perhaps his best-known work is "Lady Godiva", which was shown at the Antwerp Triennial Salon in 1870. Many of his works (especially "Lady Godiva" and "Cinderella") have been widely reproduced.


Ignatius Josephus van Regemorter was a Flemish historical, landscape, and genre painter and engraver. He studied under his father, Petrus Johannes, also in Paris, Antwerp, Brussels, and Ghent.


Gustave Vanaise is a Belgian painter. Gustave Vanaise paints historical and religious subjects, intimate scenes and is also a portrait painter. He studied at the Royal Academy of Fine Arts in Ghent in the studio of Théodore Canneel, then in Brussels. He is part of an enthusiastic group of artists and sculptors from Saint-Gilles (Brussels). In 1883, he was one of the founding members of the Brussels avant-garde group “Les Vingt”. He resigned in 1886. We owe him portraits, as well as vast decorative compositions "in which the traditional vision of the Flemish school darkens to reflect new sensibilities", as Gustave Vanzype writes
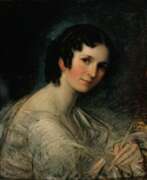

Maria Elektrine von Freyberg was a German painter. Trained by her father, Johann Baptist Stuntz, a renowned landscape painter, Maria quickly demonstrated remarkable artistic talent. Her extensive travels through France and Italy greatly influenced her work, especially her stay in Rome, which enriched her painting style.
Maria Elektrine's art is celebrated for its delicate touch and emotional depth, particularly in historical scenes and portraiture. Some of her notable works include "The Holy Family," "The Birth of St. John," and "A Boy Playing the Flute." These pieces are distinguished not only by their technical excellence but also by their tender and evocative portrayals of their subjects.
Her works are held in high esteem and can be found in various prestigious collections, such as the Munich Gallery, the Leuchtenberg Gallery, and even as far as the Hermitage in St. Petersburg. This widespread recognition underscores her contributions to the 19th-century art scene, particularly within the German Romantic movement.
For those deeply invested in the world of art and antiques, Maria Elektrine von Freyberg's works offer a rich exploration of German romanticism. Her paintings are a testament to her skill and a window into the cultural and historical milieu of her time.
If you are an enthusiast or a collector keen on early 19th-century art, ensure you stay informed about updates related to Maria Elektrine von Freyberg's works. Sign up now to receive notifications on new discoveries, auction events, and sales concerning her masterpieces. Join us in preserving and appreciating the legacy of one of Germany's illustrious painters.


Carl von Häberlin was a painter from Württemberg. He received his initial training at the National Academy of Fine Arts in Stuttgart and studied at the Academy of Fine Arts in Düsseldorf from 1852 to 1856. Häberlin then moved to Stuttgart and became a prolific illustrator. He was professor of genre painting at the Academy of Applied Arts in Stuttgart from 1868 to 1885. Häberlin also worked on large-scale murals on the Dominican island in Konstanz from 1878 to 1894, depicting scenes from the island's history. He received the Medal of Honor of the Order of the Crown of Württemberg in 1901.


Franz Sigmund von Wagner was a Swiss painter, caricaturist, engraver and historian.
Wagner contributed to art magazines, traded in art, was a member of the Bern Society of Artists, and assisted the government of Bern in building a collection of paintings, the foundation of which he laid. Wagner, who was fascinated by the history of the Swiss Confederation and Old Bern, was a member of the Bern Society for the Study of History, founded in 1811, and wrote historical studies.
Sigmund Wagner is also known for his aptly critical caricatures on social topics.


Franz Xaver Freiherr (from 1801) von Zach, Baron (Hungarian: Zách János Ferenc) was an Austro-German astronomer, surveyor, mathematician, science historian and officer of Hungarian origin. He rendered outstanding services in the exploration of the solar system and the organization of international astronomy, after whom a lunar crater (Zach) and an asteroid ((999) Zachia) were named, among others. He was also the founder of the first scientific journals and organised the first astronomical congress in 1798.


Isaac Weld was an Irish explorer, writer, and artist.
After completing his studies, Isaac Weld traveled to the new lands of America in 1795, meeting Thomas Jefferson and George Washington. The purpose of his journey was to learn of opportunities for Irish resettlement. Returning in 1797, Weld soon published his book, A Journey through the States of North America and the Provinces of Upper and Lower Canada. In general, Weld did not like the United States; he particularly noted the practice of slavery and the treatment of Native peoples by the rude new Americans. But he liked Canada and Quebec: he praised the views from the Citadel and reported that because of the low cost of land, a middle-income person could easily settle in the country for himself and his family.
This book by Weld was quite popular: it went through several editions from its first publication in 1799 to 1807. By 1820, it had also been translated into French, German, Italian, and Dutch.
In 1800 Weld was elected a member of the Royal Society of Dublin. In 1811 and 1812 he served on the library committee, and on December 4, 1828, he was elected honorary secretary. His first act in this capacity was to establish an annual exhibition of specimens of the manufactures and products of Ireland. Isaac Weld published several other books on Ireland and Great Britain, illustrated with his own drawings. Of these, his Statistical Survey of the County of Roscommon, over seven hundred pages long, published by the Royal Dublin Society in 1832, stands out.