Writers 17th century


Abraham a Sancta Clara, real name Johann Ulrich Megerle, was an Augustinian monk and satirist, court preacher in Vienna.
Possessing an inimitable style of preaching that included folksy humor and harsh acrimony, Abraham was very popular with his contemporaries. He fearlessly scourged human vices, using both high pathos and puns, while conveying religious and moral messages. Some 600 of his recorded sermons on various subjects have survived.


Robert Barrow was an American Quaker missionary, traveler, and writer.
Barrow participated in a voyage led by a Quaker trader from Jamaica, Jonathan Dickinson (1663-1722), traveling from Kingston to Philadelphia, but ran aground on the east coast of Florida. They were captured several times by the natives of the region. In March 1696, Jonathan Dickinson and his family and Robert Barrow sailed from Charles Town and reached Philadelphia fourteen days later. On April 4, 1697, three days after arriving in Philadelphia, Robert Barrow died.
Dickinson's account of their capture, release, and subsequent rescue by the Spanish was published in 1699 in Philadelphia under the title God's Patronizing Providence. The book became a bestseller. Robert Barrow had time to write his account of the adventure after their rescue by the Spanish governor of St. Augustine, who provided them with a canoe to take them to the English settlements in South Carolina.


Jacques Basnage de Beauval was a French theologian and historian, diplomat and writer.
His father was a prominent lawyer and his grandfather and great-grandfather were pastors, Jacques studied theology and languages at the Academy of Saumur, then at Geneva and Sedan. In 1676, Jacques Basnage was appointed pastor at Rouen during the revocation of the Edict of Nantes, was forced to flee France for Holland, where he worked as a theologian, polemicist, historian, and diplomat in the service of the Grand Pensioner Hensius.
In 1717, on behalf of Holland, Basnage was sent to sign the treaty of the Triple Alliance (France, Holland, England). In the Annals of the United Provinces (1719-1726), compiled from the peace negotiations held at Münster, he displays breadth of vision, wisdom, and impartiality.
About 1719 Jacques Basnage was appointed historiographer of the Dutch states. He wrote several books on the Bible, the history of the Church, and the history of the Jewish people. Among the best known of these are his History of the Religion of the Protestant Denominations (1690), History of the Church of Jesus Christ to the Present Time (1699), written from Protestant positions, and History of the Jews (1706), as well as Jewish Antiquities, or Critical Notes on the Republic of the Jews (1713).


Ismaël Boulliau (Boulliaud), also known as Ismael Bullialdus, was a French astronomer and mathematician who followed the teachings of Copernicus.
Boulliau worked as a librarian for many years and had the opportunity to study the scientific works of Copernicus, Galileo, and Kepler, and as a result became a strong supporter of the heliocentric system of the world. Boulliau was also intimately acquainted with Huygens, Gassendi, Pascal and other prominent scientists of the time, and he translated many works from Greek into Latin.
Boulliau's main astronomical work, published in 1645, was Astronomia philolaica (Astronomy of Philolaus, named after the ancient Greek Pythagorean philosopher Philolaus, who promoted the idea of the motion of the Earth). In it, he supported Kepler's first law that the planets move on ellipses, and provided new evidence for this. Isaac Newton, in Book III of The Mathematical Beginnings of Natural Philosophy, relies on measurements of the magnitudes of planetary orbits determined from observations by Kepler and Boulliau.
Boulliau was also interested in history, theology, classical studies, and philology. He was active in the Republic of Letters, an intellectual community whose members exchanged ideas.


Joachim Bouvet was a French Jesuit monk and missionary who worked in China.
Joachim Bouvet was one of six Jesuit mathematicians chosen by Louis XIV to travel to China as his envoys and work as missionaries and scholars. In 1687 in Beijing, Bouvet began this work, especially in mathematics and astronomy, and in 1697 the Chinese emperor Kangxi (1654-1722) sent him as ambassador to the French king. Kangxi expressed his wish that Bouvet should bring more missionary scientists with him. Thus, in addition to his scholarly work, Bouvet was also an accomplished diplomat and served as a liaison between the Chinese Emperor Kangxi and King Louis XIV of France.
Bouvet brought to France a manuscript describing Kangxi's life with an eye for diplomatic subtleties, as well as a collection of drawings depicting graceful Chinese figures in traditional and ceremonial dress. The first French edition of The Historical Portrait of the Emperor of China was published in Paris in 1697, and was subsequently translated and published in other languages. And Bouvet returned to China in 1699 with ten new missionaries and a collection of King Louis XIV's engravings for Emperor Kangxi. He remained in China for the rest of his life.
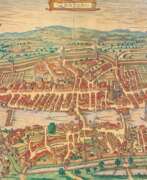

Georg Braun was a German topographical geographer, cartographer and publisher.
Braun was the editor-in-chief of the Civitates orbis terrarum, a groundbreaking atlas of cities, one of the major cartographic achievements of the 16th century. It was the first comprehensive and detailed atlas, with plans of the world's famous cities and bird's-eye views, and became one of the best-selling works of the time.
The book was prepared by Georg Braun in collaboration with the Flemish engraver and cartographer Frans Hoogenberg. Braun, as editor-in-chief, acquired tables, hired artists, and wrote the texts. They drew on existing maps as well as maps based on drawings by the Antwerp artist Joris Hofnagel and his son Jacob. Other authors include Pieter Bruegel the Elder (c. 1525-1569), Jacob van Deventer (c. 1505-1575), and more than a hundred other artists and engravers.


Edward Browne was a British physician, president of the College of Physicians, traveler, historian and writer.
Edward was the eldest son of the famous British scientist Sir Thomas Browne (1605-1682), received a Bachelor of Medicine degree from Cambridge later and a Doctor of Medicine degree from Oxford, and became a member of the Royal Society. In addition to medicine, his subjects of study included botany, literature, and theology. He lived in London and traveled throughout Europe visiting museums, churches, and libraries (Italy, France, the Netherlands, and Germany). In 1673 he published an account of his travels in Eastern Europe, notable for its scrupulous accuracy.
Edward Browne also published two other works: a historical treatise and biographies of Themistocles and Sertorius. He was physician to King Charles II of England and left many manuscript notes on medicine. The chronicle of his journey through Thessaly is a unique and valuable source of information about the region in the second half of the 17th century. He was admitted to the College of Physicians in 1675 and served as its president from 1704 to 1708.


Étienne Chauvin was a French Protestant theologian and philosopher.
Chauvin's philosophy and worldview were entirely Cartesian. After his expulsion from Nîmes, Étienne Chauvin withdrew to Rotterdam, where he preached for several years in the Walloon Church. He was succeeded as professor of Baille at Rotterdam. In 1695 the Elector of Brandenburg appointed him pastor and professor of philosophy, and afterward inspector of the French college at Berlin.
Etienne Chauvin's major work is Lexicon Rationale, sive Thesaurus Philosophicus (1692). He also wrote Theses on the Knowledge of God (1662) and published the New Journal of Scholars (1694-1698).


Jan Commelin (Dutch: Jan Commelin or Jan Commelijn), also Johannes Commelin, was a Dutch botanist.
Jan Commelin is the son of the historian Isaac Commelin. He was a professor of botany and director of the Amsterdam Botanical Gardens. Jan Commelin wrote many scientific works on botany, notably compiling the first volume of descriptions of East and West Indian plants. The second volume was written by Jan's nephew, the botanist Caspar Kommelin, who expanded the earlier descriptions and added notes on African plants.


Caspar Commelin was a Dutch botanist and mycologist.
Caspar Commelin was trained as a medical doctor, practiced botanical science and worked on books that were left unfinished due to the death of his uncle, botanist Jan Commelin. Caspar was mainly interested in exotic plants.


François Couperin was a French composer, organist and harpsichordist.
François Couperin is a member of a large dynasty of French musicians. At the age of 18, François succeeded his father, Charles Couperin (1638-1679), as organist at the Church of Saint-Gervais in Paris, and in 1693 he became one of the four organists of the Chapel Royal. He soon became a harpsichord teacher for the royal children, and in 1717 was appointed court harpsichordist.
François Couperin is known primarily for his harpsichord music; between 1713 and 1730 he published four books of more than 250 pieces for harpsichord. Some of them are characterized by complex accompaniment and dialogues between violin and bass, while others are light, graceful and expressive. Couperin's harpsichord pieces, even during the author's lifetime, gained great fame not only in France but also abroad. Couperin also wrote chamber music, including trio sonatas (for harpsichord and two violins) and "Royal Concertos", which he composed for Sunday evening royal entertainment. He also composed motets and other church music. Couperin's last and most significant liturgical work, Leçons de ténèbres (c. 1715), has no parallel in either French or Italian music of the period. Johann Sebastian Bach knew and appreciated this work by Couperin.
Couperin authored The Art of Touching the Clavier (1716), in which he explained in detail the technique of playing the harpsichord. And in his publications of the early 1720s, he suggested a wide variety of ways of combining French and Italian styles.


Romeyn de Hooghe was a Dutch painter, sculptor, engraver and caricaturist of the late Baroque period, writer and philosopher.
Hooghe became famous for his political caricatures of King Louis XIV of France and propaganda pamphlets in support of William of Orange. He portrayed the war against the French monarch and his allies as a struggle between freedom and religious despotism.
Romeyn de Hooghe was a superb engraver and created over 3,500 engravings during his lifetime. His most important work is Hieroglyphica of Merkbeelden der oude volkeren (Hieroglyphics or Symbols of the Ancient Peoples), where he appeared not only as a consummate master of engraving, but also as a historian, talented writer and philosopher. This book has long been regarded in Europe as one of the most authoritative sources on classical mythology. It contains 64 engravings illustrating all stages of the narrative of myths, ancient cults and beliefs, and the interpretation of scripture, a guide to medieval Europe.
Romeyn de Hooghe also illustrated books and painted large panels. During his lifetime he was widely recognized as a painter and sculptor not only in his own country but also in other European countries.


Juana Inés de la Cruz or Juana of Asbaje, real name Juana Inés de Asbaje Ramírez de Santillananota, was a Mexican poet, scholar, and writer of the Latin American colonial period and the Spanish Baroque, and a Jerónimo nun.
Juana Ramírez was born into a poor family (Spanish father and Creole mother) and from an early age showed a burning thirst for knowledge and giftedness, but as a woman she was almost entirely self-taught. By her teens, she had already learned Greek logic and taught Latin to young children. She also learned Nahuatl, an Aztec language spoken in Central Mexico, and wrote several short poems in the language. At the age of 16, the girl was introduced to the court, and her intelligence impressed even Viceroy Antonio Sebastian de Toledo, Marquis de Mancera, and in 1664 he invited her to serve as maid of honor.
In 1669, at the age of 21, she took her tonsure at the Convent of Santa Paula of the Hieronymite Order in Mexico City, where she remained a recluse for the rest of her life. In the convent, Sister Juana enjoyed exceptional freedom: she continued to socialize with scholars and senior members of the court, amassed one of the largest private libraries in the New World, as well as a collection of musical and scientific instruments. Her plays in verse, poetry, and compositions for state and religious festivals were frequently and successfully performed at the palace.
Sister Juana was an outstanding representative of Spain's Golden Age: she was the last significant writer of the Latin American Baroque and the first great exponent of colonial Mexican culture. Sister Juana wrote sonnets, romances, and ballads, drawing on a vast store of classical, biblical, philosophical, and mythological sources. She also composed moral, satirical, and religious texts, as well as many poems praising courtiers, but she also defended women's right to education.
At the end of her life, due to pressure from religious dogmatists, Sister Juana had to sell her extensive library of some 4,000 volumes and return to strict reclusiveness. In 1695, the plague struck the convent and, while caring for her sisters, Juana died of the disease at about the age of forty-four.
Today, Juana Inés de la Cruz is a national icon of Mexico and Mexican identity as a prominent writer of the Spanish-American colonial period. The former convent where she lived is a center of higher education, and her image adorns Mexican currency.


Pedro de Oña, full name Pedro de Oña y Villegas de Acurcio, was the first known poet born in Chile.
Pedro was the son of a military captain, Gregorio de Oña, who died during the Spanish conquest of Chile. After studying at the University of San Marcos in Lima, he joined the army and participated in several battles against rebellious Indians. De Oña is known to have spent many years in Peru.
Pedro de Oña's best-known literary work is Primera parte de Arauco domado (The First Part of the Conquest of Araucana, 1596), a verse epic in rhymed couplets depicting the deeds of the Marquis Hurtado de Mendoza, viceroy of Peru from 1556 to 1560. The realistic descriptions of violence and sensationalized accounts of Mapuche customs offended many, including the Bishop of Lima, and the book was banned. Today, however, it is valued as an eyewitness account of historical events.


Antonio de San Román de Ribadeneyra, also San Román de Rivadeneira/Ribadeneira, was a Spanish Benedictine monk and historical writer.
He served at the monastery of San Zoil near Carrión de los Condes and wrote several historical books. In particular, an account of King Sebastião I's disastrous invasion of Morocco in 1578 and his death in battle entitled Jornada y muerte del Rey Don Sebastião de Portugal (1603). Antonio de San Román de Ribadeneyra also wrote A General History of Eastern India (1603). This historical work focuses on the Portuguese expeditions to Asia and the Americas, including a description of Christopher Columbus.


Benedictus Spinoza (Spanish: Baruj Espinosa) at birth Baruch Spinoza is a Dutch philosopher-rationalist of Jewish origin, a bright representative of the Age of Enlightenment.
Spinoza was born into a family of Portuguese Jews in Amsterdam, who converted to Christianity but returned to Judaism. As a young man, he was considered an outstanding Talmudic scholar and a promising religious scholar. But, inspired by the philosophical writings of René Descartes and Francis Bacon, the young philosopher soon fell outside the orthodox tradition because of his radical views. In 1656 he was severely excommunicated for heresy.
For the rest of his life, Spinoza spent his modest life grinding lenses and privately teaching philosophy, but he also wrote anonymously published philosophical treatises and secretly exchanged letters with many philosophically inclined luminaries of the wider European Enlightenment. Spinoza's only book, published in 1663 in Amsterdam under his own name, was Renati Des Cartes Principiorum Philosophiae Pars I, & II, More Geometrico demonstrate (Principles of Cartesian Philosophy). These principles served as a preparatory work for many metaphysical views in his most important treatise, Ethics (1677).
Benedict Spinoza defended the philosophical life from religious persecution and advocated a new, liberal, democratic regime to support that life. Although Spinoza was often persecuted as an atheist in his time, his writings played an important role in shaping philosophy, theology, and politics in the centuries to come. Of all the philosophers of the seventeenth century, Spinoza is one of the most relevant today.


René Descartes was a French philosopher, mathematician, and natural scientist who is considered the founder of modern philosophy.
Descartes was a very versatile scientist: besides numerous philosophical reflections, he wrote works on optics, meteorology and geometry. Contemporaries noted his extensive knowledge in many sciences. Descartes owns the famous saying "I think, therefore I exist" (best known in the Latin formulation "Cogito, ergo sum", although it was originally written in French: "Je pense, donc je suis").
He developed a metaphysical dualism that radically distinguished between mind, whose essence is thought, and matter, whose essence is extension in three dimensions. Descartes' metaphysics is rationalistic, based on the postulation of innate ideas of mind, matter, and God, but his physics and physiology, based on sense experience, are mechanistic and empirical.
Unlike his scientific predecessors, who felt a holy awe at the incomprehensibility of the divine essence of the universe, Descartes admired the ability of the human mind to understand the cosmos and to generate happiness itself, and rejected the view that human beings were inherently unhappy and sinful. He believed that it was inappropriate to pray to God to change the state of things and the world; it was much more productive to change oneself.


Denis Dodart was a French botanist, naturalist and physician.
Dodart studied at the University of Paris, received a doctorate in medicine and was already in his youth known for his erudition, eloquence and open-mindedness. In 1673 he was elected to the French Academy of Sciences.
He is known for his early studies of plant respiration and growth. Dodart collaborated with the French engraver Nicolas Robert to illustrate his botanical works.


John Donne was a British preacher and poet, a major exponent of English Baroque literature.
His father was a wealthy merchant, and he was educated at Oxford, Cambridge, and Lincoln's Inn. Then began to write satires, which were willingly passed from hand to hand. The first three of Donne's famous satires date from 1593, and the others were written at various times before 1601. In 1594 he began his travels in Europe, accompanied the Earl of Essex on the capture of Cadiz in 1596 and on the expedition of 1597, and was in Italy and Spain.
In 1601. John Donne wrote his remarkable poem "The Progress of the Soul", in 1610 published his prose work against Catholics "Pseudo-Martyr", and in 1611. - an even harsher polemical treatise, Ignatius in Conclave. John Donne was also the author of many sonnets, love poems, elegies, epigrams, and religious sermons.
In 1621 John Donne was appointed rector of St. Paul's Cathedral in London, and near the end of his life he became a popular eloquent preacher whose sermons were eagerly printed and published. 160 of his sermons have survived, including the most famous, Death's Duel, which he delivered in Whitehall before King Charles I on February 25, 1631, a few weeks before his own death.


Armand-Jean du Plessis, duc de Richelieu, also known as Cardinal Richelieu or the Red Cardinal (French: l'Éminence rouge) was a Roman Catholic cardinal, aristocrat and statesman of France.
Armand Jean's father, François du Plessis, Signor de Richelieu, was the grand proclaimer (chief magistrate) of Henry III, but left his family devastated at his death. At the age of 22, Armand was ordained a priest and began to build a career. Thanks to his intellectual talents, he was soon appointed chaplain to the new Queen Anne of Austria, and in 1616 he was appointed Secretary of State for War and Foreign Affairs. Further events and a palace coup led to his exile, but he returned to Paris five years later.
The Duc de Richelieu became a cardinal in 1622, and from 1624 until his death in 1642 he was chief minister to King Louis XIII of France. His main goals were to establish royal absolutism in France and to end the Spanish-Habsburg hegemony in Europe. He made significant strides in reforming France, especially in terms of the administrative structure of the government.
The intrigues of his opponents accompanied the Duc de Richelieu throughout his political life. In the last years of his life he found himself involved in religious conflicts, in opposition to the pope in a struggle with the French church over the distribution of revenues intended to finance the war.
Richelieu possessed outstanding intellectual ability, willpower, and industriousness. He directed his own wealth to patronizing the arts and the University of Paris; he established the French Academy. Richelieu was also a talented playwright and musician.


Johann Sigismund Elsholtz (also Elßholtz, Elßholz, Elsholz, Latin Elsholtius) was a German physician, botanist and chemist, a pioneer of hygiene.
Elsholtz studied at the universities of Wittenberg, Königsberg, and Padua, where he received his doctorate. In 1654, he published Anthropometry, written for artists and astrologers as well as students of medicine and physiognomy. The book also explored the supposed relationship between the proportions of the human body and morbidity. Elsholtz was a very versatile scientist and worked in the fields of horticulture, botany, alchemy, astrology, dietetics and medicine, among others.
Elsholtz was later appointed court botanist, alchemist and physician to Elector Friedrich Wilhelm of Brandenburg (1620-1688), and in 1657 was placed in charge of his botanical gardens in Berlin, Potsdam and Oranienburg. In 1672 his treatise Vom Garten-Baw: Oder Unterricht von der Gärtnerey auff das Clima der Chur-Marck Brandenburg was published in Berlin. ("From the Garden Bow or Lessons in Gardening in the Climate of Chur-Marck Brandenburg." It presents the latest gardening techniques for the German climate, discussing flower gardens and their design, vegetable gardens, medicinal gardens, and vineyard care and design.
Elsholtz was a German pioneer in the field of cleanliness and nutrition. Generally speaking, the term "hygiene" first appeared in German in 1682 in his Dietetikon. It is the term he uses to describe the principle of maintaining good health. In his book, the doctor makes recommendations for healthy eating and drinking. He calls for clean water and good air and emphasizes the importance of personal hygiene. Elsholtz was one of the first to administer intravenous injections to people around 1665.


Franz Ertinger (German: Franz Ertinger) was a French painter born in Germany but working in France and Flanders, a member of the Guild of St. Luke in Antwerp.
Ertinger is a versatile artist who has applied his talents in various fields of art. He is known as a painter, illustrator and printer of books, draughtsman, designer and writer, and worked as a royal engraver in Paris.


Wilhelm Fabry von Hilden or Fabricius von Hilden (Latin: Fabricius Hildanus) was a German and Swiss Renaissance physician and surgeon, the founder of scientific surgery.
In 1576 he began a four-year apprenticeship as a surgeon with a barber in Neuss. Surgery at that time was considered the craft of bath and barbers; surgeons or wound doctors treated wounds, broken bones, inflammations, and many other ailments. After completing his apprenticeship, Fabry worked for five years as an assistant wound surgeon to Cosmas Slot (died 1585) at the court of Duke Wilhelm V in Düsseldorf. To expand his anatomical knowledge, Fabry constantly dissected and prepared cadavers. In later years, he also encouraged his students to do so and conducted public autopsies to draw attention to the importance of anatomical knowledge. He also made it a habit to do practice procedures on a cadaver before surgery.
In 1615 Fabry was appointed city physician of Bern. Here he wrote several books on gunshot wounds. In 1623 the versatile physician published a small book, "Christian and Good-Hearted Caution against Drunkenness," which he republished in more detail the following year under the title Christlicher Schlafftrunck. Fabry's most important surgical treatise was Observationem et curationem chirurgicam centuriae sex ("Six hundred surgical observations and cures"), first published in 1606. This compilation remained the most important book of German surgery until Lorenz Heister. It describes new surgical methods and surgical instruments for the treatment of amputations, nasal polyps, bladder stones, dropsy, hernias, ascites, etc., etc., etc.
For centuries, Fabricius remained one of the most respected surgeons not only in Germany and Switzerland, but throughout Europe. Among his many accomplishments in the field of surgery may be enumerated his innovation in the amputation of the thigh, for which he invented a special tourniquet; the excision of involved axillary glands in breast cancer; the first classification of burns into three degrees with the appropriate treatment for each variety; and the first description of a medical field chest for military purposes.
Although in his later years Fabritius had already given up practicing medicine, he continued to write medical papers and maintain an active scientific correspondence until his death. He authored some 20 medical books. It was his surgical works, translated into German, French, Latin, English and Dutch, that ensured his recognition centuries later.


Giovanni Battista Ferrari was an Italian Jesuit scholar, professor of Oriental languages and botanist.
Giovanni Ferrari had linguistic abilities and at the age of 21 knew Hebrew well, spoke and wrote Greek and Latin perfectly, and learned Syriac. He became professor of Hebrew and rhetoric at the Jesuit College in Rome and edited a Syriac-Latin dictionary in 1622.
Ferrari always showed great interest in the systematics and classification of fruits. He was appointed head of the chair of Hebraistics at the College of Rome and held this position for 28 years. In 1623, Ferrari became horticultural advisor to the family of Pope Urban VIII at the Palazzo Barberini, which soon became famous for its rare plants, including orange trees. Ferrari later wrote the first book on citrus trees, equating them to the mythical golden apples of the Hesperides conquered by Hercules. Orange trees became an important element of Baroque gardens, symbolizing the rewards earned by the magnanimous prince. The scientist also described the medicinal properties of citrus fruits.
In 1633, the first treatise on floriculture, De florum cultura, was published. In it, Ferrari describes garden layout with contemporary examples, flower specimens and their cultivation, and general horticulture.


Philips Galle was a Dutch publisher, best known for publishing old master prints, which he also produced as designer and engraver. He is especially known for his reproductive engravings of paintings.
As a resident of Antwerp, Galle witnessed numerous events of the Eighty Years War, notably the siege and looting of the town in 1576 by the Spaniards, called "The Spanish Fury". This rather personal book, which was translated in several languages soon after its first publication, shows Galle as a peace-loving person who intended to stay far away from the political and military turmoil of his era.


Pierre Gassendi was a French Catholic priest, Epicurean philosopher, mathematician, astronomer and researcher of ancient texts.
He taught rhetoric at Diné and philosophy at Aix-en-Provence. Gassendi's Syntagma philosophicum, the result of his historical research and philosophical reflections, is a well-known work. Several of his works on astronomy, physics and mechanics were also published in the 17th century.


Johannes Goedaert was a Dutch naturalist, entomologist and artist.
Goedaert was one of the authors on entomology and the first to write about insects in the Netherlands and Europe, based on his own observations and experiments between 1635 and 1667. In 1660, Goedaert published the first of three volumes collectively titled Metamorphoses and History of Nature, the last volume appearing in 1669.
Goedaert's work is valuable in that for the first time he used his own drawings instead of woodcuts to illustrate his insects, and they are of noticeably higher quality than those in Moffett's volume. Goedaert was a talented and observant artist and draughtsman, and he used magnifying glasses but preferred to draw insects at life-size. The book depicts detailed phases of insect growth, including their metamorphosis. The scientist not only described the process of their development, but also described and sketched the various stages that insects go through during their life cycle.


Ben Jonson or Benjamin Jonson was an English poet, playwright, actor and dramatic theorist.
Jonson came from a simple family, served in the army, seriously engaged in self-education, and in 1586 began a career in the theater. In the 1590s he had the good fortune to meet William Shakespeare. In 1598 Shakespeare was able to put in the theater "Globe" Jonson's play "Every man for his own good," where he played one of the roles. The two playwrights became friends and collaborated on productions of the plays. Jonson was one of the most erudite playwrights of his time and was sure to apply his deep knowledge of Greek and Roman classics in his work.
Jonson's daring character failed him more than once: he often got into fights and duels, and later began to prefer direct violence mockery of his opponents in his plays. But even in this case, he not once got into serious trouble and even sat in prison.
In 1605 Jonson with great success put in the "Globe" play "Volpone". A great admirer of Johnson's work was King James, and the next ten years were the most colorful in his career. His plays written between 1605 and 1615 - Epicoen, The Alchemist, Catalina, Bartholomew Fair and The Devil is an Ass - were a great success, rivaling Shakespeare himself.
Ben Jonson is a vivid representative of English literature of its Renaissance period. His best works ridicule human weaknesses with the help of comic realism, verbal brilliance and a remarkable gift for caricature and parody.


Francis Junius the Elder, born François du Jon, was a French linguist, exegete and professor of Reformed theology, and diplomat.
Junius first studied law and then theology and became a student of Jean Calvin and Theodore Beza in Geneva. For his success and knowledge of languages he was appointed minister at Antwerp, but was forced to flee to Heidelberg in 1567.
In collaboration with Immanuel Tremellius he wrote one of the significant translations of the Bible into Latin, and his theological work De Vera Theologia is the most important work on Reformed dogmatics. Some of du Jon's works were published in 1882 by Abraham Kuyper in his Reformed Library. His son François du Jon the Younger (1591 - 1677) became a noted art historian and founder of Germanic philology.


Athanasius Kircher was a German scholar, inventor, professor of mathematics and oriental studies, and a friar of the Jesuit order.
Kircher knew Greek and Hebrew, did scientific and humanities research in Germany, and was ordained in Mainz in 1628. During the Thirty Years' War he was forced to flee to Rome, where he remained for most of his life, serving as a kind of intellectual and information center for cultural and scientific information drawn not only from European sources but also from an extensive network of Jesuit missionaries. He was particularly interested in ancient Egypt and attempted to decipher hieroglyphics and other riddles. Kircher also compiled A Description of the Chinese Empire (1667), which was long one of the most influential books that shaped the European view of China.
A renowned polymath, Kircher conducted scholarly research in a variety of disciplines, including geography, astronomy, mathematics, languages, medicine, and music. He wrote some 44 books, and more than 2,000 of his manuscripts and letters have survived. He also assembled one of the first natural history collections.


Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz was a German philosopher and a prominent polymath in many fields of science.
Leibniz was a universal genius; he showed his talents in logic, mathematics, mechanics, physics, law, history, diplomacy, and linguistics, and in each of the disciplines he has serious scientific achievements. As a philosopher, he was a leading exponent of 17th-century rationalism and idealism.
Leibniz was a tireless worker and the greatest scholar of his time. In the fate of Leibniz, among other things, there is one interesting page: in 1697, he accidentally met the Russian Tsar Peter I during his trip to Europe. Their further meetings led to the realization of several grandiose projects in Russia, one of which was the establishment of the Academy of Sciences in St. Petersburg.
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz was also the founder and first president of the Berlin Academy of Sciences and a member of the Royal Society of London.


Fortunio Liceti (Latin: Fortunius Licetus) was an Italian physician, natural philosopher, writer and educator.
Liceti studied philosophy and medicine at the University of Bologna and earned doctorates in these disciplines. He taught logic and philosophy at the University of Pisa, and became professor of philosophy at the University of Padua and the University of Bologna. At the University of Padua, Liceti became friends with Galileo Galilei.
Liceti's inquisitive mind was interested in a wide range of subjects: from genetics and reproduction to gems and animals. In general, Fortunio Liceti was a very industrious and prolific scientist: he published a book each year, writing more than seventy works on a wide range of subjects, including the human soul, reproduction, and birth defects.
In 1616, Liceti wrote and published the first edition of De monstruorum causis, natura et differentiis (On the Causes, Nature, and Differences of Monsters), a chronologically ordered catalog of monsters from antiquity to the seventeenth century. Among these monsters were infants with congenital malformations. Liceti was one of the first scholars to attempt to systematically categorize birth defects according to their causes, including numerous causes not related to the supernatural. This topic interested the scientist greatly and he returned to it several times during his life, supplementing it with illustrations, among other things. From 1640 to 1650. Liceti also wrote and published seven different volumes in which he answered questions from famous people on a wide variety of medical topics.


Martin Lister was a British naturalist and physician.
It could be argued that Lister founded two fields of natural history: arachnology (the study of spiders) and conchology (the study of the shells of organisms). He wrote more than 60 articles in the Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, published several volumes on natural history, speculated on the mysterious nature of fossils, and was successful as a physician.
Lister employed his artist daughters to illustrate his books on insects and molluscs - the names of Susanna and Anne appear on the title pages of the volumes. The Lister family published Historiæ Conchyliorum between 1685 and 1692.


Marie de Rabutin-Chantal, marquise de Sévigné was a 17th-century French writer of epistolary genre.
Marie came from a noble family, but was orphaned at the age of six and raised by her uncle Philippe II de Coulanges. She received a good education and married Henri de Sévigné in 1644. In 1651 he was killed in a duel, and Madame de Sevigne was left a widow with two children. She led an ordinary social life, and only the marriage of her daughter, painful separation from her and loneliness suddenly revealed in the Marquise literary gift.
Since 1671 for thirty years, Madame de Sévigné wrote to her daughter about 1700 letters, and this correspondence has both historical and literary significance. In her letters, the woman relates current news and events of secular society, describes prominent people, comments on all of these, and reports on the details of her own life. Her letters reflect the intellectual sophistication of the salon culture of the period. Madame de Sévigné also touches on serious philosophical and religious topics, nature, art, morality, and psychology.
Her letters were read out in the salons, passed from hand to hand. Gradually they turned into a collection, the first edition of which was published in 1726, gradually expanding and supplementing. The popularity of the Letters of Madame de Sévigné grew over the years, becoming a source of historical study of the era and language. Francophone educational institutions in many countries around the world have included Sevigné's works in their curricula. The crater Sevigné on Venus is named in her honor.


Christopher Merrett was a British physician and natural scientist.
Merrett was somewhat of a polymath and natural philosopher. His interests ranged from coinage and tin mining in Cornwall to glassblowing and butterfly taxonomy (his Pinax Rerum Naturalium Britannicarum of 1666 is now recognized as the earliest complete list of birds and butterflies in England).
However, he is much better known today as the first Englishman to record the existence of the sparkling wine phenomenon. It was Christopher Merrett in 1662 who first documented the existence of bubbles in an alcoholic beverage. He described the fundamental winemaking technique that was later called the "method of champanization" and perfected the production of stronger glass in the manufacture of wine fermentation bottles, which had previously exploded easily.


John Milton was a British poet and writer-publicist, intellectual and politician of the English Revolutionary period.
Milton first planned to become a priest, studied at Cambridge University, and then abandoned this activity. Several years he spent reading and self-education, learning many languages. In 1638 Milton traveled around the continent for about a year and a half, spending much time in Italy, primarily in Rome and Florence. He befriended young Italian literati, and his encounter with Galileo further influenced his writing.
Milton became best known for his poem Paradise Lost in Ten Books, which declares its purpose to justify the ways of God to man, but also touches on both universal and personal themes. Milton was the first author to use the word "cosmos" in our modern sense of "outer space," and his space epic takes place in a confidently Copernican universe.
In his prose works, Milton advocated the abolition of the Church of England and the execution of Charles I. From the outbreak of the English Civil Wars in 1642 and long after the restoration of Charles II as king in 1660, he spoke out against tyranny and state-sanctioned religion in all his works. As a Protestant, Milton was often in conflict with the Roman Catholic Church. As a civil servant, Milton became the voice of the English Commonwealth after 1649 and then under Oliver Cromwell, conducting international correspondence and defending the government against polemical attacks from abroad.
John Milton is considered the most important English writer after William Shakespeare. Author of political pamphlets and religious treatises, he is one of the most famous writers of the 1650s, the vibrant era of the English Revolution (Civil War).


Thomas Moffet was a British naturalist-naturalist and physician.
After receiving his MD degree in 1580, Thomas Moffet studied the anatomy of the mulberry silkworm in Italy, then returned to England to study arthropods in general, especially spiders. He edited and expanded the work Insectorum sive Minimorum Animalium Theatrum ("Insect Theater"), an illustrated guide to the classification and life of insects.
Moffet was also an ardent supporter of the Paracelsian system of medicine.


Giovanni Nardi was an Italian physician and natural philosopher.
After studying at the University of Pisa, Nardi worked as a physician in Florence. He corresponded with many of the leading natural philosophers and antiquarians of his time, including members of the Accademia dei Lincei. In 1620 Nardi became court physician to Duke Ferdinando II Medici of Tuscany and accompanied him on his travels. In his Florentine home, Nardi amassed a collection of antiques and curiosities.
Nardi wrote several volumes on natural philosophy, as well as a commentary on Lucretius entitled Titi Lucretii Cari De rerum naturae libri sex (1647). Nardi's commentaries on Lucretius's natural history, medicine, physics, and theory of atomism far exceed the poem itself.


Chérubin of Orleans (French: Chérubin d'Orleans), born François or Michel Lasseré, was a French monk of the Order of the Friars Minor Capuchin, physicist, and optical instrument maker.
Cherubin was engaged in the study of optics and problems related to vision. He designed the first binocular telescope, as well as a special type of spectacle in which the lens was replaced by a short perforated tube. Many of his binoculars, binocular microscopes and telescopes survive today. Cheruben is also credited with modeling the eyeball to study the functioning of the ocular lens.
About his research and work, Cherubin of Orléans published in Paris the works La dioptrique oculaire (Dioptrique oculaire, 1671) and La vision parfaite (Perfect Vision, 1677).


Samuel Pepys was a British statesman, Secretary of the Admiralty, and writer of the Restoration era.
Despite his humble origins, Pepys had a good career. He was initially secretary of the naval council, and from 1686 to 1688 he was secretary of the Admiralty of England, where he created the modern department of state from the archaic cabinet. He was for a time a Member of Parliament, President of the Royal Society, and a confidant of Charles II.
Samuel Pepys became famous when his "Memoirs", consisting of his diary, which he kept from 1659 to 1669, were published as early as the 19th century. This book gives a unique and fascinating picture of official life, the life of the upper classes of Restoration-era London, as well as his own ordinary life. The author had a truly journalistic gift and was able to describe a scene or person with a few precise phrases or even words. The book also provides evidence of the most important events of the time, be it plague, fire or war.


John Ray was a British clergyman, naturalist, botanist and zoologist, and a Fellow of the Royal Society of London.
He came from a poor family, but through his persistence in acquiring knowledge he achieved recognition as a scientist. Ray published important works on botany, zoology, and natural history. His classification of plants in Historia Plantarum was an important step toward modern taxonomy (the scientific study of naming, defining, and classifying groups of biological organisms based on common characteristics). John Ray was the first to provide a biological definition of the term "species."


Marco Aurelio Severino was an Italian surgeon, anatomist and zoologist, one of the founders of comparative anatomy.
From childhood Severino studied Latin, Greek, rhetoric, poetry and law in various schools in Calabria, then continued his studies in Naples, soon moving from law to medicine. In Naples he met Tommaso Campanella, who had a great influence on the formation of his worldview. After receiving a medical degree in Salerno in 1606, he studied surgery in Naples with Giulio Jasolino. In 1615 Severino was appointed the first surgeon at Ospedale degli Incurabili. Severino made significant contributions to the transformation of naturophilosophy, medical and surgical practice, to which much of his printed work is devoted.
Severino's main contribution, however, lies in his anatomical works, especially the Zootomia Democritea. This work may be called the earliest comprehensive treatise on comparative anatomy. Severino is considered one of the pioneers of comparative anatomy.
Severino's cultural interests extended far beyond medicine. He corresponded with many prominent physicians and scientists of his time, including William Harvey and John Houghton in England, Thomas Bartolin and Ole Worm in Denmark, J.G. Volkamer and Johannes Wesling in Germany, and Campanella, Jasolino, and Tommaso Cornelio in Italy. Severino was tried by the Inquisition for allegedly unorthodox religious and philosophical views, but was eventually acquitted. He died of the plague in Naples.


William Shakespeare was a British poet and playwright and writer.
William's father, John Shakespeare, was a merchant and official in Stratford. There are reports that he was a sailor for a time before joining a theater company in London. Beginning in the 1590s, Shakespeare began writing plays, and in 1593 he published a poem, Venus and Adonis, which became popular. He dedicated it to the Duke of Southampton, who was a philanthropist and patron of talent, and soon his business was booming.
From 1592 to 1600 Shakespeare wrote his dramas and romantic comedies "Richard III", "The Taming of the Shrew", "Romeo and Juliet", "A Midsummer Night's Dream" and "The Merchant of Venice", as well as the comedies "Much Ado About Nothing", "Twelfth Night" and the tragedy "Julius Caesar". The playwright's business was so successful that he even bought a large house in Stratford. In 1599, Shakespeare became one of the owners, playwright and actor of the new theater "Globe". In 1603 King James took Shakespeare's troupe under his direct patronage. In the mature period, the great playwright turned to tragedies, there were "Hamlet", "Othello", "King Lear", "Macbeth" and others.
Although in the 19th century researchers had some doubts about the authorship of many of these works, William Shakespeare is considered the greatest English playwright, one of the best playwrights in the world. His plays have been translated into all major languages and to this day form the basis of the world theatrical repertoire, most of them have been screened many times. According to the Guinness Book of Records, Shakespeare remains the world's best-selling playwright, and his plays and poems have sold more than 4 billion copies in the nearly 400 years since his death.


Jonathan Swift was a British-Irish writer, essayist, philosopher, and author of the world-famous satirical novel Gulliver's Travels.
Swift also wrote numerous works, including The Tale of the Barrel (1704), An Argument Against the Abolition of Christianity (1712), and A Modest Proposal (1729). Almost all of Swift's satirical works were published anonymously, giving the author wide latitude in expressing his talent as a satirist.
Swift was a clergyman, made a career in London, became the chief pamphleteer and political writer of the Tories and headed the Tory journal "The Inspector", and then returned to Ireland, where he created his major life's work.
The four-part novel Gulliver's Travels, Jonathan Swift's greatest satire, was first published in 1726 and has since been reprinted hundreds of times in many languages around the world. The author describes in an engaging style the different races and societies that Gulliver encounters on his travels to ridicule the many errors, follies, weaknesses and vices to which people and society at large are subject. The author's boundless imagination, bitter irony, keen intellect and brilliant language give this work a world-class scope.


André Valladier was a French Jesuit, theologian and writer.
Valladier served as abbot of the Benedictine abbey of Saint-Arnoux and worked as professor of rhetoric at Avignon. He published about ten works on various subjects. The first of these was The Royal Labyrinth, a book describing the visit of King Henry IV and his new wife, Maria de' Medici, to the city of Avignon. This illustrated book was a great success and went through many editions.


Adriaen Pietersz. van de Venne was a Dutch painter, graphic artist, and poet of the Golden Age and a member of the Guild of St. Luke in The Hague. He is known for his paintings of genre scenes, allegories, portraits, and historical scenes. De Venne painted many engravings illustrating genre scenes depicting peasants, old men, vagabonds, madmen, and thieves. These works often illustrate aphorisms and proverbs.
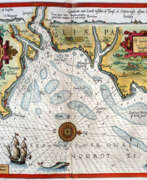
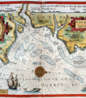
Lucas Waghenaer, full name Lucas Janszoon Waghenaer, was a famous Dutch cartographer, navigator, navigator and writer of the Golden Age.
Between 1550 and 1579, Waghenaer sailed the seas as a senior assistant captain and probably socialized with Portuguese, Spanish, and Italian navigators. The knowledge of nautical charts and the instructions Waghenaer received as a result of these contacts had a great influence on his later work as a cartographer. It is evident that the charts he made had to be based on his observations, and in all his work he had to draw on his own extensive experience of practical navigation. His book Spieghel der Zeevaerdt ("The Navigator's Mirror") or Speculum nauticum super navigatione, first published in 1584, occupies a unique place among the nautical printed works of the sixteenth century, for it is the first printed work with maps.
Moreover, in terms of the magnificent design of the maps and text, it surpasses all other editions of this period and served as a model for pilotage guides and folios with maps even a century later. It is an atlas of nautical charts with instructions for navigation in the western and northwestern coastal waters of Europe. Thanks to the unrivaled skill of engravers Baptiste and Johannes van Deitekom, Waghenaer's original maps were transformed into the most beautiful maps of the time. This book was a huge success, reprinted several times and translated into English, German, Latin and French.
In 1592, Waghenaer's second pilot book Thresoor der zeevaert ("Treasure of Navigation") was published, and in 1598, the third and last publication Enchuyser zeecaertboeck ("Enkhuizen Book of Nautical Charts").


Georg Hieronymus Welsch (or Welschius) was a German physician, translator and writer.
He studied medicine in Tübingen, Strasbourg and Padua. Having lost the ability to speak as a result of illness, he decided to settle in Augsburg and educate himself. Welsch studied Greek, Latin, Hebrew and Arabic. Then in Italy he visited numerous libraries, including the Vatican library, and collected books, including the Turkish calendar.
Georg Welsch wrote several books on medicine and fossil curiosities, and researched texts on astronomy and medicine from the Ottoman Empire. He is best known for his translation of the calendar of Avicenna and Sheikh Abul-Wafa. Welsch was also a member of the Academia Naturae Curiosorum.


Martin Zeiler (also Zeiller) was a Baroque era German author.
Zeiler was schooled in Ulm, moving to Wittenberg in 1608 to study jurisprudence and history. He worked several jobs as private teacher and notary. He lived in Ulm from 1629, working as teacher and inspector at local schools.













































































































































